|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ogólne informacje | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wzór sumaryczny |
CH3NO2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masa molowa |
61,04 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wygląd |
żółty gaz[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identyfikacja | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Numer CAS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jeżeli nie podano inaczej, dane dotyczą stanu standardowego (25 °C, 1000 hPa) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Azotyn metylu – organiczny związek chemiczny, ester kwasu azotawego i metanolu. Najprostszy azotyn alkilowy.
W temperaturze pokojowej azotan metylu występuje w postaci mieszaniny izomerów cis i trans, przy czym forma cis jest nieco stabilniejsza niż trans[3].
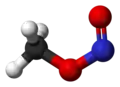 izomer cis
izomer cis izomer trans
izomer trans
Przypisy
- 1 2 3 4 5 Haynes 2014 ↓, s. 3-382.
- 1 2 3 4 Methyl nitrite, [w:] ChemIDplus, United States National Library of Medicine [dostęp 2015-09-06] (ang.).
- ↑ B.J. Van der Veken i inni, Infrared spectrum, ab initio calculations, barriers to internal rotation and structural parameters for methyl nitrite, „Journal of Physical Chemistry”, 10, 94, 1990, s. 4029–4039, DOI: 10.1021/j100373a028.
Bibliografia
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, William M. Haynes (red.), wyd. 95, Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014, ISBN 978-1-4822-0867-2 (ang.).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.