Lipis District | |
|---|---|
| Daerah Lipis | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Jawi | ﻟﻴﭭﻴﺲ |
| • Chinese | 立卑县 |
| • Tamil | லிப்பிஸ் |
 Seal | |
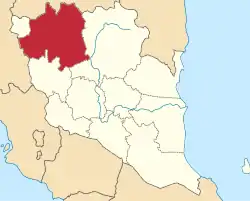 Location of Lipis District in Pahang | |
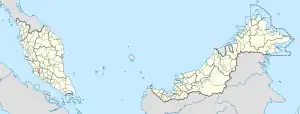 Lipis District Location of Lipis District in Malaysia | |
| Coordinates: 4°15′N 101°50′E / 4.250°N 101.833°E | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Seat | Kuala Lipis |
| Local area government(s) | Lipis District Council |
| Government | |
| • District officer | YH Dato' Mohd Hafizi Bin Ibrahim[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,168 km2 (1,995 sq mi) |
| Population (2010)[3] | |
| • Total | 85,341 |
| • Density | 17/km2 (43/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+08:00 (MST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+08:00 (Not observed) |
| Postcode | 27xxx |
| Calling code | +6-09 |
| Vehicle registration plates | C |
The Lipis District is a district located in north-west of Pahang, Malaysia. The district covers an area of 5,198 km2. Lipis district is bordered by Cameron Highlands and Perak on the west, Jerantut on the east, Kelantan and Raub on the north and south, respectively. Lipis has 10 mukim or subdistricts, the largest being Ulu Jelai. The district capital is Kuala Lipis. During the British colonization, Kuala Lipis was made the state's capital city. Kuala Lipis was the administrative capital of Pahang for 57 years from 1898 until 27 August 1955, when Kuantan was picked as the new capital. Lipis had many types of minerals such as tin and gold, and products from the surrounding forests.
Sungai Relau, near Merapoh, is an alternative entry point (there are about four entry points) into Taman Negara, Malaysia's Premier National park and one of the three embarkation points to Gunung Tahan, the highest mountain in Peninsular Malaysia standing at 2,187 meters above sea level.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 68,276 | — |
| 2000 | 73,557 | +7.7% |
| 2010 | 86,484 | +17.6% |
| 2020 | 96,620 | +11.7% |
| Source: [4] | ||
Lipis is home to 74,581 people (as of 2010), with the Malay/Bumiputra formed the majority (85.3%), the Chinese with 10.5%, the Indian with 4%, while the others 0.2%.[5]
There are 400 speakers of Mintil, a language of the Mayah (Orang Asli) people, remaining in Lipis District.[6]
Federal Parliament and State Assembly Seats
Lipis district representative in the Federal Parliament (Dewan Rakyat)
| Parliament | Seat Name | Member of Parliament | Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| P78 | Cameron Highlands | Ramli Mohd Nor | BN (UMNO) |
| P79 | Lipis | Abdul Rahman Mohamad | BN (UMNO) |
List of Lipis district representatives in the State Legislative Assembly (Dewan Undangan Negeri)
| Parliament | State | Seat Name | State Assemblyman | Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P78 | N2 | Jelai | Wan Rosdy Wan Ismail | BN (UMNO) |
| P79 | N3 | Padang Tengku | Mustapa Long | BN (UMNO) |
| P79 | N4 | Cheka | Tuan Ibrahim Tuan Man | PN (PAS) |
| P79 | N5 | Benta | Mohammad Soffi Abdul Razak | BN (UMNO) |
There is also another state seat, Jelai, which is governed by the Lipis District Council but is represented by the Cameron Highlands parliamentary constituency instead.
Subdistricts

Lipis District is divided into 10 mukims, which are:[7]
- Batu Yon (115,100 Ha)
- Budu (7,400 Ha)
- Cheka (22,900 Ha)
- Gua (7,588 Ha)
- Hulu Jelai (213,500 Ha)
- Kechau (68,600 Ha)
- Kuala Lipis (9,773 Ha) (Capital)
- Penjom (17,200 Ha)
- Tanjong Besar (13,300 Ha)
- Telang (43,900 Ha)
Demographics
The following is based on Department of Statistics Malaysia 2010 census.[3]
| Ethnic groups in Lipis, 2010 census | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Population | Percentage |
| Bumiputera | 74,694 | 87.5% |
| Chinese | 7,630 | 8.9% |
| Indian | 2,872 | 3.4% |
| Others | 145 | 0.2% |
| Total | 85,341 | 100% |
References
- ↑ Laman, Pentadbir. "SENARAI PEGAWAI DAERAH". pdtlipis.pahang.gov.my. Archived from the original on 2018-03-15. Retrieved 2017-11-28.
- ↑ primuscoreadmin (9 November 2015). "Latar Belakang".
- 1 2 "Population Distribution and Basic Demographic Characteristics, 2010" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 May 2014. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ↑ "Key Findings of Population and Housing Census of Malaysia 2020" (pdf) (in Malay and English). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. ISBN 978-967-2000-85-3.
- ↑ "Key Summary Statistics For Local Authority Areas, Malaysia 2010" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2015. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ↑ Lim, Teckwyn. 2020. Ethnolinguistic Notes on the Language Endangerment Status of Mintil, an Aslian Language. Journal of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society (JSEALS) 13.1 (2020): i-xiv. ISSN 1836-6821. University of Hawaiʼi Press.
- ↑ http://apps.water.gov.my/jpskomuniti/dokumen/LIPIS_PROFIL_May_2012.pdf