笙
| ||||||||
Translingual
Han character
笙 (Kangxi radical 118, 竹+5, 11 strokes, cangjie input 竹竹手一 (HHQM), four-corner 88104, composition ⿱𥫗生)
- a sheng; a hand-held free-reed mouth organ made from a dried gourd and 13 or more bamboo pipes
Derived characters
- 𪡾
References
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 879, character 29
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 25913
- Dae Jaweon: page 1307, character 21
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 5, page 2955, character 6
- Unihan data for U+7B19
Chinese
| trad. | 笙 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. # | 笙 | |
Glyph origin
| Old Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 猜 | *sʰlɯː |
| 輤 | *sʰleːns |
| 綪 | *sʰleːns, *ʔsreːŋ |
| 倩 | *sʰleːns, *sʰleŋs |
| 棈 | *sʰleːns |
| 蒨 | *sʰeːns |
| 篟 | *sʰeːns |
| 生 | *sʰleːŋ, *sreŋs |
| 牲 | *sreŋ |
| 笙 | *sreŋ |
| 甥 | *sreŋ |
| 鉎 | *sreŋ, *sleːŋ |
| 珄 | *sreŋ |
| 鼪 | *sreŋ, *sreŋs |
| 猩 | *sreŋ, *seːŋ |
| 狌 | *sreŋ |
| 眚 | *sreŋʔ |
| 貹 | *sreŋs |
| 崝 | *zreːŋ |
| 精 | *ʔsleŋ, *ʔsleŋs |
| 菁 | *ʔsleŋ |
| 鶄 | *ʔsleŋ, *sʰleːŋ |
| 蜻 | *ʔsleŋ, *sʰleːŋ |
| 鼱 | *ʔsleŋ |
| 婧 | *ʔsleŋ, *zleŋs, *zleŋʔ |
| 睛 | *ʔsleŋ, *sʰleŋʔ |
| 箐 | *ʔsleŋ |
| 聙 | *ʔsleŋ |
| 旌 | *ʔsleŋ |
| 清 | *sʰleŋ |
| 圊 | *sʰleŋ |
| 請 | *sʰleŋʔ, *zleŋs, *zleŋ |
| 凊 | *sʰleŋs |
| 䝼 | *zleŋs, *zleŋ |
| 靚 | *zleŋs |
| 情 | *zleŋ |
| 晴 | *zleŋ |
| 夝 | *zleŋ |
| 靜 | *zleŋʔ |
| 靖 | *zleŋʔ |
| 睲 | *seŋʔ, *seːŋs |
| 惺 | *seŋʔ, *seːŋ |
| 性 | *sleŋs |
| 姓 | *sleŋs |
| 靗 | *l̥ʰeŋs |
| 鯖 | *ʔljeŋ, *sʰleːŋ |
| 青 | *sʰleːŋ |
| 靘 | *sʰleːŋ, *sʰleːŋs |
| 掅 | *sʰleːŋs |
| 胜 | *sleːŋ |
| 曐 | *sleːŋ |
| 星 | *sleːŋ |
| 鮏 | *sleːŋ |
| 腥 | *seːŋ, *seːŋs |
| 鯹 | *seːŋ |
| 醒 | *seːŋ, *seːŋʔ, *seːŋs |
| 篂 | *seːŋ |
Phono-semantic compound (形聲/形声, OC *sreŋ) : semantic 竹 (“bamboo”) + phonetic 生 (OC *sʰleːŋ, *sreŋs).
Etymology
From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *mriŋ (“sound; noise; animal cry”); cognate with 鳴 (OC *mreŋ, “to make a sound”), 鈴 (OC *reːŋ, “bell”), Burmese မြည် (mrany, “to make a sound”) (Schuessler, 2007; STEDT).
Pronunciation
Definitions
笙

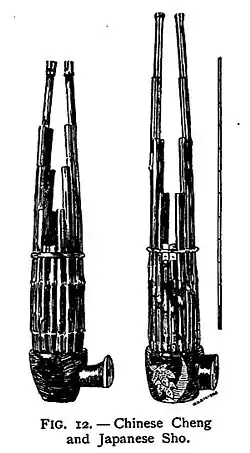
- (music) sheng (a Chinese mouth-blown free reed instrument consisting of vertical pipes)
See also
- 樦 (zhù)
Descendants
References
- “笙”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database), 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
Readings
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 笙 |
| しょう Jinmeiyō |
| goon |
/ɕau/ → /ɕɔː/ → /ɕoː/
From Middle Chinese 笙 (MC sraeng). The goon reading, so likely the original reading as first borrowed from Middle Chinese. Compare modern Mandarin 笙 (shēng).
The shō was developed from the Chinese shēng that was introduced to Japan during the Nara period.
Noun
- a free-reed woodwind musical instrument used in Japanese court music, consisting of a mouthpiece and seventeen pipes, each similar to an organ pipe
- Synonym: 鳳管 (hōkan)
Derived terms
- 笙の笛 (shō no fue, “type of simplified sho used as a toy”)
- 笙歌 (shōka, “singing to a sho accompaniment; to sing to a sho accompaniment; song sung to a sho accompaniment”)
- 笙岩屋, 笙窟 (Shō no Iwaya, “cave and pilgrimage destination in central Nara Prefecture”)
- 鳳笙 (hōshō, “sho”)
Descendants
- → English: sho
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 笙 |
| そう Jinmeiyō |
| kan’on |
/sau/ → /sɔː/ → /soː/
From Middle Chinese 笙 (MC sraeng). The kan'on, so likely a historically later reading.
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): [so̞ː]
Noun
- (obsolete) a free-reed woodwind musical instrument consisting of a mouthpiece and seventeen pipes, each similar to an organ pipe
References
- Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 [Daijirin] (in Japanese), Third edition, Tōkyō: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, editor (1998), NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 [NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary] (in Japanese), Tōkyō: NHK Publishing, →ISBN
Korean
Hanja
笙 • (saeng) (hangeul 생, revised saeng, McCune–Reischauer saeng, Yale sayng)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.