 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate | |
| Other names
1-Butanaminium, N,N,N-tributyl-, hexafluorophosphate(1-) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.520 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H36F6NP | |
| Molar mass | 387.4279 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Melting point | 244–246 °C (471–475 °F; 517–519 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
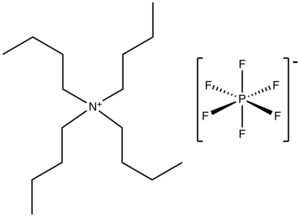
Tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate is a salt with the formula NBu4PF6. It is a white powder that is used as an electrolyte in nonaqueous electrochemistry. It is highly soluble in polar organic solvents such as acetone and acetonitrile.
The salt consists of a positively charged tetrabutylammonium, a quaternary ammonia cation and a weakly basic hexafluorophosphate anion. These species are chemically inert, which allows the salt to serve as an inert electrolyte over a wide potential range. Given the sensitivity of electrochemical experiments, this salt is usually further purified, e.g., by recrystallization from aqueous or absolute ethanol.[1]
References
- ↑ Zoski, Cynthia G. (2007). Handbook of Electrochemistry (1st ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.