| Partial eclipse | |||||||||||||
 Kuwait City, Kuwait, 19:14 UTC | |||||||||||||
| Date | 7 August 2017 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.8668 | ||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 0.2464 | ||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 119 (62 of 83) | ||||||||||||
| Partiality | 115 minutes, 15 seconds | ||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 300 minutes, 54 seconds | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
A partial lunar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node on the evening of 7 August and the morning pre-dawn on 8 August 2017, the second of two lunar eclipses in 2017. The Moon was only slightly covered by the Earth's umbral shadow at maximum eclipse. The Moon's apparent diameter was smaller because the eclipse occurred only 5 days after apogee (Apogee on 2 August 2017).
The Moon inside the umbral shadow was a subtle red, but hard to see in contrast to the much brighter Moon in the outer penumbral shadow. The Moon looks red because it is illuminated by sunlight refracted through Earth's atmosphere. The blue light is scattered and absorbed by the atmosphere, leaving red light to shine onto the lunar surface.[1]
The solar eclipse of 21 August 2017, occurred fourteen days later, in the same eclipse season (Middle of the eclipse season occurred on 16 August 2017). It was the first total solar eclipse visible in the contiguous United States since the solar eclipse of 26 February 1979.
Visibility
It was visible over eastern Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia with maximal visibility centered on Indian Ocean.
  |
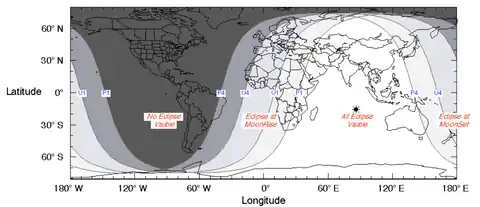 Visibility map |
Gallery
 Reggio Calabria, Italy, 17:36 UTC
Reggio Calabria, Italy, 17:36 UTC Lysychansk, Ukraine, 17:54 UTC
Lysychansk, Ukraine, 17:54 UTC Florence, Italy, 17:55 UTC
Florence, Italy, 17:55 UTC Lucerne, Switzerland, 18:16 UTC
Lucerne, Switzerland, 18:16 UTC Pune, India
Pune, India
At maximum, 18:20 UTC Seoul, South Korea, 18:22 UTC
Seoul, South Korea, 18:22 UTC Omsk, Russia, 18:28 UTC
Omsk, Russia, 18:28 UTC_(39648242360).jpg.webp) Constanța, Romania, 18:43 UTC
Constanța, Romania, 18:43 UTC Gdańsk, Poland, 18:50 UTC
Gdańsk, Poland, 18:50 UTC.jpg.webp) Farasan Island, Saudi Arabia, 18:53 UTC
Farasan Island, Saudi Arabia, 18:53 UTC Karviná, Czech Republic, 18:56 UTC
Karviná, Czech Republic, 18:56 UTC Helsinki, Finland, 18:57 UTC
Helsinki, Finland, 18:57 UTC Sayada, Tunisia, 19:01 UTC
Sayada, Tunisia, 19:01 UTC Gaborone, Botswana, 19:02 UTC
Gaborone, Botswana, 19:02 UTC.jpg.webp) Albershausen, Germany, 19:14 UTC
Albershausen, Germany, 19:14 UTC Rethymno, Greece, 19:21 UTC
Rethymno, Greece, 19:21 UTC.jpg.webp) Progression from Oria, Italy
Progression from Oria, Italy
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2017
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on 11 February.
- An annular solar eclipse on 26 February.
- A partial lunar eclipse on 7 August.
- A total solar eclipse on 21 August.
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2016–2020 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date | Type Viewing |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 109 | 2016 Aug 18 |
Penumbral |
1.56406 | 114 |
2017 Feb 11 |
Penumbral |
−1.02548 | |
119 |
2017 Aug 07 |
Partial |
0.86690 | 124 |
2018 Jan 31 |
Total |
−0.30143 | |
129_(43696968392)_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
2018 Jul 27 |
Total |
0.11681 | 134_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
2019 Jan 21 |
Total |
0.36842 | |
139 |
2019 Jul 16 |
Partial |
−0.64300 | 144 |
2020 Jan 10 |
Penumbral |
1.07270 | |
| 149 | 2020 Jul 05 |
Penumbral |
−1.36387 | |||||
| Last set | 2016 Sep 16 | Last set | 2016 Mar 23 | |||||
| Next set | 2020 Jun 05 | Next set | 2020 Nov 30 | |||||
Saros series
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 126.
| 1 August 2008 | 12 August 2026 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
See also
References
- ↑ "Why does moon in total eclipse look red? | Astronomy Essentials | EarthSky". earthsky.org. January 18, 2019.
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- 2017 Aug 07 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Hermit Eclipse: Partial Lunar Eclipse of 7 Aug, 2017 AD
- Partial Lunar Eclipse 7 Aug, 2017 - Live Webcast
- August's Lunar Eclipse APOD: Aug 9, 2017
_(cropped).jpg.webp)