| Noreán Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Sinemurian-Toarcian | |
 | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Sub-units | See text |
| Underlies | Tablazo & La Luna Formations |
| Overlies | Bocas, Morrocoyal & Sudán Formations Norosí Batholith, San Lucas & Bucaramanga Gneiss |
| Thickness | 2,062 m (6,765 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Andesitic-rhyolitic lavas & pyroclastics |
| Other | Ignimbrites, thin sandstones |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 8°00′00″N 74°00′00″W / 8.00000°N 74.00000°W |
| Region | Bolívar, Cesar & Santander |
| Country | |
| Extent | Serranía de San Lucas & Eastern Ranges, Andes VIM & VMM (subsurface) |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Caserío Noreán |
| Named by | Clavijo |
| Location | Aguachica |
| Year defined | 1995 |
| Coordinates | 8°22′54″N 73°36′38″W / 8.38167°N 73.61056°W |
| Region | Cesar |
| Country | |
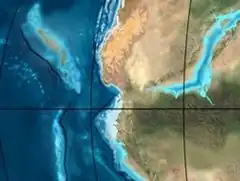 Paleogeography of Northern South America 200 Ma, by Ron Blakey | |
The Noreán Formation (Spanish: Formación Noreán, J1-2n,[2][3] J1n)[4] is a geological formation of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, the Serranía de San Lucas and as basement underlying the southernmost Lower and northern Middle Magdalena Valleys. The formation consists of volcanic and pyroclastic lavas that range from andesites to rhyolites. Vitric, lithic and crystal tuffs and andesitic dikes and hypabyssal bodies are also present in the formation.
The more than 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) thick formation was deposited in a continental arc magmatic setting in an Early Jurassic graben that presently forms the basement of the Middle Magdalena Valley (VMM). A positive anomaly of Pb suggests a subduction-related genesis dominated by explosive volcanism.
Etymology
The Noreán Formation was first defined as the "Unidad Volcanoclástica de Noreán" ("Volcanoclastic Unit of Noreán") in 1995 and in the same year elevated to a formal formation by Clavijo in 1995 as part of the geologic mapping for Plancha 65 Tamalameque and named after the caserío Noreán, 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) north of Aguachica, Cesar.[5] The type locality of the Noreán Formation is along the road between Buturama and Bombeadero in Aguachica.[6]
Description
The Noreán Formation is found in the northern part of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, stretching from the Cesar Department in the north, towards the Serranía de San Lucas in Bolívar to the Santander Massif in Santander in the south. The formation forms the economic basement in the southern Lower Magdalena Valley (VIM) and the northern Middle Magdalena Valley (VMM). The formation is interpreted as characteristic of an important explosive volcanic phase, the materials of which were deposited in a graben setting of the Middle Magdalena Valley. The Early Jurassic basin was covered by a shallow sea and in part drained by rivers and lakes. The basin at time of deposition was bordered by a volcanic arc, characterized by basaltic to calc-alkaline magmas.[7] The formation also comprises less than 1 metre (3.3 ft) thin very fine to fine sandstone beds constituting quartz (90 to 60%), feldspars (10 to 40%) and lithic fragments (1-2 %).[8]
The volcanic and pyroclastic rocks of the Noreán Formation are composed of lavas that range from andesitic to rhyolitic, together with vitric, lithic and crystal tuffs. Mainly andesitic dikes and hypabyssal bodies are also present. Geochemically, the volcanic and pyroclastic rocks exhibit chemical similarities, belong to the calc-alkaline series and have negative anomalies of Nb, P and Ti and a positive anomaly of Pb, suggesting a subduction-related genesis.[9]
U-Pb zircon geochronology resulted in ages of 192.4 ± 2.2 Ma in a basaltic andesite, 184.9 ± 2.0 Ma in an andesitic lava and 175.9 ± 1.1 Ma in a rhyolitic lava, indicating the occurrence of volcanic events in this section of the Noreán Formation from the Lower to the earliest Middle Jurassic. Zircon inheritance suggests that the volcanic arc was emplaced in a Meso- to Neoproterozoic basement. The Noreán Formation represents continental arc magmatism,[9] which occurred during a phase of extensional tectonics along the continental margin of northwestern South America from approximately 195 to 168 Ma.[10]
Stratigraphy
To the northwest of the Santander Massif, the formation overlies the Bocas Formation and is unconformably overlain by the Tablazo Formation.[6] In some locations in this area, the formation is found in faulted contact with the Bucaramanga Gneiss, La Virgen Formation and the Tablazo and La Luna Formations. In the Serranía de San Lucas, the Noreán Formation conformably overlies the Morrocoyal Formation and in this area is overlain by the Tablazo Formation and the Arenal Conglomeratic Unit. Across the San Lucas mountains, the formation is in faulted and discordant contact with the Norosí Batholith, the San Lucas Gneiss and the Sudán Formation.[7]
The formation is offset by the megaregional Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault.[3][1]
Subdivision
On the western flanks of the Eastern Cordillera, the formation is subdivided into six units and in the Serranía de San Lucas into four (1, 3, 5 and 6 of the six named below), from young to old:
- Hypobyssal Andesitic Unit (Jnha) - 12 metres (39 ft)[11]
- Effusive Rhyolitic Unit (Jner) - 150 metres (490 ft)[12]
- Dacitic Effusive Unit (Jned) - 350 metres (1,150 ft)[13]
- Pyroclastic and Effusive Dacitic Unit (Jnpd) - 450 metres (1,480 ft)[14]
- Effusive Spherulitic Unit (Jnee) - 300 metres (980 ft)[15]
- Pyroclastic-epiclastic Unit (Jnpe) - 800 metres (2,600 ft)[16]
Age

The age of the Noreán Formation has been established using potassium-argon (K-Ar), rubidium-strontium (Rb-Sr), and uranium-lead dating (U-Pb). The first method gave an age range of 194 ± 6 Ma, the Rb-Sr dating method provided a range of 161 ± 27 Ma and U-Pb dating of zircons resulted in ages of 201.6 ± 3.6 and 196.1 ± 4.4.[7] Refined dating of the formation performed in 2019 by Correa Martínez et al. concluded an age range between 192.4 ± 2.2 and 175.9 ± 1.1 Ma, spanning most of the Early Jurassic, from Sinemurian to Toarcian.[17] The Noreán Formation was intruded by the San Lucas Granitoid in the Middle Jurassic, dated at 166.9 ± 6 Ma.[18] A 2020 thermochronological study concluded that the Jurassic volcanic rocks covering the Santander Massif were exhumed during the latest Cretaceous to early Paleocene.[19]
Outcrops
The northernmost outcrop of the Noreán Formation is found in Chimichagua, Cesar.[2] In Cesar, outcrops occur south of the village of Saloa and around the town of Pailitas,[3] east of Tamalameque and Pelaya and west of La Gloria,[1] in the western part of Morales, Bolívar, north and east of Aguachica where its type locality is situated,[20] in the Serranía de San Lucas, where the urban center of Santa Rosa del Sur rests on top of the formation,[21] in the west of San Pablo, Bolívar,[22] and in the western part of Cantagallo, Bolívar.[23]
Regional correlations
In the Santander Massif, the Noreán Formation has been correlated to the Jordán Formation, while in the Serranía de San Lucas the formation correlates with and is partly overlying the Morrocoyal Formation. In the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta of northern Colombia, the Noreán Formation is considered equivalent with the Guatapurí Formation, the Corual and Los Indios Formations and the ignimbrite complexes of Caja de Ahorros, La Paila and La Piña. In the Serranía del Perijá to the east of the extent of the formation, the Noreán Formation correlates with La Quinta Formation. In the La Guajira peninsula, the formation is time-equivalent with the Rancho Grande Formation while to the south of its area in the Upper Magdalena Valley the Noreán Formation is correlated with the Saldaña Formation.[7] The Lower Jurassic is missing in the Llanos Basin to the southeast of the extent of the Eastern Cordillera.[24]
| Ma | Age | Paleomap | Regional events | Catatumbo | Cordillera | proximal Llanos | distal Llanos | Putumayo | VSM | Environments | Maximum thickness | Petroleum geology | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | Holocene |  | Holocene volcanism Seismic activity | alluvium | Overburden | ||||||||
| 1 | Pleistocene |  | Pleistocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 Glaciations | Guayabo | Soatá Sabana | Necesidad | Guayabo | Gigante Neiva | Alluvial to fluvial (Guayabo) | 550 m (1,800 ft) (Guayabo) | [25][26][27][28] | ||
| 2.6 | Pliocene |  | Pliocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 GABI | Subachoque | |||||||||
| 5.3 | Messinian | Andean orogeny 3 Foreland | Marichuela | Caimán | Honda | [27][29] | |||||||
| 13.5 | Langhian | Regional flooding | León | hiatus | Caja | León | Lacustrine (León) | 400 m (1,300 ft) (León) | Seal | [28][30] | |||
| 16.2 | Burdigalian | Miocene inundations Andean orogeny 2 | C1 | Carbonera C1 | Ospina | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C1) | 850 m (2,790 ft) (Carbonera) | Reservoir | [29][28] | ||||
| 17.3 | C2 | Carbonera C2 | Distal lacustrine-deltaic (C2) | Seal | |||||||||
| 19 | C3 | Carbonera C3 | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C3) | Reservoir | |||||||||
| 21 | Early Miocene | Pebas wetlands | C4 | Carbonera C4 | Barzalosa | Distal fluvio-deltaic (C4) | Seal | ||||||
| 23 | Late Oligocene |  | Andean orogeny 1 Foredeep | C5 | Carbonera C5 | Orito | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C5) | Reservoir | [26][29] | ||||
| 25 | C6 | Carbonera C6 | Distal fluvio-lacustrine (C6) | Seal | |||||||||
| 28 | Early Oligocene | C7 | C7 | Pepino | Gualanday | Proximal deltaic-marine (C7) | Reservoir | [26][29][31] | |||||
| 32 | Oligo-Eocene | C8 | Usme | C8 | onlap | Marine-deltaic (C8) | Seal Source | [31] | |||||
| 35 | Late Eocene |  | Mirador | Mirador | Coastal (Mirador) | 240 m (790 ft) (Mirador) | Reservoir | [28][32] | |||||
| 40 | Middle Eocene | Regadera | hiatus | ||||||||||
| 45 | |||||||||||||
| 50 | Early Eocene |  | Socha | Los Cuervos | Deltaic (Los Cuervos) | 260 m (850 ft) (Los Cuervos) | Seal Source | [28][32] | |||||
| 55 | Late Paleocene | PETM 2000 ppm CO2 | Los Cuervos | Bogotá | Gualanday | ||||||||
| 60 | Early Paleocene | SALMA | Barco | Guaduas | Barco | Rumiyaco | Fluvial (Barco) | 225 m (738 ft) (Barco) | Reservoir | [25][26][29][28][33] | |||
| 65 | Maastrichtian |  | KT extinction | Catatumbo | Guadalupe | Monserrate | Deltaic-fluvial (Guadalupe) | 750 m (2,460 ft) (Guadalupe) | Reservoir | [25][28] | |||
| 72 | Campanian | End of rifting | Colón-Mito Juan | [28][34] | |||||||||
| 83 | Santonian | Villeta/Güagüaquí | |||||||||||
| 86 | Coniacian | ||||||||||||
| 89 | Turonian | Cenomanian-Turonian anoxic event | La Luna | Chipaque | Gachetá | hiatus | Restricted marine (all) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Gachetá) | Source | [25][28][35] | |||
| 93 | Cenomanian |  | Rift 2 | ||||||||||
| 100 | Albian | Une | Une | Caballos | Deltaic (Une) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Une) | Reservoir | [29][35] | |||||
| 113 | Aptian |  | Capacho | Fómeque | Motema | Yaví | Open marine (Fómeque) | 800 m (2,600 ft) (Fómeque) | Source (Fóm) | [26][28][36] | |||
| 125 | Barremian | High biodiversity | Aguardiente | Paja | Shallow to open marine (Paja) | 940 m (3,080 ft) (Paja) | Reservoir | [25] | |||||
| 129 | Hauterivian |  | Rift 1 | Tibú- Mercedes | Las Juntas | hiatus | Deltaic (Las Juntas) | 910 m (2,990 ft) (Las Juntas) | Reservoir (LJun) | [25] | |||
| 133 | Valanginian | Río Negro | Cáqueza Macanal Rosablanca | Restricted marine (Macanal) | 2,935 m (9,629 ft) (Macanal) | Source (Mac) | [26][37] | ||||||
| 140 | Berriasian | Girón | |||||||||||
| 145 | Tithonian | Break-up of Pangea | Jordán | Arcabuco | Buenavista Batá | Saldaña | Alluvial, fluvial (Buenavista) | 110 m (360 ft) (Buenavista) | "Jurassic" | [29][38] | |||
| 150 | Early-Mid Jurassic | 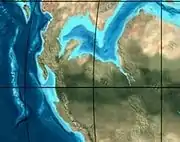 | Passive margin 2 | La Quinta | Montebel Noreán | hiatus | Coastal tuff (La Quinta) | 100 m (330 ft) (La Quinta) | [39] | ||||
| 201 | Late Triassic |  | Mucuchachi | Payandé | [29] | ||||||||
| 235 | Early Triassic |  | Pangea | hiatus | "Paleozoic" | ||||||||
| 250 | Permian |  | |||||||||||
| 300 | Late Carboniferous |  | Famatinian orogeny | Cerro Neiva () | [40] | ||||||||
| 340 | Early Carboniferous | Fossil fish Romer's gap | Cuche (355-385) | Farallones () | Deltaic, estuarine (Cuche) | 900 m (3,000 ft) (Cuche) | |||||||
| 360 | Late Devonian |  | Passive margin 1 | Río Cachirí (360-419) | Ambicá () | Alluvial-fluvial-reef (Farallones) | 2,400 m (7,900 ft) (Farallones) | [37][41][42][43][44] | |||||
| 390 | Early Devonian |  | High biodiversity | Floresta (387-400) El Tíbet | Shallow marine (Floresta) | 600 m (2,000 ft) (Floresta) | |||||||
| 410 | Late Silurian | Silurian mystery | |||||||||||
| 425 | Early Silurian | hiatus | |||||||||||
| 440 | Late Ordovician |  | Rich fauna in Bolivia | San Pedro (450-490) | Duda () | ||||||||
| 470 | Early Ordovician | First fossils | Busbanzá (>470±22) Chuscales Otengá | Guape () | Río Nevado () | Hígado () | [45][46][47] | ||||||
| 488 | Late Cambrian |  | Regional intrusions | Chicamocha (490-515) | Quetame () | Ariarí () | SJ del Guaviare (490-590) | San Isidro () | [48][49] | ||||
| 515 | Early Cambrian | Cambrian explosion | [47][50] | ||||||||||
| 542 | Ediacaran |  | Break-up of Rodinia | pre-Quetame | post-Parguaza | El Barro () | Yellow: allochthonous basement (Chibcha Terrane) Green: autochthonous basement (Río Negro-Juruena Province) | Basement | [51][52] | ||||
| 600 | Neoproterozoic | Cariri Velhos orogeny | Bucaramanga (600-1400) | pre-Guaviare | [48] | ||||||||
| 800 |  | Snowball Earth | [53] | ||||||||||
| 1000 | Mesoproterozoic |  | Sunsás orogeny | Ariarí (1000) | La Urraca (1030-1100) | [54][55][56][57] | |||||||
| 1300 | Rondônia-Juruá orogeny | pre-Ariarí | Parguaza (1300-1400) | Garzón (1180-1550) | [58] | ||||||||
| 1400 |  | pre-Bucaramanga | [59] | ||||||||||
| 1600 | Paleoproterozoic | Maimachi (1500-1700) | pre-Garzón | [60] | |||||||||
| 1800 | Tapajós orogeny | Mitú (1800) | [58][60] | ||||||||||
| 1950 | Transamazonic orogeny | pre-Mitú | [58] | ||||||||||
| 2200 | Columbia | ||||||||||||
| 2530 | Archean |  | Carajas-Imataca orogeny | [58] | |||||||||
| 3100 | Kenorland | ||||||||||||
| Sources | |||||||||||||
- Legend
- group
- important formation
- fossiliferous formation
- minor formation
- (age in Ma)
- proximal Llanos (Medina)[note 1]
- distal Llanos (Saltarin 1A well)[note 2]
See also
- Geology of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense
- Geology of the Eastern Hills
- Cesar-Ranchería Basin, sedimentary basin to the northeast of the Noreán extent
- Central Atlantic magmatic province, megaregional igneous province of the Early Jurassic
- Nacientes del Biobío Formation, contemporaneous volcanic formation of central Chile and western Argentina
- Pan de Azúcar Formation, contemporaneous volcanic formation of northern Chile
Notes
References
- 1 2 3 Plancha 65, 1994
- 1 2 Plancha 47, 2001
- 1 2 3 Plancha 55, 2006
- ↑ González Iregui et al., 2015, p.56
- ↑ Royero, 1996, p.10
- 1 2 Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.31
- 1 2 3 4 Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.32
- ↑ González Iregui et al., 2015, p.58
- 1 2 Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.29
- ↑ Rodríguez García et al., 2020, p.43
- ↑ Royero, 1996, p.16
- ↑ Royero, 1996, pp.15-16
- ↑ Royero, 1996, p.15
- ↑ Royero, 1996, pp.13-15
- ↑ Royero, 1996, p.12
- ↑ Royero, 1996, pp.11-12
- ↑ Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.43
- ↑ Clavijo et al., 2008, p.52
- ↑ Amaya Ferreira et al., 2020, p.11
- ↑ Plancha 75, 1992
- ↑ Plancha 85, 2006
- ↑ Plancha 96, 2006
- ↑ Plancha 108, 2012
- ↑ Barrero et al., 2007, p.70
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 García González et al., 2009, p.27
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 García González et al., 2009, p.50
- 1 2 García González et al., 2009, p.85
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Barrero et al., 2007, p.60
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Barrero et al., 2007, p.58
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.29
- 1 2 Plancha 177, 2015, p.39
- 1 2 Plancha 111, 2001, p.26
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.24
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.23
- 1 2 Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.32
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.30
- 1 2 Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.21-26
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.28
- ↑ Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.49
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.27
- ↑ Terraza et al., 2008, p.22
- ↑ Plancha 229, 2015, pp.46-55
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.26
- ↑ Moreno Sánchez et al., 2009, p.53
- ↑ Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.43
- ↑ Manosalva Sánchez et al., 2017, p.84
- 1 2 Plancha 303, 2002, p.24
- 1 2 Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.42
- ↑ Arango Mejía et al., 2012, p.25
- ↑ Plancha 350, 2011, p.49
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.17-21
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.13
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.23
- ↑ Plancha 348, 2015, p.38
- ↑ Planchas 367-414, 2003, p.35
- ↑ Toro Toro et al., 2014, p.22
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.21
- 1 2 3 4 Bonilla et al., 2016, p.19
- ↑ Gómez Tapias et al., 2015, p.209
- 1 2 Bonilla et al., 2016, p.22
- 1 2 Duarte et al., 2019
- ↑ García González et al., 2009
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001
- ↑ García González et al., 2009, p.60
Bibliography
- Amaya Ferreira, Sergio; Carlos Augusto Zuluaga, and Matthias Bernet. 2020. Different Levels of Exhumation across the Bucaramanga Fault in the Cepitá Area of the Southwestern Santander Massif, Colombia: Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the Northern Andes in Northwestern South America. Servicio Geológico Colombiano Publicaciones Especiales 37. 1–17. Accessed 2020-07-13.
- Rodríguez García, Gabriel; Ana María Correa Martínez; Gilberto Zapata García; María Isabel Arango Mejía; Gloria Obando Erazo; Juan Pablo Zapata Villada, and José Gilberto Bermúdez. 2020. Diverse Jurassic Magmatic Arcs of the Colombian Andes: Constraints from Petrography, Geochronology, and Geochemistry. Servicio Geológico Colombiano Publicaciones Especiales 36. 1–54. Accessed 2020-07-13.
- Correa Martínez, Ana María; Gabriel Rodríguez; María Isabel Arango, and Gilberto Zapata García. 2019. Petrografía, geoquímica y geocronología U-Pb de las rocas volcánicas y piroclásticas de la Formación Noreán al NW del Macizo de Santander, Colombia. Boletín de Geología 41. 29–54. Accessed 2019-10-31.
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. - González Iregui, Humberto; Rosalba Salinas Echeverri; Jorge Ignacio Cárdenas; Carlos Muñoz Taborda; Germán Ayala Montoya, and Wilson Vélez Giraldo. 2015. Memoria de la Plancha 56 - San Roque - 1:100,000, 1–147. Servicio Geológico Colombiano.
- Clavijo, Jairo; Luís Mantilla; Jorge Pinto; Luís Bernal, and Adrián Pérez. 2008. Evolución geológica de la Serranía de San Lucas, norte del Valle Medio del Magdalena y noroeste de la Cordillera Oriental. Boletín de Geología 30. 45–62. Accessed 2020-07-13.
- Barrero, Dario; Andrés Pardo; Carlos A. Vargas, and Juan F. Martínez. 2007. Colombian Sedimentary Basins: Nomenclature, Boundaries and Petroleum Geology, a New Proposal, 1–92. ANH.
- Royero, José María. 1996. Memoria de la Plancha 65 - Tamalameque - 1:100,000, 1–78. INGEOMINAS.
Maps
- Hernández, Marina; Jairo Clavijo, and Javier González. 2001. Plancha 47 - Chiriguaná - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Bernal Vargas, Luis Enrique, and Luis Carlos Mantilla Figueroa. 2006. Plancha 55 - El Banco - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Royero, José María; Jairo Clavijo; Hernando Mendoza; Gonzalo Barbosa; G. Vargas; R.E. Bernal, and P. Ferreira. 1994. Plancha 65 - Tamalameque - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Clavijo, Jairo; Gonzalo Barbosa; J.A. Camacho; L.E. Bernal; José María Royero, and E. Castro. 1992. Plancha 75 - Aguachica - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Bernal Vargas, Luis Enrique, and Luis Carlos Mantilla Figueroa. 2006. Plancha 85 - Simití - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Bernal Vargas, Luis Enrique, and Luis Carlos Mantilla Figueroa. 2006. Plancha 96 - Bocas del Rosario - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- UPTC, _. 2012. Plancha 108 - Puerto Wilches - 1:100,000, 1. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2018-06-01.