Welcome to the shark portal

Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorpha (or Selachii) and are the sister group to the Batoidea (rays and kin). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as Cladoselache and Doliodus first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The oldest confirmed modern sharks (selachimorphs) are known from the Early Jurassic, about 200 million years ago, though records of true sharks may extend back as far as the Permian.
Sharks range in size from the small dwarf lanternshark (Etmopterus perryi), a deep sea species that is only 17 centimetres (6.7 in) in length, to the whale shark (Rhincodon typus), the largest fish in the world, which reaches approximately 12 metres (40 ft) in length. They are found in all seas and are common to depths up to 2,000 metres (6,600 ft). They generally do not live in freshwater, although there are a few known exceptions, such as the bull shark and the river shark, which can be found in both seawater and freshwater. Sharks have a covering of dermal denticles that protects their skin from damage and parasites in addition to improving their fluid dynamics. They have numerous sets of replaceable teeth.
Several species are apex predators, which are organisms that are at the top of their food chain. Select examples include the tiger shark, blue shark, great white shark, mako shark, thresher shark, and hammerhead shark. (Full article...)
Selected article -

Longfin mako sharks are predators that feed on small schooling bony fishes and cephalopods. It is uncertain whether this shark is capable of elevating its body temperature above that of the surrounding water like the other members of its family, though it possesses the requisite physiological adaptations. Reproduction in this species is ovoviviparous, meaning that the embryos hatch from eggs inside the uterus. In the latter stages of development, the unborn young are fed non-viable eggs by the mother (oophagy). The litter size is typically two but may be as many as eight. The longfin mako is of limited commercial value as its meat and fins are of lower quality than those of other pelagic sharks; it is caught unintentionally in low numbers across its range. The World Conservation Union has assessed this species as Vulnerable due to its rarity, low reproductive rate, and continuing bycatch mortality.
Did you know (auto-generated)
- ... that Hixxy and Sharkey created a schism in the UK rave music scene in 1995?
- ... that Timo Meier became the first player in San Jose Sharks franchise history to score five goals in one game when he was 25?
- ... that Alexis Sharkey's last Instagram post before her murder documented her travels to Tulum, Mexico?
- ... that the ampullae of Lorenzini enable sharks to sense electric fields?
- ... that "the Hurricane Shark is real"?
- ... that since 2018, IKEA's stuffed toy shark Blåhaj has become a popular Internet meme and an icon of the online transgender community?
Categories
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects related to sharks:
- WikiProject Science
- WikiProject Biology
- WikiProject Tree of Life
- WikiProject Animals
- WikiProject Fishes
- WikiProject Sharks
- WikiProject Fishes
- WikiProject Animals
- WikiProject Tree of Life
- WikiProject Biology
- WikiProject Aquarium Fishes
- WikiProject Fishing
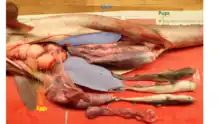
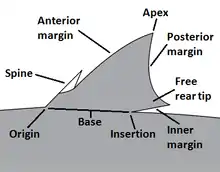
Selected picture -

More Did you know? -
- ... that the whitefin dogfish has light-producing organs on its upper eyelids?
- ... that the spinner shark is named for the spinning leaps it makes out of the water as part of its feeding strategy?
- ...that John Singleton Copley's painting, Watson and the Shark, was based on a real-life shark attack that occurred in Havana, Cuba in 1749?
- ... that, like the related cookiecutter shark, the kitefin shark sometimes feeds by taking bites out of animals larger than itself?
- ... that the first successful artificial insemination of a shark was performed in the cloudy catshark?
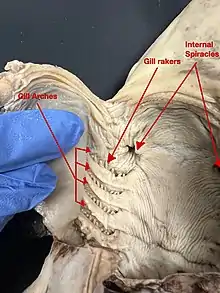
General images
Topics
 See also
See also 
For additional lists of marine life-related featured articles and good articles see:
- WikiProject Cetaceans § Featured and Good Content
- Portal:Fish/Recognized content
- Portal:Marine life/Recognized content
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals




.jpg.webp)



_(46722837981).jpg.webp)