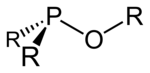
Structural formula of a generic phosphinite, R represents a side chain.
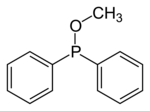
Skeletal formula of methyl diphenylphosphinite
In organic chemistry, phosphinites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula P(OR)R2. They are used as ligands in homogeneous catalysis and coordination chemistry.[1]
Preparation
Phosphinites are prepared by alcoholysis of organophosphinous chlorides. For example, treatment of chlorodiphenylphosphine with methanol and base gives methyl diphenylphosphinite:
- ClPPh2 + CH3OH → CH3OPPh2 + HCl
Although they are esters of phosphinous acids (R2POH), phosphinites are not made via such intermediates.
Reactions
Oxidation of phosphinites gives phosphinates:
- 2 P(OR)R2 + O2 → 2 OP(OR)R2
Phosphinites are ligands, giving derivatives similar to metal phosphine complexes. They are stronger pi-acceptors than typical phosphine ligands.[2]
References
- ↑ D. E. C. Corbridge (1995). Phosphorus: An Outline of its Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Technology (5th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. ISBN 0-444-89307-5.
- ↑ Rajanbabu, T. V. Babu (2012). "Phosphinite and Phosphonite Ligands". Phosphorus(III) Ligands in Homogeneous Catalysis: Design and Synthesis. pp. 159–232. doi:10.1002/9781118299715.ch5. ISBN 9781118299715.
See also
- Phosphine - PR3
- Phosphine oxide - OPR3
- Phosphonite - P(OR)2R
- Phosphite - P(OR)3
- Phosphinate - OP(OR)R2
- Phosphonate - OP(OR)2R
- Phosphate - OP(OR)3
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.