| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
 Telescopic view, from North Billerica, Massachusetts at 3:25 UT, near greatest eclipse. | |||||||||||||||||
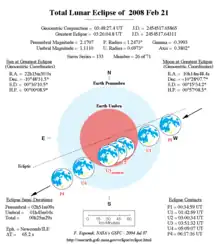
| Date | 21 February 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | −0.39923 | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.10618 | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 133 (26 of 71) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 49 minutes, 46 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 205 minutes, 28 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 339 minutes, 3 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
A total lunar eclipse occurred on February 20 and February 21, 2008. It was visible in the eastern evening sky on February 20 for all of North and South America, and on February 21 in the predawn western sky from most of Africa and Europe. Greatest Eclipse occurring on Thursday, February 21, 2008, at 03:26:03 UTC, totality lasting 49 minutes and 45.6 seconds.
Occurring 7.1 days after perigee (Perigee on February 14, 2008) and 6.9 days before apogee (Apogee on February 28, 2008), the Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter.
The total lunar eclipse was the first of the two lunar eclipses in 2008, with the second, the August 16, 2008 event being partial.[1] The next total lunar eclipse occurred on December 21, 2010. The tables below contain detailed predictions and additional information on the Total Lunar Eclipse of 21 February 2008.
The Moon's apparent diameter was 26.2 arcseconds larger than the August 16, 2008 partial lunar eclipse.
Eclipse season
This is the second eclipse this season.
First eclipse this season: 7 February 2008 Annular Solar Eclipse
Date = 21 February 2008
- Penumbral Magnitude = 2.14507
- Umbral Magnitude = 1.10618
- Gamma: -0.39923
- Greatest Eclipse: 21 Feb 2008 03:26:03.3 UTC (03:27:08.8 TD)
- Ecliptic Opposition: 21 Feb 2008 03:30:30.8 UTC (03:31:36.3 TD)
- Equatorial Opposition: 21 Feb 2008 03:48:25.7 UTC (03:49:31.2 TD)
- Sun right ascension: 22 hours, 15 minutes, 30.0 seconds
- Moon right ascension: 10 hours, 14 minutes, 48.5 seconds
- Earth's shadow right ascension: 10 hours, 15 minutes, 30.0 seconds
- Sun declination: 10 degrees, 48 minutes, 31.3 seconds south of Celestial Equator
- Moon declination: 10 degrees, 28 minutes, 7.6 seconds north of Celestial Equator
- Earth's shadow declination: 10 degrees, 48 minutes, 31.3 seconds north of Celestial Equator
- Sun diameter: 1941.0 arcseconds
- Moon diameter: 1868.4 arcseconds
- Penumbra diameter: 2 degrees, 1684.08 arcseconds (8884.08 arcseconds)
- Umbra diameter: 1 degree, 1402.56 arcseconds (5002.56 arcseconds)
- Saros Series: 133rd (26 of 71)
- Node: Descending Node
Viewing
The eclipse was visible in the eastern evening sky on February 20 for all of North and South America, and on February 21 in the predawn western sky from most of Africa and Europe.
 These simulated views of the earth from the center of the moon during the lunar eclipse show where the eclipse is visible on earth. |
The penumbral eclipse began at 00:35 UTC (February 21), and ended at 6:17. A partial eclipse existed from 1:43 until 3:00, followed by 51 minutes of totality (3:00 - 3:51), and then partial again from 3:51 until 5:09. (For local times, see Timing.)
It is possible to mistake the appearance of partial eclipse as the Moon being in a different phase, but the shadow from the eclipse changes much more rapidly.[2]
The bright star Regulus of Leo and the planet Saturn were prominent very near the Moon during the total eclipse portion. Shortly before the eclipse began, Regulus was occulted by the Moon in parts of the far Southern Atlantic Ocean and Antarctica.
Map

Relation to other lunar eclipses
Eclipses of 2008
- An annular solar eclipse on February 7.
- A total lunar eclipse on February 21.
- A total solar eclipse on August 1.
- A partial lunar eclipse on August 16.
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2006–2009 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros # and photo |
Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros # and photo |
Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
113.jpg.webp) |
2006 Mar 14 |
penumbral |
1.0211 | 118 |
2006 Sep 7 |
partial |
−0.9262 | |
123 |
2007 Mar 03 |
total |
0.3175 | 128 |
2007 Aug 28 |
total |
−0.2146 | |
133 |
2008 Feb 21 |
total |
−0.3992 | 138 |
2008 Aug 16 |
partial |
0.5646 | |
143 |
2009 Feb 09 |
penumbral |
−1.0640 | 148 |
2009 Aug 06 |
penumbral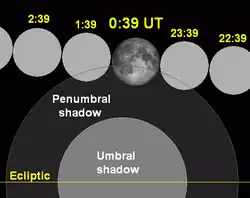 |
1.3572 | |
| Last set | 2005 Apr 24 | Last set | 2005 Oct 17 | |||||
| Next set | 2009 Dec 31 | Next set | 2009 Jul 07 | |||||
Saros series
This lunar eclipse is part of series 133 of the Saros cycle, which repeats every 18 years and 11 days. Series 133 runs from the year 1557 until 2819. The previous eclipse of this series occurred on February 9, 1990, and the next will occur on March 3, 2026.
It is the 6th of 21 total lunar eclipses in series 133. The first was on December 28, 1917. The last (21st) will be on August 3, 2278. The longest two occurrences of this series (14th and 15th) will last for a total of 1 hour and 42 minutes on May 18, 2152, and May 30, 2170. Solar saros 140 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
Lunar saros series 133, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 71 lunar eclipse events including 54 umbral lunar eclipses (33 partial lunar eclipses and 21 total lunar eclipses).
| Greatest | First | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
The greatest eclipse of the series will occur on 2170 May 30, lasting 102 minutes. |
Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
| 1557 May 13 |
1683 Aug 07 |
1917 Dec 28 |
2098 Apr 15 | |
| Last | ||||
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral | |
| 2224 Jul 01 |
2278 Aug 03 |
2429 Dec 11 |
2754 Jun 26 | |
There are 10 series events between 1901 and 2100, grouped into threes (called an exeligmos), each column with approximately the same viewing longitude on earth.
| 1917 Dec 28 | 1936 Jan 08 | 1954 Jan 19 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1972 Jan 30 | 1990 Feb 09 | 2008 Feb 21 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2026 Mar 03 | 2044 Mar 13 | 2062 Mar 25 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| 2080 Apr 04 | 2098 Apr 15 | ||||
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
Metonic cycle (19 years)
This is the fourth of five Metonic lunar eclipses.
The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the Earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date | Type | Saros | Date | Type | |
| 103 | 1951 Feb 21.88 | Penumbral | 108 | 1951 Aug 17.13 | Penumbral | |
 |
 | |||||
| 113 | 1970 Feb 21.35 | Partial | 118 | 1970 Aug 17.14 | Partial | |
 |
 | |||||
| 123 | 1989 Feb 20.64 | Total | 128 | 1989 Aug 17.13 | Total | |
 |
 | |||||
| 133 | 2008 Feb 21.14 | Total | 138 | 2008 Aug 16.88 | Partial | |
 |
 | |||||
| 143 | 2027 Feb 20.96 | Penumbral | 148 | 2027 Aug 17.30 | Penumbral | |
 |
 | |||||
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[4] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 140.
| February 16, 1999 | February 26, 2017 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Timing
The Moon entered the penumbral shadow at 0:36 UTC, and the umbral shadow at 1:43. Totality lasted for 50 minutes, between 3:01 and 3:51. The Moon left the umbra shadow at 5:09 and left the penumbra shadow at 6:16.[5]
| Event | North and South America | Europe and Africa | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evening of February 20th | Morning of February 21st | |||||||||
| AKST (-9h) |
PST (-8h) |
MST (-7h) |
CST (-6h) |
EST (-5h) |
AST (-4h) |
GMT (0h) |
CET (+1h) |
EET (+2h) | ||
| P1 | Penumbral began | Under Horizon | Under Horizon | Under Horizon | 18:36 | 19:36 | 20:36 | 0:36 | 1:36 | 2:36 |
| U1 | Partial began | Under Horizon | Under Horizon | 18:43 | 19:43 | 20:43 | 21:43 | 1:43 | 2:43 | 3:43 |
| U2 | Total began | Under Horizon | 19:01 | 20:01 | 21:01 | 22:01 | 23:01 | 3:01 | 4:01 | 5:01 |
| Mid-eclipse | 18:26 | 19:26 | 20:26 | 21:26 | 22:26 | 23:26 | 3:26 | 4:26 | 5:26 | |
| U3 | Total ended | 18:51 | 19:51 | 20:51 | 21:51 | 22:51 | 23:51 | 3:51 | 4:51 | Set |
| U4 | Partial ended | 20:09 | 21:09 | 22:09 | 23:09 | 0:09 | 1:09 | 5:09 | Set | Set |
Photo gallery
Composites
 Eclipse observed from Sandim, Portugal. 41°02′22″N 8°30′50″W / 41.03944°N 8.51389°W. |
 Eclipse observed from Regina, Saskatchewan. Each image is roughly taken 5 minutes apart. |
 Images taken in 3-5 minute Intervals - from Bradley, Illinois. |
 Eclipse observed from Halton Hills, Ontario. From 01:47 to 03:15 UTC, each image is roughly taken 5min apart. |
Eclipse observed from Winnipeg, Manitoba | |
Lunar eclipse observed from Burlington, Ontario | |
 Observed from Baltimore, Maryland, from 2:30 to 3:01 UTC. Lunar north is near left. | |
North America
Canada
 Eclipse Observed from Burlington, Ontario, at 2:00 UTC.
Eclipse Observed from Burlington, Ontario, at 2:00 UTC. Eclipse observed from Victoria, British Columbia, at 2:49 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left.
Eclipse observed from Victoria, British Columbia, at 2:49 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left. Eclipse observed from Victoria, British Columbia at 2:56 UTC, just prior to total. Lunar north is near top-left.
Eclipse observed from Victoria, British Columbia at 2:56 UTC, just prior to total. Lunar north is near top-left. Eclipse observed from Salmon Arm, Canada at 3:11 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left.
Eclipse observed from Salmon Arm, Canada at 3:11 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left. Eclipse observed from Burlington, Ontario at 4:05 UTC.
Eclipse observed from Burlington, Ontario at 4:05 UTC.
USA (west)
 Eclipse observed from Salem, Oregon. Lunar north is near top-left.
Eclipse observed from Salem, Oregon. Lunar north is near top-left. Observed from Urbana, Illinois, at 3:06 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left.
Observed from Urbana, Illinois, at 3:06 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left. Observed from Boulder, Colorado, at 4:17 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left. Mare Humorum appears at bottom, Tycho's rays at bottom right.
Observed from Boulder, Colorado, at 4:17 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left. Mare Humorum appears at bottom, Tycho's rays at bottom right.
USA (east)
 Moon observed from West Hartford, Connecticut, at 1:42 UTC. Lunar north is left.
Moon observed from West Hartford, Connecticut, at 1:42 UTC. Lunar north is left. Eclipse observed from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, at 2:49 UTC.
Eclipse observed from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, at 2:49 UTC. Eclipse observed from Millersville, Pennsylvania, at 3:15 UTC. Lunar north is near left.
Eclipse observed from Millersville, Pennsylvania, at 3:15 UTC. Lunar north is near left. Eclipse observed from West Hartford, Connecticut, at 3:17 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left.
Eclipse observed from West Hartford, Connecticut, at 3:17 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left. Eclipse observed from West Hartford, Connecticut, at 3:18 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left.
Eclipse observed from West Hartford, Connecticut, at 3:18 UTC. Lunar north is near top-left. Eclipse observed from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania at 3:36 UTC. Lunar north is top-left.
Eclipse observed from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania at 3:36 UTC. Lunar north is top-left..jpg.webp) Eclipse observed from Wellesley, Massachusetts, at 3:52 UTC
Eclipse observed from Wellesley, Massachusetts, at 3:52 UTC Eclipse observed from Fredericksburg, Virginia, at 3:57 UTC.
Eclipse observed from Fredericksburg, Virginia, at 3:57 UTC.
South America
 Eclipse observed from São Joaquim, Brazil at 3:52 UTC.
Eclipse observed from São Joaquim, Brazil at 3:52 UTC.
Europe and Africa
 Eclipse observed from Rostock, Germany, at 1:50 UTC. Lunar north is near top.
Eclipse observed from Rostock, Germany, at 1:50 UTC. Lunar north is near top. Eclipse observed from Sasolburg, South Africa - around 2:55 UTC. Lunar north is right.
Eclipse observed from Sasolburg, South Africa - around 2:55 UTC. Lunar north is right. Eclipse observed from Prague, Czech Republic at 3:41 UTC
Eclipse observed from Prague, Czech Republic at 3:41 UTC
See also
- List of lunar eclipses in the 21st century
- Lists of lunar eclipses
- Solar eclipse
- File:2008-02-21 Lunar Eclipse Sketch.gif Chart
Notes
- ↑ "Partial Lunar Eclipse of 16 Aug 2008" (PDF). eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
- ↑ "John-Doukoumopoulos2".
- ↑ "NASA - Catalog of Lunar Eclipses in Saros 133". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
- ↑ "Total lunar eclipse of 2008 Feb 21" (PDF). NASA. 21 February 2008. Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA's GSFC
- ↑ "NASA - Total Lunar Eclipse: February 20, 2008". 2008. Archived from the original on 21 February 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
External links
- NASA: Total Lunar Eclipse: February 20, 2008
- NASA Saros series 133
- 2008 Feb 21 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Hermit eclipse (Ian Cameron Smith) Total Lunar Eclipse: February 21, 2008
- Photos
- Astronet: Information and live webcasts of the February 20-21 total lunar eclipse from the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, Spain and Argentina
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day: February 20, 2008, February 22, 2008 March 1, 2008
- Sky&Telescope, Eclipses of 2008
- Example Images from Dr. Eric S. Ackerman - Fort Lauderdale, Florida Archived 26 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- Various Animations of the Eclipse Astronight Observatory - Billerica MA
- SpaceWeather Lunar Eclipse Photo Gallery: February 20, 2008
- Philadelphia, PA: A timelapse of the total lunar eclipse on February 20th, 2008. Recorded with still images.
- Feature No Longer Available | Weather Underground

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
