rḏj
See also: RDJ
Egyptian
Pronunciation
- (reconstructed) IPA(key): /(ɾV)ˈcʼiːjit/ → /(ɾV)ˈtʼiːjiʔ/ → /(ɾə)ˈtʼiːʔə/ → /ˈtʼiːʔ/
- (modern Egyptological) IPA(key): /rɛd͡ʒi/
- Conventional anglicization: redji
Verb
anom.
- (transitive) to give, to provide with
- (transitive) to serve as a source of (water, dew, etc.), to provide (something) passively
- (transitive) to extend (one’s hand or arm), to give (one’s hand) (+ n or r: to)
- (transitive) to send forth, to emit
- (transitive) to give forth (blood, air, one’s voice, etc.), to exude, to run with, to emit
- (transitive) to throw or thrust (a weapon)
- (transitive) to send (a letter)
- (transitive) to issue, to promulgate (laws, decrees, prescriptions, commands)
- (transitive) to put, to set, to place (+ r: in, on, at (a place); + ḥr: upon; + m: in)
- c. 2000 BCE – 1900 BCE, Tale of the Shipwrecked Sailor (pHermitage/pPetersburg 1115) lines 39–41:
![P6 [aHa] aHa](../I/hiero_P6.png.webp)
![D36 [a] a](../I/hiero_D36.png.webp)
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
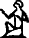
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![D36 [a] a](../I/hiero_D36.png.webp)
![V31 [k] k](../I/hiero_V31.png.webp)
![G43 [w] w](../I/hiero_G43.png.webp)
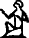
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![N18 [iw] iw](../I/hiero_N18.png.webp)

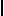
![M17 [i] i](../I/hiero_M17.png.webp)
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
![V4 [wA] wA](../I/hiero_V4.png.webp)
![G1 [A] A](../I/hiero_G1.png.webp)
![G43 [w] w](../I/hiero_G43.png.webp)
![N35A [mw] mw](../I/hiero_N35A.png.webp)
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)

![G36 [wr] wr](../I/hiero_G36.png.webp)
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)

- ꜥḥꜥ.n.j rḏj.kw r jw jn wꜣw n(j) wꜣḏ-wr
- Then I was put on an island by a wave of the sea.
- (transitive) to appoint (+ m or + r: as; + r or ḥr: to do (something))
- c. 2000 BCE – 1900 BCE, Tale of the Shipwrecked Sailor (pHermitage/pPetersburg 1115) lines 177–179:
![P6 [aHa] aHa](../I/hiero_P6.png.webp)
![D36 [a] a](../I/hiero_D36.png.webp)
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![D36 [a] a](../I/hiero_D36.png.webp)
![V31 [k] k](../I/hiero_V31.png.webp)
![G43 [w] w](../I/hiero_G43.png.webp)
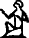
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![T18 [Sms] Sms](../I/hiero_T18.png.webp)
![Z7 [W] W](../I/hiero_Z7.png.webp)
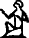
![S29 [s] s](../I/hiero_S29.png.webp)
![Aa17 [sA] sA](../I/hiero_Aa17.png.webp)
![G1 [A] A](../I/hiero_G1.png.webp)
![V28 [H] H](../I/hiero_V28.png.webp)
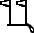

![V31 [k] k](../I/hiero_V31.png.webp)
![G43 [w] w](../I/hiero_G43.png.webp)
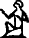
![G17 [m] m](../I/hiero_G17.png.webp)
![D1 [tp] tp](../I/hiero_D1.png.webp)
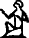

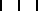
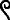
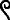
- ꜥḥꜥ.n(.j) rdj.kw r šmsw sꜣḥ.kw m štj tpw
- Then I was appointed as a retainer and endowed with two hundred servants (literally, “heads”).
- (transitive) to set down in writing (+ m or r: in (a document))
- (transitive) to set (fire) (+ m or r: to)
- (reflexive) to set oneself or lay oneself in some position, particularly prostrate on the ground
- (transitive) to turn (one’s face, back, etc.) (+ n or r: to, toward)
- (reflexive, often of the sun or gods) to reveal oneself
- (catenative, with a verb in the subjunctive) to cause, make, let, allow
- c. 1900 BCE, The Instructions of Kagemni (pPrisse/pBN 183) lines 2.3–2.4:
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![D36 [a] a](../I/hiero_D36.png.webp)
![M17 [i] i](../I/hiero_M17.png.webp)
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
![G47 [TA] TA](../I/hiero_G47.png.webp)
![X1 [t] t](../I/hiero_X1.png.webp)
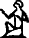
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
![M17 [i] i](../I/hiero_M17.png.webp)
![S29 [s] s](../I/hiero_S29.png.webp)
![X1 [t] t](../I/hiero_X1.png.webp)
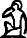
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
![G1 [A] A](../I/hiero_G1.png.webp)
![M17 [i] i](../I/hiero_M17.png.webp)
![M17 [i] i](../I/hiero_M17.png.webp)
![I9 [f] f](../I/hiero_I9.png.webp)
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
![F32 [X] X](../I/hiero_F32.png.webp)
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![D46 [d] d](../I/hiero_D46.png.webp)
![G43 [w] w](../I/hiero_G43.png.webp)

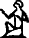
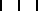
![G17 [m] m](../I/hiero_G17.png.webp)
![M3 [xt] xt](../I/hiero_M3.png.webp)
![Aa1 [x] x](../I/hiero_Aa1.png.webp)
![X1 [t] t](../I/hiero_X1.png.webp)
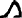
![D36 [a] a](../I/hiero_D36.png.webp)
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![N29 [q] q](../I/hiero_N29.png.webp)
![V12 [arq] arq](../I/hiero_V12.png.webp)
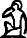
![I9 [f] f](../I/hiero_I9.png.webp)
![O34 [z] z](../I/hiero_O34.png.webp)
![Aa1 [x] x](../I/hiero_Aa1.png.webp)
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)

![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![V13 [T] T](../I/hiero_V13.png.webp)
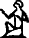

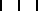
![D58 [b] b](../I/hiero_D58.png.webp)
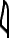
![X1 [t] t](../I/hiero_X1.png.webp)

![F18 [bH] bH](../I/hiero_F18.png.webp)
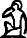
![S29 [s] s](../I/hiero_S29.png.webp)
![N35 [n] n](../I/hiero_N35.png.webp)
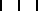
![G17 [m] m](../I/hiero_G17.png.webp)
![M18 [ii] ii](../I/hiero_M18.png.webp)
![M17 [i] i](../I/hiero_M17.png.webp)
![X1 [t] t](../I/hiero_X1.png.webp)
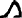
![D2 [Hr] Hr](../I/hiero_D2.png.webp)
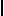
![D21 [r] r](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![I9 [f] f](../I/hiero_I9.png.webp)
- rdj.jn ṯꜣt(j) njs.t(w) nꜣy.f n(j) ẖrdw m ḫt ꜥrq.f sḫr r(m)ṯw bj(ꜣ)t.sn m jjt ḥr.f
- So the vizier let his children be summoned after he understood the conduct of people, their character being what had come upon him.
Inflection
Conjugation of rḏj (anomalous / anom.) — base stem: rḏj, ḏj, geminated stem: ḏḏ
| infinitival forms | imperative | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| infinitive | negatival complement | complementary infinitive1 | singular | plural |
| rḏjt, ḏjt |
rḏj |
— |
jmj, ḏj |
jmj, ḏj, ḏy |
| ‘pseudoverbal’ forms | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| stative stem | periphrastic imperfective2 | periphrastic prospective2 | |
| rḏj6, ḏj6 |
ḥr rḏjt, ḥr ḏjt |
m rḏjt, m ḏjt |
r rḏjt, r ḏjt |
| suffix conjugation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aspect / mood | active | passive | contingent | ||
| aspect / mood | active | passive | |||
| perfect | rḏj.n, ḏj.n |
rḏj, rḏjw, rḏy, ḏj, ḏjw, ḏy |
consecutive | rḏj.jn, ḏj.jn |
active + .tj1, .tw2 |
| active + .tj1, .tw2 | |||||
| terminative | — | ||||
| perfective3 | rḏj |
active + .tj1, .tw2 |
obligative1 | rḏj.ḫr |
active + .tj1, .tw2 |
| imperfective | ḏj |
active + .tj1, .tw2 | |||
| prospective3 | rḏj, rḏjw |
rḏj, rḏjw |
potentialis1 | rḏj.kꜣ |
active + .tj1, .tw2 |
| active + .tj1, .tw2 | |||||
| subjunctive | ḏj |
active + .tj1, .tw2 | |||
| verbal adjectives | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aspect / mood | relative (incl. nominal / emphatic) forms | participles | ||
| active | passive | active | passive | |
| perfect | rḏj.n, ḏj.n |
active + .tj1, .tw2 |
— | — |
| perfective | rḏj, ḏj |
active + .tj1, .tw2 |
rḏj, ḏj |
rḏy, rḏj, ḏy, ḏj |
| imperfective | ḏḏ, ḏḏw, ḏḏy |
active + .tj1, .tw2 |
ḏḏ |
ḏḏ, ḏḏw5 |
| prospective | — |
— | rḏjtj4, rḏjt4 | |
| ||||
In Late Egyptian the masculine third-person singular of the stative is commonly written
.
Alternative forms
By Middle Egyptian times, this verb had most likely become rdj, although sometimes written identically to its older form. By Late Egyptian it was likely dj.
Alternative hieroglyphic writings of rḏj
| rḏj | rdj | rdj | rdj | rtj | |||||||||||
| [chiefly Old Kingdom] | [Middle Kingdom] | [Middle Kingdom] | [Late Period] | [Late Period] |
Derived terms
References
- “rḏi̯ (lemma ID 851711)”, in Thesaurus Linguae Aegyptiae, Corpus issue 17, Web app version 2.01 edition, Tonio Sebastian Richter & Daniel A. Werning by order of the Berlin-Brandenburgische Akademie der Wissenschaften and Hans-Werner Fischer-Elfert & Peter Dils by order of the Sächsische Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Leipzig, 2004–15 December 2022
- Erman, Adolf, Grapow, Hermann (1928) Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache, volume 2, Berlin: Akademie-Verlag, →ISBN, pages 464.1–468.15
- Faulkner, Raymond Oliver (1962) A Concise Dictionary of Middle Egyptian, Oxford: Griffith Institute, →ISBN, pages 154–156
- James P[eter] Allen (2010) Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs, 2nd edition, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, →ISBN, pages 159, 357.
- Hoch, James (1997) Middle Egyptian Grammar, Mississauga: Benben Publications, →ISBN, pages 93–94
- Junge, Friedrich (2005) Late Egyptian Grammar: An Introduction, second English edition, Oxford: Griffith Institute, page 82
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.