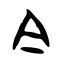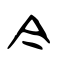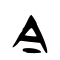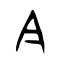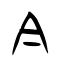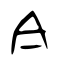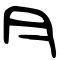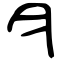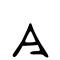今
| ||||||||
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
| Mainland China | |||
| Stroke order | |||
All regions except mainland China | |||
Alternative forms
- In all regions except mainland China, the stroke between 𠆢 and ㇇ for 今 (and its derived characters) is written with a horizontal 一 line.
- In mainland China (based on Xin Zixing standardized form), the stroke between 𠆢 and ㇇ for 今 (and its derived characters) is written with a slanting 丶 dot instead.
- In the historical Kangxi dictionary, the component below 𠆢 is written 一 followed by 𠃍 instead.
Han character
今 (Kangxi radical 9, 人+2, 4 strokes, cangjie input 人戈弓 (OIN) or 人一弓 (OMN), four-corner 80207, composition ⿱亽㇇(G) or ⿱亼㇇(HTJKV))
Derived characters
References
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 91, character 18
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 358
- Dae Jaweon: page 194, character 3
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 105, character 5
- Unihan data for U+4ECA
Chinese
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 今 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Spring and Autumn | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
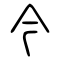 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
References: Mostly from Richard Sears' Chinese Etymology site (authorisation),
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Old Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 貪 | *kʰl'uːm |
| 嗿 | *l̥ʰuːmʔ |
| 僋 | *l̥ʰuːms, *luːms |
| 酓 | *qʰɯːm, *qlamʔ, *qlɯːms |
| 馠 | *qʰɯːm |
| 谽 | *qʰɯːm |
| 唅 | *qʰɯːm, *ɡɯːms |
| 含 | *ɡɯːm |
| 肣 | *ɡɯːm, *ɡɯːmʔ |
| 頷 | *ɡɯːm, *ɡɯːmʔ |
| 筨 | *ɡɯːm |
| 梒 | *ɡɯːm |
| 鋡 | *ɡɯːm |
| 莟 | *ɡɯːmʔ, *ɡɯːms |
| 琀 | *ɡɯːms |
| 浛 | *ɡɯːms |
| 盦 | *qɯːm, *qaːb |
| 韽 | *qɯːm, *qrɯːms |
| 玪 | *krɯːm |
| 妗 | *qʰrɯːm, *kʰjam, *qʰlɯːm, *ɡrɯms |
| 欦 | *qʰrɯːmʔ, *qʰram, *kʰlam, *kʰlamʔ, *qʰlɯːm |
| 黔 | *ɡram, *ɡrɯm |
| 鈐 | *ɡram |
| 鳹 | *ɡram |
| 雂 | *ɡram, *ɡrɯm |
| 念 | *nɯːms |
| 梣 | *sɡɯm, *sɡrɯm |
| 枔 | *sɢrɯm |
| 岑 | *sɡrɯm |
| 笒 | *sɡrɯm, *ɡrɯms |
| 涔 | *sɡrɯm |
| 侺 | *ɡjɯms |
| 今 | *krɯm |
| 黅 | *krɯm |
| 衿 | *krɯm |
| 衾 | *kʰrɯm |
| 坅 | *kʰrɯmʔ |
| 搇 | *kʰrɯms |
| 琴 | *ɡrɯm |
| 禽 | *ɡrɯm |
| 芩 | *ɡrɯm |
| 庈 | *ɡrɯm |
| 耹 | *ɡrɯm |
| 靲 | *ɡrɯm |
| 擒 | *ɡrɯm |
| 檎 | *ɡrɯm |
| 紟 | *ɡrɯms |
| 吟 | *ŋɡrɯm, *ŋɡrɯms |
| 訡 | *ŋɡrɯm |
| 廞 | *qʰrɯm, *qʰrɯmʔ |
| 陰 | *qrɯm |
| 霠 | |
| 飲 | *qrɯmʔ, *qrɯms |
| 蔭 | *qrɯms |
| 廕 | *qrɯms |
| 矜 | *ɡrɯn, *ɡɯn, *kɯŋ |
Ideogram (指事) – An inverted 曰 (yuē) ("to speak"), so the inverted one means "not to speak". Another theory suggests that it depicts something in the mouth. Maybe the original form of 噤 (OC *ɡrɯmʔ, *ɡrɯms) or 吟 (OC *ŋɡrɯm, *ŋɡrɯms). The derivative 含 (OC *ɡɯːm) refers to the original word.
Etymology 1
| trad. | 今 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. # | 今 | |
| alternative forms | 𫢉 ⿱𠆢𬼽 𱎜 | |
Etymology not clear. The word's root may be 其 (OC *ɡɯ, “this”) (Schuessler, 2007).
Pronunciation
Definitions
今
- now; at present; current
- modern times
- 王之好樂甚,則國其庶幾乎。今之樂,猶古之樂也。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: Mencius, c. 4th century BCE
- Wáng zhī hào yuè shèn, zé guó qí shù jǐ hū. Jīn zhī yuè, yóu gǔ zhī yuè yě. [Pinyin]
- If your Majesty's love of music were very great, Qi would be near to a state of good government! The music of the present day is just like the music of antiquity, as regards effecting that.
王之好乐甚,则国其庶几乎。今之乐,犹古之乐也。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- this
- (literary) thus; promptly
- 子為我反,無見王矣。十日之內,數萬之眾,今涉魏境。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: Zhanguo Ce, circa 5th – 3rd centuries BCE
- Zǐ wèi wǒ fǎn, wú jiàn wáng yǐ. Shírì zhī nèi, shù wàn zhī zhòng, jīn shè wèi jìng. [Pinyin]
- (please add an English translation of this usage example)
子为我反,无见王矣。十日之内,数万之众,今涉魏境。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- (literary) if
- 此無他,與民同樂也。今王與百姓同樂,則王矣。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: Mencius, c. 4th century BCE
- Cǐ wú tā, yǔ mín tóng yuè yě. Jīn wáng yǔ bǎixìng tóng yuè, zé wàng yǐ. [Pinyin]
- Their feeling thus is from no other reason but that you cause them to have their pleasure as you have yours. If your Majesty now will make pleasure a thing common to the people and yourself, the royal sway awaits you.
此无他,与民同乐也。今王与百姓同乐,则王矣。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]- 今兩虎共鬥,其勢不俱生。 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Records of the Grand Historian, by Sima Qian, c. 91 BCE
- Jīn liǎng hǔ gòng dòu, qí shì bù jù shēng. [Pinyin]
- If we (the two tigers) fight against one another, it is certainly not possible that both of us will survive.
今两虎共斗,其势不俱生。 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- a surname
Synonyms
Compounds
- 不今不古
- 乃今 (nǎijīn)
- 事到如今 (shìdàorújīn)
- 于今 (yújīn)
- 于今為烈
- 亙古亙今/亘古亘今
- 今上 (jīnshàng)
- 今下 (jīnxià)
- 今上官家
- 今不如昔 (jīnbùrúxī)
- 今且
- 今世 (jīnshì)
- 今世說/今世说
- 今人 (jīnrén)
- 今代
- 今來/今来
- 今來古往/今来古往
- 今個/今个 (jīngè)
- 今兒/今儿 (jīnr)
- 今兒個/今儿个 (jīnrgè)
- 今典
- 今分
- 今古 (jīngǔ)
- 今古奇觀/今古奇观
- 今古學派/今古学派
- 今回
- 今士
- 今夕 (jīnxī)
- 今夕何夕
- 今夜 (jīnyè)
- 今夫 (jīnfú)
- 今天
- 今字 (jīnzì)
- 今學/今学
- 今宵 (jīnxiāo)
- 今年 (jīnnián)
- 今律
- 今後/今后 (jīnhòu)
- 今愁古恨
- 今接輿/今接舆
- 今故
- 今文 (jīnwén)
- 今文學/今文学
- 今文家
- 今文尚書/今文尚书
- 今文經/今文经
- 今文經學/今文经学
- 今日 (jīnrì)
- 今日事,今日畢/今日事,今日毕 (jīnrì shì, jīnrì bì)
- 今日個/今日个
- 今日箇/今日个
- 今旦
- 今早 (jīnzǎo)
- 今昔 (jīnxī)
- 今昔之感
- 今是昔非
- 今是昨非
- 今時/今时
- 今晚 (jīnwǎn)
- 今曏/今向
- 今月 (jīnyuè)
- 今月古月
- 今有術/今有术
- 今朝 (jīnzhāo)
- 今本 (jīnběn)
- 今樣/今样
- 今次 (jīncì)
- 今歲/今岁
- 今段
- 今王
- 今生 (jīnshēng)
- 今生今世 (jīnshēngjīnshì)
- 今番 (jīnfān)
- 今草
- 今茲/今兹 (jīnzī)
- 今董狐
- 今蚤
- 今蟬蛻殼/今蝉蜕壳
- 今語/今语
- 今譯/今译 (jīnyì)
- 今隸/今隶
- 今雨
- 今非昔比 (jīnfēixībǐ)
- 今音 (jīnyīn)
- 今韻/今韵
- 今體/今体
- 今體詩/今体诗
- 以古制今
- 以古方今
- 以古非今
- 來今/来今
- 修今
- 借古諷今/借古讽今 (jiègǔfěngjīn)
- 傍今
- 傷今/伤今
- 傳譽古今/传誉古今
- 其今
- 冠絕古今/冠绝古今
- 凡今
- 博古知今
- 博古通今 (bógǔtōngjīn)
- 博覽古今/博览古今
- 即今 (jíjīn)
- 厚今薄古
- 厚古薄今 (hòugǔbójīn)
- 去來今/去来今
- 及今
- 只今 (zhǐjīn)
- 古今 (gǔjīn)
- 古今中外 (gǔjīnzhōngwài)
- 古今兒/古今儿
- 古今小說/古今小说
- 古今少有
- 古今注
- 古今絕色/古今绝色
- 古往今來/古往今来 (gǔwǎngjīnlái)
- 古為今用/古为今用
- 古爲今用/古为今用
- 如今 (rújīn)
- 如今晚兒/如今晚儿
- 尊古卑今
- 居今稽古
- 引古喻今
- 引古證今/引古证今
- 往古來今/往古来今
- 從今/从今 (cóngjīn)
- 從今以後/从今以后 (cóngjīn yǐhòu)
- 從古至今/从古至今
- 感今思昔
- 感今惟昔
- 感今懷昔/感今怀昔
- 慕古薄今
- 指古摘今
- 援古刺今
- 援古證今/援古证今
- 撫今思昔/抚今思昔
- 撫今悼昔/抚今悼昔
- 撫今痛昔/抚今痛昔
- 撫今追昔/抚今追昔 (fǔjīnzhuīxī)
- 攀今吊古
- 攀今弔古/攀今吊古
- 攀今掉古
- 攀今攬古/攀今揽古
- 攀今比昔
- 攀今覽古/攀今览古
- 方今 (fāngjīn)
- 於今/于今 (yújīn)
- 日今
- 是今
- 是古非今
- 昨非今是 (zuófēijīnshì)
- 時今/时今
- 暨今 (jìjīn)
- 格古通今
- 極古窮今/极古穷今
- 榮古虐今/荣古虐今
- 榮古陋今/荣古陋今
- 泥古非今
- 洞鑒古今/洞鉴古今
- 演古勸今/演古劝今
- 為今之計/为今之计
- 現今/现今 (xiànjīn)
- 現如今/现如今
- 現而今/现而今 (xiàn'érjīn)
- 當今/当今 (dāngjīn)
- 當今無輩/当今无辈
- 目今 (mùjīn)
- 知今博古
- 知古今
- 知古今兒/知古今儿
- 知往鑒今/知往鉴今
- 祗今
- 秪今
- 稽古振今
- 稽古揆今
- 空古絕今/空古绝今
- 競今疏古/竞今疏古
- 繼古開今/继古开今
- 而今 (érjīn)
- 而今而後/而今而后
- 自今 (zìjīn)
- 至今 (zhìjīn)
- 舊雨今雨/旧雨今雨
- 茹古涵今
- 行古志今
- 見今/见今
- 見如今/见如今
- 訖今/讫今
- 說今道古/说今道古
- 說古談今/说古谈今
- 說古道今/说古道今 (shuōgǔdàojīn)
- 論今說古/论今说古
- 談今論古/谈今论古
- 談古說今/谈古说今
- 談古論今/谈古论今
- 講古論今/讲古论今
- 貫穿今古/贯穿今古
- 貴古賤今/贵古贱今
- 貽範古今/贻范古今
- 起今
- 超今冠古
- 超今絕古/超今绝古
- 超今越古
- 超古冠今
- 越古超今
- 迄今 (qìjīn)
- 近今
- 迺今
- 通今 (tōngjīn)
- 通今博古
- 通今達古/通今达古
- 通古博今
- 透古通今
- 邁古超今/迈古超今
- 酌古准今
- 酌古參今/酌古参今
- 酌古御今
- 酌古斟今
- 酌古沿今
- 酌古準今/酌古准今
- 鎔今鑄古/镕今铸古
- 鎔古鑄今/镕古铸今
- 鑑古推今/鉴古推今
- 鑠古切今/铄古切今
- 陳古刺今/陈古刺今
- 隆古賤今/隆古贱今
- 雕今
- 震古鑠今/震古铄今
- 非昔是今
- 頌古非今/颂古非今 (sònggǔfēijīn)
- 黑索今
Pronunciation
Definitions
今
- (Southern Min, Puxian Min) now
- (Southern Min) then; in that case
- (Taiwanese Hokkien) nowadays
Synonyms
References
- “今”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database), 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
Alternative forms
Readings
Compounds
- 今日 (kyō): today
- 今朝 (kesa): this morning
- 今年 (kotoshi): this year
- 今宵 (koyoi): tonight; this evening
- 今回 (konkai): this time; lately
- 今月 (kongetsu): this month
- 今後 (kongo): from now on
- 今週 (konshū): this week
- 今度 (kondo): this time; recent; previous; another
- 今晩 (konban): tonight; this evening
- 今迄
- 今際
- 今夏
- 今期
- 今暁
- 今古
- 今更
- 今国会
- 今々, 今今
- 今次
- 今秋
- 今出来
- 今春
- 今尚
- 今上
- 今人
- 今世界
- 今世紀
- 今是昨非
- 今生
- 今昔
- 今川焼
- 今程
- 今冬
- 今道心
- 今般
- 今風
- 今方
- 今明日
- 今夜
- 今夕
- 今様
Etymology
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 今 |
| いま Grade: 2 |
| kun’yomi |
From Old Japanese. First attested in the Kojiki of 712 CE.[1] From Proto-Japonic *ima.
Noun
今 • (ima)
Derived terms
- 今一度 (imaichido): once more
- 今どき (imadoki): these days
- 今時 (imadoki), 今どき (imadoki)
- 今頃 (imagoro), 今ごろ (imagoro): around this time
- 今一つ (imahitotsu): one more; another; slightly lacking
- 今まで (ima made): until now; so far
- 今や (imaya): nowadays
- 中今 (nakaima, “the present; as a privileged moment in eternity”)
- 今村 (Imamura)
- 今が今まで (ima ga ima made): up to this very moment
- 今し方 (imashigata)
- 今では (imadeha)
- 今の所 (ima no tokoro)
- 今めかしい (imamekashī)
- 今めかす (imamekasu)
- 今もって (imamotte)
- 今や遅しと (imaya ososhi to)
- 今少し (imasukoshi)
- 今思うと (imaomōto)
- 今直ぐ (imasugu)
Prefix
今 • (kon-)
References
- “今”, in 日本国語大辞典 (Nihon Kokugo Daijiten, “Nihon Kokugo Daijiten”) (in Japanese), concise edition, Tōkyō: Shogakukan, 2000
- Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 [Daijirin] (in Japanese), Third edition, Tōkyō: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, editor (1998), NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 [NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary] (in Japanese), Tōkyō: NHK Publishing, →ISBN
Korean
Etymology
From Middle Chinese 今 (MC kim). Recorded as Middle Korean ⿱𠆢𬼽/금 (kum) (Yale: kum) in Hunmong Jahoe (訓蒙字會 / 훈몽자회), 1527.
Pronunciation
- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [kɯm]
- Phonetic hangul: [금]
Compounds
- 금방 (今方, geumbang)
- 방금 (方今, banggeum)
- 지금 (只今, jigeum)
- 작금 (昨今, jakgeum)
- 금번 (今番, geumbeon)
- 금년 (今年, geumnyeon)
- 금래 (今來, geumnae)
- 금차 (今次, geumcha)
- 금주 (今週, geumju)
- 금일 (今日, geumil)
- 목금 (目今, mokgeum)
- 상금 (尙今, sanggeum)
- 금명 (今明, geummyeong)
- 금석 (今夕, geumseok)
- 금기 (今期, geumgi)
- 금야 (今夜, geumya)
- 금월 (今月, geumwol)
- 금조 (今朝, geumjo)
- 금대 (今代, geumdae)
- 금세 (今歲, geumse)
- 금시 (今時, geumsi)
- 당금 (當今, danggeum)
- 금효 (今曉, geumhyo)
- 금반 (今般, geumban)
- 금세 (今世, geumse)
- 금후 (今後, geumhu)
- 고금 (古今, gogeum)
- 즉금 (卽今, jeukgeum)
- 금세기 (今世紀, geumsegi)
- 금시초문 (今始初聞, geumsichomun)
Vietnamese
Han character
今: Hán Việt readings: kim[1][2][3], câm (
今: Nôm readings: kim[1][2][4][5], câm[1][2], căm[1], cầm[1], ngấm[1]
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
References
- Nguyễn (2014).
- Nguyễn et al. (2009).
- Trần (2004).
- Bonet (1899).
- Génibrel (1898).