The Walls of Felipe IV (Spanish: Real Cerca de Felipe IV) surrounded the city of Madrid between 1625 and 1868. Philip IV ordered their construction to replace the earlier Walls of Philip II and the Walls del Arrabal, which had already been surpassed by the growth of population of Madrid. These were not defensive walls, but essentially served fiscal and surveillance purposes: to control the access of goods to the city, ensure the collection of taxes, and to monitor who went in and out of Madrid. The materials used for construction were brick, mortar and compacted earth.

It was one of five walls that surrounded the city of Madrid at different times.[1]
Location
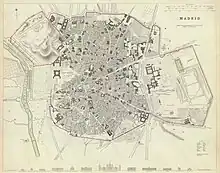
The wall began from the current Cuesta de la Vega, continuing via the Rondas of Segovia, Toledo, Valencia and Atocha, plaza del Emperador Carlos V, the avenues of Ciudad de Barcelona and Menéndez Pelayo, Calle de Alcalá, plaza de la Independencia, the streets of Serrano, Jorge Juan, plaza de Colón, Génova, Sagasta, Carranza, and then turning left in San Bernardo going by Santa Cruz de Marcenado, Serrano Jover, la Princesa, Ventura Rodríguez, Ferraz, Cuesta de San Vicente, Paseo de la Virgen del Puerto and running alongside the Campo del Moro, until finally linking again with Cuesta de la Vega.[1]
History
During the reign of Philip IV "the Great" the population of Madrid was three times that of his grandfather's reign, and so, in 1590, construction in the city exceeded the Walls of Philip II. As a result, it was necessary to expand the boundaries of Madrid. The idea of new walls started in 1614 and the project was commissioned to Juan Gómez de Mora, chief architect of the king and of the City Council. Gómez de Mora marked the boundaries of the new walls in a report in 1617 stating that the various sections of the walls should be carried out by master architects.[2]
In 1625, Philip IV ordered the construction of other new walls using brick, mortar and earth. These fiscal and surveillance walls served to ensure that all products and foodstuffs that entered the city pay their corresponding taxes in addition to monitoring people entering Madrid. In order to finance its construction a tax on wine was levied. It was built in separate sectors of the city, in each of which a gate of certain importance was placed. Gates and portillos took their names from nearby buildings. The route of the wall was adapted to the configuration of the terrain, which made it very irregular. By 1650 it covered the Mountain del Príncipe Pío, the Buen Retiro and the Hermitage of Atocha. Its biggest drawback was that it prevented the city's growth, thereby keeping its population in overcrowded conditions for over two hundred years.[2]
.jpg.webp)
The new walls were about thirteen kilometers long and enclosed an area of 500 hectares, of which more than 150 belonged to the Buen Retiro Royal Site.[2] This area includes all present-day Centro district plus Buen Retiro Park and the Los Jerónimos neighbourhood. The walls were partially rebuilt in the 18th century and were demolished in 1868 during the Glorious Revolution, as they were considered an Isabelline symbol.[2]
The exits from Madrid were flanked by five royal gates, or gates of registration (where taxes were paid): Puerta de Segovia, Puerta de Toledo, Puerta de Atocha, Puerta de Alcalá and Puerta de Bilbao; and fourteen minor gates or portillos, opened at different dates: Portillo de la Vega, Portillo de las Vistillas, Portillo de Gilimón, Portillo de del Campillo del Mundo Nuevo, Portillo de Embajadores, Portillo de Valencia, Portillo de Campanilla, Portillo de Recoletos, Portillo de Santa Bárbara, Portillo de Maravillas, Portillo de Santo Domingo, Portillo de del Conde Duque, Portillo de San Bernardino and Portillo de San Vicente.
The main gates remained open until 10pm in winter and 11pm in summer. After this time, if necessary, passage was permitted through a checkpoint. The portillos were opened at dawn and closed at sunset, remaining closed overnight. Except for the Puerta de San Vicente – built by Sabatini – the portillos are not noted for their architecture.
Current status

Remnants of the walls are visible in two places. One forms part of the retaining wall of the Jardines de Las Vistillas, next to the access staircase, where the Casa de Gil Imón was once located. It is in a ruinous state and some sections have collapsed.[2] The other is connected to the fire station of Ronda de Segovia by the Puerta de Toledo roundabout; it is no more than five meters in length, and carries a commemorative plaque. This section dates back to the 18th-century reconstruction.[2]
There is another fragment in the garden area of the Seminario Conciliar, which was demolished without permission by the archbishopric of Madrid. The Directorate General of Heritage of the Community of Madrid ordered the reconstruction of this section, but it was carried out without using the original materials.[2] The interim plan for the Manzanares riverbank, approved by the city council of Madrid, will allow the archbishopric of Madrid to erect five buildings in the Cornisa park, threatening the existing remains of the Walls. These facts have led to the inclusion of the Cornisa park on the Hispania Nostra association's "Red List" of endangered heritage sites.[3]
A new section was found in 2009 during work on Calle de Serrano.[4][5]
See also
Bibliography
- María Isabel Gea (2002). "Walls of Philip IV". Diccionario Enciclopédico de Madrid. Madrid: La Librería. Retrieved July 5, 2013.
References
- 1 2 "Un Madrid con Horarios". Secretos de Madrid (in Spanish). 22 September 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Adrián Delgado (2012-03-10). "Objetivo: salvar la Real Cerca de Felipe IV" [Goal: to save the Real Cerca de Felipe IV] (in Spanish). ABC. Archived from the original on 13 March 2012. Retrieved 2013-07-08.
- ↑ Hispania Nostra. "Red List of the Heritage: Jardines de las Vistillas". Archived from the original on December 31, 2013. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ↑ Francisco Seco (July 11, 2009). "The works on Serrano will be delayed by several months in order to save the walls of Philip IV". ABC. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
- ↑ Rafael Fraguas (May 6, 2009). "The works in Serrano uncover the Walls of Philip IV". ABC. Retrieved July 8, 2013.