| Loma Gorda Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Turonian-Coniacian ~ | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Güagüaquí Group |
| Underlies | Oliní Group |
| Overlies | Hondita Formation |
| Thickness | up to 167 m (548 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Siltstone, shale |
| Other | Calcareous concretions |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 4°15′37.5″N 74°43′28.7″W / 4.260417°N 74.724639°W |
| Region | Cundinamarca, Huila & Tolima |
| Country | |
| Extent | Upper Magdalena Valley, Central & Eastern Ranges, Andes |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Loma Gorda ("Fat Hill") |
| Named by | De Porta |
| Location | Ricaurte, Cundinamarca |
| Year defined | 1966 |
| Coordinates | 4°15′37.5″N 74°43′28.7″W / 4.260417°N 74.724639°W |
| Region | Cundinamarca, Huila, Tolima |
| Country | |
 Paleogeography of Northern South America 90 Ma, by Ron Blakey | |
The Loma Gorda Formation (Spanish: Formación Loma Gorda, Kl, Kslg) is a fossiliferous geological formation of the Upper Magdalena Valley (VSM) and surrounding Central and Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, extending from Cundinamarca in the north to Huila and easternmost Tolima in the south. The uppermost unit of the Güagüaquí Group, a sequence of laminated siltstones and shales, dates to the Late Cretaceous period; Turonian to Coniacian epochs, and has a maximum thickness of 167 metres (548 ft).
Etymology
The formation was named in 1966 by De Porta, named Loma Gorda ("Fat Hill") in Ricaurte, Cundinamarca.[1]
Description
Lithologies
The Loma Gorda Formation is characterised by laminated siltstones and shales with calcareous concretions.[2] The formation has provided fossils of Ankinatsytes venezolanus, Barroisiceras onilahyense, Codazziceras ospinae, Eulophoceras jacobi, Fagesia catinus, Hauericeras madagascarensis, Hoplitoides ingens, H. lagiraldae, Mitonia gracilis, Mytiloides kossmati, M. goppelnensis, M. scupini, Neoptychites cf. andinus, Paralenticeras sieversi, Paramammites sp., Peroniceras subtricarinatum, Prionocycloceras guayabanum, Reesidites subtuberculatum, Subprionotropis colombianus, Allocrioceras sp., Anagaudryceras sp., Anomia sp., Benueites sp., Choffaticeras sp., Dydimotis sp., Forresteria sp., Gauthiericeras sp., Morrowites sp., Nannovascoceras sp., and Quitmaniceras sp..[3]
Stratigraphy and depositional environment
The Loma Gorda Formation is the uppermost unit of the Güagüaquí Group.[1] It overlies the Hondita Formation and is overlain by the Oliní Group. The age has been estimated on the basis of ammonites to be ranging from Turonian to Coniacian.[2] Stratigraphically, the formation is time equivalent with the upper parts of the Chipaque, La Luna and La Frontera Formations.[4] The formation was deposited in a relative highstand sequence with an oceanic oxygen depletion event, sharply marked in Colombia and characterised by the appearance of calcareous concretions with a thick pyrite rim.[5]
Outcrops

The type locality of the Loma Gorda Formation is located close to Loma Gorda in Ricaurte, Cundinamarca.[6] Other outcrops of the Loma Gorda Formation have been noted east of the Magdalena River northeast of Honda,[7] west of Nariño,[8] west across the Magdalena River in San Luis, Tolima,[9] between the Tetuán and Saldaña Rivers west of Coyaima and east and west of Ataco,[10] to the east of the Prado River reservoir,[11] north and west of Aipe,[12] surrounding Alpujarra, Tolima,[13] south of Palermo, Huila, displaced by the Baché Fault,[14] east of Iquira,[15] north of Yaguará,[16] south of La Plata where the formation is cut by the Itaibe Fault,[17] a small patch east of Gigante, Huila,[18] northwest and northeast of San Agustín,[19] and north of Timaná surrounding the Magdalena River.[20]
Regional correlations
| Age | Paleomap | VMM | Guaduas-Vélez | W Emerald Belt | Villeta anticlinal | Chiquinquirá- Arcabuco | Tunja- Duitama | Altiplano Cundiboyacense | El Cocuy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maastrichtian | 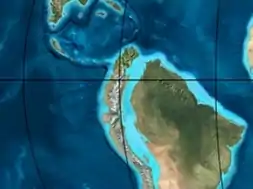 | Umir | Córdoba | Seca | eroded | Guaduas | Colón-Mito Juan | ||||||
| Umir | Guadalupe | ||||||||||||
| Campanian | Córdoba | ||||||||||||
| Oliní | |||||||||||||
| Santonian | La Luna | Cimarrona - La Tabla | La Luna | ||||||||||
| Coniacian | Oliní | Villeta | Conejo | Chipaque | |||||||||
| Güagüaquí | Loma Gorda | undefined | La Frontera | ||||||||||
| Turonian |  | Hondita | La Frontera | Otanche | |||||||||
| Cenomanian | Simití | hiatus | La Corona | Simijaca | Capacho | ||||||||
| Pacho Fm. | Hiló - Pacho | Churuvita | Une | Aguardiente | |||||||||
| Albian |  | Hiló | Chiquinquirá | Tibasosa | Une | ||||||||
| Tablazo | Tablazo | Capotes - La Palma - Simití | Simití | Tibú-Mercedes | |||||||||
| Aptian | Capotes | Socotá - El Peñón | Paja | Fómeque | |||||||||
| Paja | Paja | El Peñón | Trincheras | Río Negro | |||||||||
| La Naveta | |||||||||||||
| Barremian |  | ||||||||||||
| Hauterivian | Muzo | Cáqueza | Las Juntas | ||||||||||
| Rosablanca | Ritoque | ||||||||||||
| Valanginian | Ritoque | Furatena | Útica - Murca | Rosablanca | hiatus | Macanal | |||||||
| Rosablanca | |||||||||||||
| Berriasian |  | Cumbre | Cumbre | Los Medios | Guavio | ||||||||
| Tambor | Arcabuco | Cumbre | |||||||||||
| Sources | |||||||||||||
| Ma | Age | Paleomap | Regional events | Catatumbo | Cordillera | proximal Llanos | distal Llanos | Putumayo | VSM | Environments | Maximum thickness | Petroleum geology | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | Holocene |  | Holocene volcanism Seismic activity | alluvium | Overburden | ||||||||
| 1 | Pleistocene |  | Pleistocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 Glaciations | Guayabo | Soatá Sabana | Necesidad | Guayabo | Gigante Neiva | Alluvial to fluvial (Guayabo) | 550 m (1,800 ft) (Guayabo) | [21][22][23][24] | ||
| 2.6 | Pliocene |  | Pliocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 GABI | Subachoque | |||||||||
| 5.3 | Messinian | Andean orogeny 3 Foreland | Marichuela | Caimán | Honda | [23][25] | |||||||
| 13.5 | Langhian | Regional flooding | León | hiatus | Caja | León | Lacustrine (León) | 400 m (1,300 ft) (León) | Seal | [24][26] | |||
| 16.2 | Burdigalian | Miocene inundations Andean orogeny 2 | C1 | Carbonera C1 | Ospina | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C1) | 850 m (2,790 ft) (Carbonera) | Reservoir | [25][24] | ||||
| 17.3 | C2 | Carbonera C2 | Distal lacustrine-deltaic (C2) | Seal | |||||||||
| 19 | C3 | Carbonera C3 | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C3) | Reservoir | |||||||||
| 21 | Early Miocene | Pebas wetlands | C4 | Carbonera C4 | Barzalosa | Distal fluvio-deltaic (C4) | Seal | ||||||
| 23 | Late Oligocene |  | Andean orogeny 1 Foredeep | C5 | Carbonera C5 | Orito | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C5) | Reservoir | [22][25] | ||||
| 25 | C6 | Carbonera C6 | Distal fluvio-lacustrine (C6) | Seal | |||||||||
| 28 | Early Oligocene | C7 | C7 | Pepino | Gualanday | Proximal deltaic-marine (C7) | Reservoir | [22][25][27] | |||||
| 32 | Oligo-Eocene | C8 | Usme | C8 | onlap | Marine-deltaic (C8) | Seal Source | [27] | |||||
| 35 | Late Eocene |  | Mirador | Mirador | Coastal (Mirador) | 240 m (790 ft) (Mirador) | Reservoir | [24][28] | |||||
| 40 | Middle Eocene | Regadera | hiatus | ||||||||||
| 45 | |||||||||||||
| 50 | Early Eocene |  | Socha | Los Cuervos | Deltaic (Los Cuervos) | 260 m (850 ft) (Los Cuervos) | Seal Source | [24][28] | |||||
| 55 | Late Paleocene | PETM 2000 ppm CO2 | Los Cuervos | Bogotá | Gualanday | ||||||||
| 60 | Early Paleocene | SALMA | Barco | Guaduas | Barco | Rumiyaco | Fluvial (Barco) | 225 m (738 ft) (Barco) | Reservoir | [21][22][25][24][29] | |||
| 65 | Maastrichtian |  | KT extinction | Catatumbo | Guadalupe | Monserrate | Deltaic-fluvial (Guadalupe) | 750 m (2,460 ft) (Guadalupe) | Reservoir | [21][24] | |||
| 72 | Campanian | End of rifting | Colón-Mito Juan | [24][30] | |||||||||
| 83 | Santonian | Villeta/Güagüaquí | |||||||||||
| 86 | Coniacian | ||||||||||||
| 89 | Turonian | Cenomanian-Turonian anoxic event | La Luna | Chipaque | Gachetá | hiatus | Restricted marine (all) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Gachetá) | Source | [21][24][31] | |||
| 93 | Cenomanian |  | Rift 2 | ||||||||||
| 100 | Albian | Une | Une | Caballos | Deltaic (Une) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Une) | Reservoir | [25][31] | |||||
| 113 | Aptian |  | Capacho | Fómeque | Motema | Yaví | Open marine (Fómeque) | 800 m (2,600 ft) (Fómeque) | Source (Fóm) | [22][24][32] | |||
| 125 | Barremian | High biodiversity | Aguardiente | Paja | Shallow to open marine (Paja) | 940 m (3,080 ft) (Paja) | Reservoir | [21] | |||||
| 129 | Hauterivian |  | Rift 1 | Tibú- Mercedes | Las Juntas | hiatus | Deltaic (Las Juntas) | 910 m (2,990 ft) (Las Juntas) | Reservoir (LJun) | [21] | |||
| 133 | Valanginian | Río Negro | Cáqueza Macanal Rosablanca | Restricted marine (Macanal) | 2,935 m (9,629 ft) (Macanal) | Source (Mac) | [22][33] | ||||||
| 140 | Berriasian | Girón | |||||||||||
| 145 | Tithonian | Break-up of Pangea | Jordán | Arcabuco | Buenavista Batá | Saldaña | Alluvial, fluvial (Buenavista) | 110 m (360 ft) (Buenavista) | "Jurassic" | [25][34] | |||
| 150 | Early-Mid Jurassic |  | Passive margin 2 | La Quinta | Montebel Noreán | hiatus | Coastal tuff (La Quinta) | 100 m (330 ft) (La Quinta) | [35] | ||||
| 201 | Late Triassic |  | Mucuchachi | Payandé | [25] | ||||||||
| 235 | Early Triassic |  | Pangea | hiatus | "Paleozoic" | ||||||||
| 250 | Permian |  | |||||||||||
| 300 | Late Carboniferous |  | Famatinian orogeny | Cerro Neiva () | [36] | ||||||||
| 340 | Early Carboniferous | Fossil fish Romer's gap | Cuche (355-385) | Farallones () | Deltaic, estuarine (Cuche) | 900 m (3,000 ft) (Cuche) | |||||||
| 360 | Late Devonian |  | Passive margin 1 | Río Cachirí (360-419) | Ambicá () | Alluvial-fluvial-reef (Farallones) | 2,400 m (7,900 ft) (Farallones) | [33][37][38][39][40] | |||||
| 390 | Early Devonian | 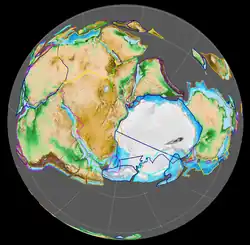 | High biodiversity | Floresta (387-400) El Tíbet | Shallow marine (Floresta) | 600 m (2,000 ft) (Floresta) | |||||||
| 410 | Late Silurian | Silurian mystery | |||||||||||
| 425 | Early Silurian | hiatus | |||||||||||
| 440 | Late Ordovician |  | Rich fauna in Bolivia | San Pedro (450-490) | Duda () | ||||||||
| 470 | Early Ordovician | First fossils | Busbanzá (>470±22) Chuscales Otengá | Guape () | Río Nevado () | Hígado () | [41][42][43] | ||||||
| 488 | Late Cambrian |  | Regional intrusions | Chicamocha (490-515) | Quetame () | Ariarí () | SJ del Guaviare (490-590) | San Isidro () | [44][45] | ||||
| 515 | Early Cambrian | Cambrian explosion | [43][46] | ||||||||||
| 542 | Ediacaran |  | Break-up of Rodinia | pre-Quetame | post-Parguaza | El Barro () | Yellow: allochthonous basement (Chibcha Terrane) Green: autochthonous basement (Río Negro-Juruena Province) | Basement | [47][48] | ||||
| 600 | Neoproterozoic | Cariri Velhos orogeny | Bucaramanga (600-1400) | pre-Guaviare | [44] | ||||||||
| 800 |  | Snowball Earth | [49] | ||||||||||
| 1000 | Mesoproterozoic |  | Sunsás orogeny | Ariarí (1000) | La Urraca (1030-1100) | [50][51][52][53] | |||||||
| 1300 | Rondônia-Juruá orogeny | pre-Ariarí | Parguaza (1300-1400) | Garzón (1180-1550) | [54] | ||||||||
| 1400 |  | pre-Bucaramanga | [55] | ||||||||||
| 1600 | Paleoproterozoic | Maimachi (1500-1700) | pre-Garzón | [56] | |||||||||
| 1800 | Tapajós orogeny | Mitú (1800) | [54][56] | ||||||||||
| 1950 | Transamazonic orogeny | pre-Mitú | [54] | ||||||||||
| 2200 | Columbia | ||||||||||||
| 2530 | Archean | 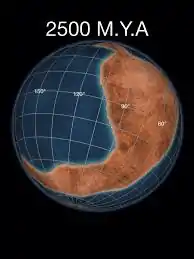 | Carajas-Imataca orogeny | [54] | |||||||||
| 3100 | Kenorland | ||||||||||||
| Sources | |||||||||||||
- Legend
- group
- important formation
- fossiliferous formation
- minor formation
- (age in Ma)
- proximal Llanos (Medina)[note 1]
- distal Llanos (Saltarin 1A well)[note 2]
See also
Notes
References
- 1 2 Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.23
- 1 2 Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.24
- ↑ Patarroyo, 2011
- ↑ Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.22
- ↑ Villamil, 2012, p.173
- ↑ Acosta & Ulloa, 2001, p.43
- ↑ Plancha 207, 2010
- ↑ Plancha 245, 1999
- ↑ Plancha 264, 2002
- ↑ Plancha 282, 1993
- ↑ Plancha 283, 2009
- ↑ Plancha 302, 1993
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002
- ↑ Plancha 323, 1998
- ↑ Plancha 344, 1999
- ↑ Plancha 345, 1999
- ↑ Plancha 366, 1998
- ↑ Plancha 367, 2003
- ↑ Plancha 388, 2002
- ↑ Plancha 389, 2003
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 García González et al., 2009, p.27
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 García González et al., 2009, p.50
- 1 2 García González et al., 2009, p.85
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Barrero et al., 2007, p.60
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Barrero et al., 2007, p.58
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.29
- 1 2 Plancha 177, 2015, p.39
- 1 2 Plancha 111, 2001, p.26
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.24
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.23
- 1 2 Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.32
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.30
- 1 2 Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.21-26
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.28
- ↑ Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.49
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.27
- ↑ Terraza et al., 2008, p.22
- ↑ Plancha 229, 2015, pp.46-55
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.26
- ↑ Moreno Sánchez et al., 2009, p.53
- ↑ Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.43
- ↑ Manosalva Sánchez et al., 2017, p.84
- 1 2 Plancha 303, 2002, p.24
- 1 2 Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.42
- ↑ Arango Mejía et al., 2012, p.25
- ↑ Plancha 350, 2011, p.49
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.17-21
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.13
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.23
- ↑ Plancha 348, 2015, p.38
- ↑ Planchas 367-414, 2003, p.35
- ↑ Toro Toro et al., 2014, p.22
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.21
- 1 2 3 4 Bonilla et al., 2016, p.19
- ↑ Gómez Tapias et al., 2015, p.209
- 1 2 Bonilla et al., 2016, p.22
- 1 2 Duarte et al., 2019
- ↑ García González et al., 2009
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001
- ↑ García González et al., 2009, p.60
Bibliography
- Acosta, Jorge E., and Carlos E. Ulloa. 2002. Mapa geológico del Departamento de Cundinamarca 1:250,000 - Memoria Explicativa, 1–108. INGEOMINAS.
- Patarroyo, Pedro. 2011. Sucesión de Amonitas del Cretácico Superior (Cenomaniano-Coniaciano) de la parte más alta de la Formación Hondita y de la Formación Loma Gorda en la Quebrada Bambucá, Aipe - Huila (Colombia). Boletín de Geología 33. 69–92. Accessed 2019-03-13.
- Villamil, Tomas. 2012. Chronology Relative Sea Level History and a New Sequence Stratigraphic Model for Basinal Cretaceous Facies of Colombia, 161–216. Society for Sedimentary Geology (SEPM).
Maps
- Barrero L., Darío, and Carlos J. Vesga O. 2009. Plancha 188 - La Dorada - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Barrero, Darío, and Carlos J. Vesga. 2010. Plancha 207 - Honda - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Acosta, Jorge E.; Rafael Guatame; Oscar Torres, and Frank Solano. 1999. Plancha 245 - Girardot - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Calcedo, Juan Carlos, and Roberto Terraza. 2000. Plancha 264 - Espinal - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Carvajal, Cesar; Jaime Fuquen, and Luis Gómez. 1993. Plancha 282 - Chaparral - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Cossio, Ubaldo; Gabriel Rodríguez, and Miguel Rodríguez. 1995. Plancha 283 - Purificación - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Fuquen, Jaime; Gabriel Rodríguez; Ubaldo Cossio, and Alberto Núñez. 1993. Plancha 302 - Aipe - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Acosta, Jorge; Pablo Caro; Jaime Fuquen, and José Osorno. 2002. Plancha 303 - Colombia - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS.
- Ferreira, Paulina; Alberto Núñez, and Miguel Rodríguez. 1998. Plancha 323 - Neiva - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Marquínez, Germán; C. Morales, and Alberto Núñez. 1999. Plancha 344 - Tesalia - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Velandia, F.; C.J. Morales; J.C. Caicedo, and Alberto Núñez. 1999. Plancha 345 - Campoalegre - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Marquínez, Germán; Yohana Rodríguez; Roberto Terraza, and Mario Martínez. 2003. Plancha 365 - Coconuco - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Rodríguez, Gabriel; Paulina Ferreira; Francisco Velandia, and Alberto Núñez. 1998. Plancha 366 - Garzón - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Rodríguez, Gabriel; Gilberto Zapata, and M. Velázquez. 2003. Plancha 367 - Gigante - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Cárdenas, Jorge; Jaime Fuquen, and Alberto Núñez. 2002. Plancha 388 - Pitalito - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Rodríguez, Gabriel; Gilberto Zapata, and M. Velázquez. 2003. Plancha 389 - Timaná - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
External links
- Gómez, J.; N.E. Montes; Á. Nivia, and H. Diederix. 2015. Plancha 5-09 del Atlas Geológico de Colombia 2015 – escala 1:500,000, 1. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2017-03-16.