| Main page | Main topics & Categories | Related portals & WikiProjects | Things you can do |
Science portal
Science is a rigorous, systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the world. Modern science is typically divided into three major branches: the natural sciences (e.g., physics, chemistry, and biology), which study the physical world; the social sciences (e.g., economics, psychology, and sociology), which study individuals and societies; and the formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science), which study formal systems, governed by axioms and rules. There is disagreement whether the formal sciences are science disciplines, because they do not rely on empirical evidence. Applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as in engineering and medicine.
The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest written records of identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to Bronze Age Egypt and Mesopotamia from around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes, while further advancements, including the introduction of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, were made during the Golden Age of India. Scientific research deteriorated in these regions after the fall of the Western Roman Empire during the early middle ages (400 to 1000 CE), but in the Medieval renaissances (Carolingian Renaissance, Ottonian Renaissance and the Renaissance of the 12th century) scholarship flourished again. Some Greek manuscripts lost in Western Europe were preserved and expanded upon in the Middle East during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek manuscripts from the dying Byzantine Empire to Western Europe in the Renaissance.
The recovery and assimilation of Greek works and Islamic inquiries into Western Europe from the 10th to 13th century revived "natural philosophy", which was later transformed by the Scientific Revolution that began in the 16th century as new ideas and discoveries departed from previous Greek conceptions and traditions. The scientific method soon played a greater role in knowledge creation and it was not until the 19th century that many of the institutional and professional features of science began to take shape, along with the changing of "natural philosophy" to "natural science".
New knowledge in science is advanced by research from scientists who are motivated by curiosity about the world and a desire to solve problems. Contemporary scientific research is highly collaborative and is usually done by teams in academic and research institutions, government agencies, and companies. The practical impact of their work has led to the emergence of science policies that seek to influence the scientific enterprise by prioritizing the ethical and moral development of commercial products, armaments, health care, public infrastructure, and environmental protection. (Full article...)
Featured article -
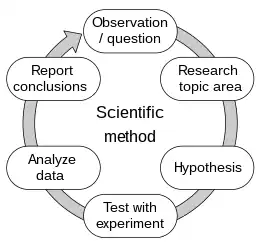
Selected image

Selected biography

However, much of Galen's understanding is flawed from the modern point of view. For example, he did not recognize blood circulation and thought that venous and arterial systems were separate. This view did not change until William Harvey's work in the 17th century.
More did you know...

- ...that the gestation period of the ring-tailed lemur (pictured) is approximately 146 days?
- ...that the Late November 2006 Nor'easter caused winds up to 80 mph (70 knots) in the Outer Banks of North Carolina, the earliest snowfall on record for Savannah, Georgia and Charleston, South Carolina, as well as Charleston, South Carolina's only occurrence of thundersnow on record?
- ...that the Rufous-crowned Sparrow, a medium-sized sparrow of the southwestern United States and Mexico, has a subspecies endemic to the Todos Santos Islands that has not been seen since the 1970s?
- ...that the Christmas 1994 Nor'easter led to wind gusts of 99 mph/86 knots in Massachusetts, and briefly formed an eye?
- ...that the Northern Red-legged Frog is a near-threatened species, whose male defends breeding pond territory with nocturnal displays?
Topics and categories
Science News
- 24 November 2023 –
- Astronomers at the Telescope Array Project in Utah, United States, observe the second largest cosmic ray ever detected, the so-called Amaterasu particle, with an energy of 244 EeV. (Cosmos Magazine)
- 2 November 2023 –
- Colombian Environment Minister Susana Muhamad announces plans to sterilize 20 of 166 hippopotamuses, descendants of those imported by drug lord Pablo Escobar, and cull some others, citing environmental concerns. (AFP via ABS-CBN News)
- 30 October 2023 –
- In a study published in Nature Geoscience, researchers suggest that solid particulates (predominantly silicate) from the Chicxulub asteroid impact played a dominant role in the radiative forcing leading to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (impact winter), contrary to the widely accepted theory that sulfur aerosols led to the mass extinction. (AFP via RFI) (Nature)
- 23 October 2023 – 2023 in arthropod paleontology
- A new species of prehistoric millipede named Lauravolsella willemeni is discovered in the Netherlands. (NOS)
General images -
Sources
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals













.png.webp)





_Venenbild.jpg.webp)






.jpeg.webp)
















.jpg.webp)






.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)