| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Ogólne informacje | |||||||||||||
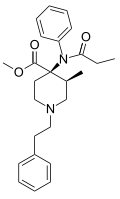
| Wzór sumaryczny |
C25H32N2O3 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masa molowa |
408,54 g/mol | ||||||||||||
| Identyfikacja | |||||||||||||
| Numer CAS | |||||||||||||
| PubChem | |||||||||||||
| DrugBank | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Lofentanyl – organiczny związek chemiczny, analog fentanylu. Jest najsilniejszym znanym opioidem[1].
Lofentanyl ma bardzo podobne działanie do karfentanylu, ale dłuższe[2]. Długość działania i wysoka lipofilowość sprawiają, że lofentanyl zdaje się być dobrym związkiem służącym do niektórych typów znieczuleń[3], ale aktualnie wykorzystywany jest jedynie w badaniach nad receptorami opioidowymi[4][5].
Przypisy
- ↑ W. Gommeren, J.E. Leysen. Binding properties of 3H-lofentanil at the opiate receptor. „Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Thérapie”. 258 (1), s. 171–173, 1982. DOI: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90331-X. PMID: 6132825.
- ↑ P.M. Laduron, P.F. Janssen. Axoplasmic transport and possible recycling of opiate receptors labelled with 3H-lofentanil. „Life Sciences”. 31 (5), s. 457–462, 1982. PMID: 6182434.
- ↑ F.F. Foldes. Pain control with intrathecally and peridurally administered opioids and other drugs. „Anaesthesiologie und Reanimation”. 16 (5), s. 287–298, 1991. PMID: 1683773.
- ↑ P. Maguire i inni, Pharmacological profiles of fentanyl analogs at mu, delta and kappa opiate receptors, „European Journal of Pharmacology”, 213 (2), 1992, s. 219–325, DOI: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90685-W, PMID: 1355735.
- ↑ X.Q. Huang i inni, Study on mechanism of interaction of nociceptin and opioids binding with opioid receptor-like 1 receptor, „Acta Pharmacologica Sinica”, 21 (6), 2000, s. 536–546, PMID: 11360688.
![]() Przeczytaj ostrzeżenie dotyczące informacji medycznych i pokrewnych zamieszczonych w Wikipedii.
Przeczytaj ostrzeżenie dotyczące informacji medycznych i pokrewnych zamieszczonych w Wikipedii.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.