遠
| ||||||||
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
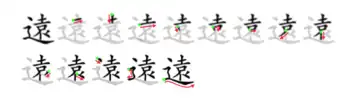 | |||
Han character
遠 (Kangxi radical 162, 辵+10, 14 strokes in traditional Chinese and Korean, 13 strokes in mainland China and Japanese, cangjie input 卜土口女 (YGRV), four-corner 34303, composition ⿺辶袁)
Related characters
Descendants
- を (Hiragana character derived from Man'yōgana)
References
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 1263, character 12
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 39047
- Dae Jaweon: page 1757, character 15
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 6, page 3869, character 7
- Unihan data for U+9060
Chinese
| trad. | 遠 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. | 远* | |
| alternative forms | 逺 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 遠 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Phono-semantic compound (形聲/形声, OC *ɢʷanʔ, *ɢʷans) : semantic 辵 (“walk”) + phonetic 袁 (OC *ɢʷan).
Etymology
From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *g-wəj-n (“far”) (STEDT). Cognate with Proto-Lolo-Burmese *wəj² (“far”), whence Burmese ဝေး (we:, “far”).
Pronunciation 1
Definitions
遠
- distant; remote; far
- not intimate; distant
- profound
- (intensifier in a comparison) much; by far
- 倘要「對證古本」,則《水滸傳》裡的一句「那雪正下得緊」,就是接近現代的大眾語的說法,比「大雪紛飛」多兩個字,但那「神韻」卻好得遠了。 [MSC, trad.]
- From: 1934, Lu Xun, 「大雪紛飛」
- Tǎng yào “duìzhèng gǔběn”, zé “Shuǐhǔzhuàn” lǐ de yī jù “nà xuě zhèng xià de jǐn”, jiùshì jiējìn xiàndài de dàzhòngyǔ de shuōfǎ, bǐ “dàxuě fēnfēi” duō liǎng ge zì, dàn nà “shényùn” què hǎo dé yuǎn le. [Pinyin]
- (please add an English translation of this usage example)
倘要「对证古本」,则《水浒传》里的一句「那雪正下得紧」,就是接近现代的大众语的说法,比「大雪纷飞」多两个字,但那「神韵」却好得远了。 [MSC, simp.]
Synonyms
| Variety | Location | Words |
|---|---|---|
| Classical Chinese | 遠, 遙, 悠, 迥, 遼 | |
| Formal (Written Standard Chinese) | 遠, 遙遠, 遼遠 | |
| Mandarin | Beijing | 遠 |
| Taiwan | 遠 | |
| Jinan | 遠 | |
| Xi'an | 遠 | |
| Wuhan | 遠 | |
| Chengdu | 遠 | |
| Yangzhou | 遠 | |
| Hefei | 遠 | |
| Singapore | 遠 | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | 遠 |
| Hong Kong | 遠 | |
| Yangjiang | 遠 | |
| Singapore (Guangfu) | 遠 | |
| Gan | Nanchang | 遠 |
| Hakka | Meixian | 遠 |
| Miaoli (N. Sixian) | 遠 | |
| Hsinchu County (Zhudong; Hailu) | 遠 | |
| Taichung (Dongshi; Dabu) | 遠 | |
| Hsinchu County (Qionglin; Raoping) | 遠 | |
| Yunlin (Lunbei; Zhao'an) | 遠 | |
| Jin | Taiyuan | 遠 |
| Northern Min | Jian'ou | 𨱵 |
| Jian'ou (Dikou) | 𨱵 | |
| Songxi | 𨱵 | |
| Zhenghe | 𨱵 | |
| Zhenghe (Zhenqian) | 𨱵 | |
| Jianyang | 𨱵 | |
| Wuyishan | 𨱵 | |
| Pucheng (Shibei) | 𨱵 | |
| Eastern Min | Fuzhou | 遠 |
| Southern Min | Xiamen | 遠 |
| Singapore (Hokkien) | 遠 | |
| Manila (Hokkien) | 遠 | |
| Chaozhou | 遠 | |
| Wu | Suzhou | 遠 |
| Wenzhou | 遠 | |
| Xiang | Changsha | 遠 |
| Shuangfeng | 遠 | |
Compounds
- 三級跳遠/三级跳远 (sānjítiàoyuǎn)
- 不遠/不远
- 不遠不近/不远不近
- 不遠千里 (bùyuǎnqiānlǐ)
- 不遠萬里/不远万里 (bùyuǎnwànlǐ)
- 久遠/久远 (jiǔyuǎn)
- 人無遠慮,必有近憂/人无远虑,必有近忧 (rén wú yuǎnlǜ, bì yǒu jìnyōu)
- 以德懷遠/以德怀远
- 伯遠帖/伯远帖
- 偏遠/偏远 (piānyuǎn)
- 僻遠/僻远 (pìyuǎn)
- 先識遠量/先识远量
- 出遠門/出远门 (chū yuǎnmén)
- 前程遠大/前程远大
- 劉知遠/刘知远
- 勞師襲遠/劳师袭远
- 壙遠/圹远
- 大老遠/大老远 (dàlǎoyuǎn)
- 大遠景/大远景
- 天差地遠/天差地远 (tiānchādìyuǎn)
- 天遠地隔/天远地隔
- 天長地遠/天长地远
- 天高地遠/天高地远
- 天高日遠/天高日远
- 天高聽遠/天高听远
- 奧遠/奥远
- 好高騖遠/好高骛远 (hàogāowùyuǎn)
- 定遠/定远 (Dìngyuǎn)
- 室邇人遠/室迩人远
- 寧遠/宁远 (Níngyuǎn)
- 山遙水遠/山遥水远
- 山長水遠/山长水远 (shānchángshuǐyuǎn)
- 山高水遠/山高水远
- 年湮代遠/年湮代远
- 幽遠/幽远
- 弘遠/弘远
- 思深憂遠/思深忧远
- 恤近忽遠/恤近忽远
- 悅近來遠/悦近来远
- 悠遠/悠远 (yōuyuǎn)
- 愛遠惡近/爱远恶近
- 慎終追遠/慎终追远 (shènzhōngzhuīyuǎn)
- 憂深思遠/忧深思远
- 慧遠/慧远
- 憑高望遠/凭高望远
- 懷遠/怀远 (Huáiyuǎn)
- 拖枝馬遠/拖枝马远
- 捨近務遠/舍近务远
- 捨近即遠/舍近即远
- 捨近求遠/舍近求远 (shějìnqiúyuǎn)
- 料遠若近/料远若近
- 明遠樓/明远楼
- 曠遠/旷远
- 會心不遠/会心不远
- 望遠鏡/望远镜 (wàngyuǎnjìng)
- 望遠鏡頭/望远镜头 (wàngyuǎn jìngtóu)
- 格高意遠/格高意远
- 機謀遠慮/机谋远虑
- 殷鑑不遠/殷鉴不远 (yīnjiànbùyuǎn)
- 殷鑒不遠/殷鉴不远 (yīnjiànbùyuǎn)
- 水遠山遙/水远山遥
- 水遠山長/水远山长
- 永遠/永远 (yǒngyuǎn)
- 沉遠/沉远
- 深圖遠慮/深图远虑
- 深思遠慮/深思远虑
- 深藏遠遁/深藏远遁
- 深計遠慮/深计远虑
- 深謀遠慮/深谋远虑 (shēnmóuyuǎnlǜ)
- 深謀遠猷/深谋远猷
- 深識遠慮/深识远虑
- 深遠/深远 (shēnyuǎn)
- 淵遠流長/渊远流长
- 源遠流長/源远流长 (yuányuǎnliúcháng)
- 潛身遠禍/潜身远祸
- 潛身遠跡/潜身远迹
- 潛身遠遁/潜身远遁
- 為期不遠/为期不远
- 無遠弗屆/无远弗届 (wúyuǎnfújiè)
- 玄遠/玄远
- 疏遠/疏远 (shūyuǎn)
- 登高望遠/登高望远
- 相去不遠/相去不远
- 窵遠/窎远 (diàoyuǎn)
- 窵遠子/窎远子
- 綏遠/绥远 (suíyuǎn)
- 老遠/老远 (lǎoyuǎn)
- 聞風遠揚/闻风远扬
- 聲名遠播/声名远播
- 臭名遠揚/臭名远扬
- 致遠/致远
- 致遠任重/致远任重
- 舍近謀遠/舍近谋远
- 行遠自邇/行远自迩
- 規模遠舉/规模远举
- 親疏遠近/亲疏远近
- 言微旨遠/言微旨远
- 言近指遠/言近指远
- 言近旨遠/言近旨远
- 計深慮遠/计深虑远
- 謀慮深遠/谋虑深远
- 謹終追遠/谨终追远
- 負重涉遠/负重涉远
- 負重致遠/负重致远
- 貴遠賤近/贵远贱近
- 貴遠鄙近/贵远鄙近
- 超然遠引/超然远引
- 超然遠舉/超然远举
- 路遠/路远
- 跳遠/跳远 (tiàoyuǎn)
- 身遠心近/身远心近
- 辭微旨遠/辞微旨远
- 近悅遠來/近悦远来
- 迥遠/迥远
- 追遠/追远
- 道遠任重/道远任重
- 道遠日暮/道远日暮
- 道遠知驥/道远知骥
- 遠不如/远不如
- 遠不間親/远不间亲
- 遠交近攻/远交近攻 (yuǎnjiāojìngōng)
- 遠人/远人
- 遠兄弟/远兄弟
- 遠古/远古 (yuǎngǔ)
- 遠古時代/远古时代
- 遠因/远因 (yuǎnyīn)
- 遠圖長慮/远图长虑
- 遠大/远大 (yuǎndà)
- 遠安/远安 (Yuǎn'ān)
- 遠客/远客
- 遠山眉/远山眉
- 遠山黛/远山黛
- 遠引曲喻/远引曲喻
- 遠引深潛/远引深潜
- 遠征 (yuǎnzhēng)
- 遠征軍/远征军
- 遠志/远志 (yuǎnzhì)
- 遠惡/远恶
- 遠意/远意
- 遠愁/远愁
- 遠愁近慮/远愁近虑
- 遠慮/远虑 (yuǎnlǜ)
- 遠慮深思/远虑深思
- 遠慮深計/远虑深计
- 遠房/远房 (yuǎnfáng)
- 遠打週折/远打周折
- 遠播/远播
- 遠方/远方 (yuǎnfāng)
- 遠景/远景 (yuǎnjǐng)
- 遠望/远望 (yuǎnwàng)
- 遠期外匯/远期外汇
- 遠期支票/远期支票
- 遠東/远东 (Yuǎndōng)
- 遠洋/远洋 (yuǎnyáng)
- 遠洋漁業/远洋渔业
- 遠渡重洋/远渡重洋 (yuǎndùchóngyáng)
- 遠略/远略
- 遠眺/远眺 (yuǎntiào)
- 遠矚/远瞩
- 遠祖/远祖 (yuǎnzǔ)
- 遠視/远视 (yuǎnshì)
- 遠視眼/远视眼
- 遠程/远程 (yuǎnchéng)
- 遠端會議/远端会议
- 遠端簽入/远端签入
- 遠紅外線/远红外线
- 遠舉高飛/远举高飞
- 遠處/远处 (yuǎnchù)
- 遠行/远行 (yuǎnxíng)
- 遠裔/远裔
- 遠見/远见 (yuǎnjiàn)
- 遠見卓識/远见卓识
- 遠親/远亲 (yuǎnqīn)
- 遠話/远话
- 遠謀/远谋 (yuǎnmóu)
- 遠走高飛/远走高飞 (yuǎnzǒugāofēi)
- 遠赴/远赴 (yuǎnfù)
- 遠超過/远超过
- 遠足/远足 (yuǎnzú)
- 遠距教學/远距教学
- 遠距醫療/远距医疗
- 遠路/远路
- 遠近/远近 (yuǎnjìn)
- 遠迎/远迎
- 遠近知名/远近知名
- 遠近聞名/远近闻名
- 遠近馳名/远近驰名 (yuǎnjìnchímíng)
- 遠道/远道 (yuǎndào)
- 遠遊/远游 (yuǎnyóu)
- 遠遁/远遁 (yuǎndùn)
- 遠遁山林/远遁山林
- 遠遠/远远 (yuǎnyuǎn)
- 遙遠/遥远 (yáoyuǎn)
- 遠遠的/远远的
- 遠遠落後/远远落后
- 遠郊/远郊
- 遠鄉牌/远乡牌
- 遠離/远离 (yuǎnlí)
- 遠颺/远飏 (yuǎnyáng)
- 遷善遠罪/迁善远罪
- 遼遠/辽远 (liáoyuǎn)
- 邊遠/边远 (biānyuǎn)
- 鄙遠/鄙远
- 醜聲遠播/丑声远播
- 鉤深致遠/钩深致远
- 長算遠略/长算远略
- 長轡遠御/长辔远御
- 長轡遠馭/长辔远驭
- 長遠/长远 (chángyuǎn)
- 防微慮遠/防微虑远
- 離山窵遠/离山窎远
- 馳名遠近/驰名远近
- 高情遠意/高情远意
- 高情遠致/高情远致
- 高才遠識/高才远识
- 高掌遠蹠/高掌远蹠
- 高明遠見/高明远见
- 高明遠識/高明远识
- 高瞻遠矚/高瞻远瞩 (gāozhānyuǎnzhǔ)
- 高翔遠引/高翔远引
- 高舉遠蹈/高举远蹈
- 高見遠識/高见远识
- 高識遠度/高识远度
- 高識遠見/高识远见
- 高蹈遠引/高蹈远引
- 高蹈遠舉/高蹈远举
- 高飛遠翔/高飞远翔
- 高飛遠舉/高飞远举
- 高飛遠走/高飞远走
- 高飛遠遁/高飞远遁
- 高飛遠集/高飞远集
Pronunciation 2
References
- “遠”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database), 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
- “Entry #10890”, in 臺灣閩南語常用詞辭典 [Dictionary of Frequently-Used Taiwan Minnan] (overall work in Mandarin and Hokkien), Ministry of Education, R.O.C., 2023.
Japanese
| Shinjitai | 遠 | |
| Kyūjitai [1][2][3] |
遠󠄁 遠+ 󠄁?(Adobe-Japan1) |
 |
| 遠󠄄 遠+ 󠄄?(Hanyo-Denshi) (Moji_Joho) | ||
| The displayed kanji may be different from the image due to your environment. See here for details. | ||
Kanji
Readings
From Middle Chinese 遠 (MC hjwonX); compare Mandarin 遠/远 (yuǎn):
From native Japanese roots:
- Kun: とおい (tōi, 遠い, Jōyō)←とほい (tofoi, 遠い, historical); とおざかる (tōzakaru, 遠ざかる)←とほざかる (tofozakaru, 遠ざかる, historical); とおざける (tōzakeru, 遠ざける)←とほざける (tofozakeru, 遠ざける, historical); おち (ochi)←をち (woti, historical); おと (oto)←をと (woto, historical)
- Nanori: おに (oni)←をに (woni, historical); ど (do); とお (tō); どお (dō)←どほ (dofo, historical); とおし (tōshi)←とほし (tofosi, historical); とおる (tōru)←とほる (toforu, historical)
Compounds
- 遠近 (ochikochi)
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 遠 |
| とお Grade: 2 |
| kun’yomi |
⟨to2po⟩ → */təpo/ → /tofo/ → /towo/ → /toː/
From Old Japanese.
Stem of classical adjective 遠し (tōshi), modern 遠い (tōi, “distant, far”).[4]
Derived terms
- 遠つ (tō tsu)
- 遠の (tō no)
- 遠め (tōme)
- 遠らか (tōraka)
- 遠遠しい (tōdōshii)
- 遠浅 (tōasa)
- 遠歩き (tōaruki)
- 遠縁 (tōen)
- 遠香 (tōka)
- 遠駆け (tōgake), 遠懸け (tōgake)
- 遠篝 (tō-kagari)
- 遠笠懸 (tō-kasagake)
- 遠霞 (tōgasumi)
- 遠蛙 (tō-kawazu)
- 遠聞 (tōgiki)
- 遠声 (tōgoe)
- 遠ざかる (tōzakaru)
- 遠ざける (tōzakeru)
- 遠侍 (tō-saburai)
- 遠攻め (tōzeme)
- 遠退く (tōsoku)
- 遠夫 (tōzuma)
- 遠妻 (tōzuma)
- 遠出 (tōde)
- 遠長 (tōnaga)
- 遠長し (tōnagashi)
- 遠鳴り (tōnari)
- 遠音 (tōne)
- 遠野 (Tōno)
- 遠退く (tōnoku), 遠退ける (tōnokeru)
- 遠乗り (tōnori)
- 遠っ走り (tōppashiri)
- 遠火 (tōbi)
- 遠干潟 (tō-higata)
- 遠菱 (tōbishi)
- 遠人 (tōhito), 遠人 (tōbito)
- 遠吠え (tōboe)
- 遠巻 (tōmaki), 遠巻き (tōmaki)
- 遠勝り (tōmasari)
- 遠回し (tōmawashi)
- 遠回り (tōmawari)
- 遠見 (tōmi)
- 遠目 (tōme), 遠眼 (tōme)
- 遠物見 (tō-monomi)
- 遠文 (tōmon)
- 遠矢 (tōya)
- 遠山 (tōyama), 遠山 (Tōyama)
- 遠寄せ (tōyose)
- 遠輪廻 (tō-rinne)
- 高遠 (Takatō)
Alternative forms
Pronoun
Etymology 3
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 遠 |
| おと Grade: 2 |
| kun’yomi |
⟨woto2⟩ → */wotə/ → /woto/ → /oto/
Shift from Old Japanese ochi, ancient woti (see above).[4][5]
Alternative forms
Pronoun
Derived terms
Etymology 4
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 遠 |
| えん Grade: 2 |
| kan’on |
From Middle Chinese 遠 (MC hjwonX, “distant; remote; far”), corresponding to modern Mandarin yuǎn, Cantonese jyun5.
As a verb in Chinese compounds like 遠色 (enshoku, “keep aloof from beauty”, kun'yomi iro o tōzaku), from Middle Chinese 遠 (MC hjwonH, “keep at a distance; keep away from”), corresponding to Mandarin yuàn, Cantonese jyun6.
The kan'on pronunciation, so likely a later borrowing.
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): [ẽ̞ɴ]
Affix
Derived terms
- 遠因 (en'in)
- 遠隔 (enkaku)
- 遠忌 (enki)
- 遠近 (enkin)
- 遠見 (enken)
- 遠交近攻 (enkōkinkō)
- 遠国 (engoku)
- 遠山 (enzan)
- 遠州 (Enshū)
- 遠称 (enshō)
- 遠心 (enshin)
- 遠征 (ensei)
- 遠戚 (enseki)
- 遠足 (ensoku)
- 遠大 (endai)
- 遠藤 (Endō)
- 遠聞 (enbun)
- 遠方 (enpō)
- 遠望 (enbō)
- 遠謀 (enbō)
- 遠来 (enrai)
- 遠離 (enri)
- 遠慮 (enryo)
- 遠流 (enru)
- 以遠 (ien)
- 永遠 (eien)
- 敬遠 (keien)
- 広遠 (kōen), 宏遠 (kōen)
- 高遠 (kōen)
- 深遠 (shin'en)
- 疎遠 (soen)
- 平遠 (heien)
- 僻遠 (hekien)
- 望遠 (bōen)
- 悠遠 (yūen)
- 遼遠 (ryōen)
Etymology 5
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 遠 |
| おん Grade: 2 |
| goon |
From Middle Chinese 遠 (MC hjwonX, “distant; remote; far”).
The goon pronunciation, so likely the initial borrowing.
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): [õ̞ɴ]
Derived terms
References
- “遠”, in 漢字ぺディア (Kanjipedia) (in Japanese), 日本漢字能力検定協会, 2015–2024
- Haga, Gōtarō (1914) 漢和大辞書 [The Great Kanji-Japanese Dictionary] (in Japanese), Fourth edition, Tōkyō: Kōbunsha, , page 2124 (paper), page 1114 (digital)
- Shōundō Henshūjo, editor (1927), 新漢和辞典 [The New Kanji-Japanese Dictionary] (in Japanese), Ōsaka: Shōundō, , page 1226 (paper), page 626 (digital)
- Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 [Daijirin] (in Japanese), Third edition, Tōkyō: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- Matsumura, Akira (1995) 大辞泉 [Daijisen] (in Japanese), First edition, Tōkyō: Shogakukan, →ISBN