Suqian
宿迁市 Sutsien, Su-ch'ien | |
|---|---|
 | |
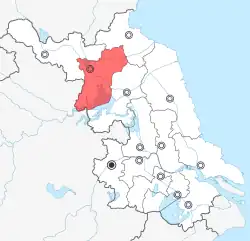 Location of Suqian City (red) in Jiangsu | |
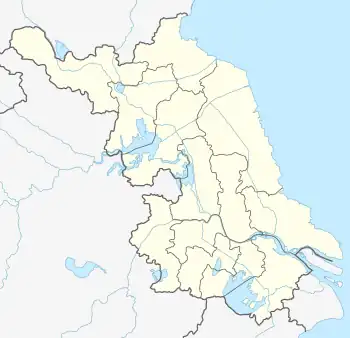 Suqian Location of the city center in Jiangsu  Suqian Suqian (Eastern China)  Suqian Suqian (China) | |
| Coordinates (Suqian municipal government): 33°57′47″N 118°16′30″E / 33.963°N 118.275°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Jiangsu |
| Municipal seat | Sucheng District |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Wang Tianqi (王天琦) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 8,555 km2 (3,303 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,108 km2 (814 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,108 km2 (814 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,986,192 |
| • Density | 580/km2 (1,500/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,622,912 |
| • Urban density | 770/km2 (2,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,622,912 |
| • Metro density | 770/km2 (2,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code |
|
| Area code | 527 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-JS-13 |
| GDP | ¥193.6 billion (2011) |
| GDP per capita | ¥40,930 (2011) |
| Major Nationalities | Han |
| County-level divisions | 5 |
| Township-level divisions | 115 |
| License Plate Prefix | 苏N |
| Website | www |
Suqian (simplified Chinese: 宿迁; traditional Chinese: 宿遷; pinyin: Sùqiān, IPA: [sû.tɕʰjɛ́n]) is a prefecture-level city in northern Jiangsu Province, China. It borders Xuzhou to the northwest, Lianyungang to the northeast, Huai'an to the south, and the province of Anhui to the west.
History

Suqian was said to be the site of a military grain store built when the Emperor Yuan of Jin reigned. Thus, the former Xiaxiang county where the store located was renamed Suyu (宿預; means "prepared" or "usually prepared") in 405. Then the county was annexed by Xuzhou and renamed Suqian in 762 because the homophone "yu (豫)" as the given name of the Emperor Daizong of Tang was deemed to be ineffable.[2] The county was put under the jurisdiction of Huaiyang military prefecture during the Song dynasty, then was transferred to Pizhou after Jurchen's Jin took it. The county was administered by Huai'an military prefecture during 1272–75, but restored as a part of Pizhou afterwards. It was annexed by Xuzhou again in 1733.
The area was rife with banditry during the early years of the Republic of China. In Autumn 1917, six persons were executed as bandits in Suqian. "They cut off their arms, broke their legs, cut off their ears, punched out their eyes, skinned them, then cut off their heads, and finally cut out their hearts."[3] Suqian was put under the jurisdiction of Huaiyin in 1934. The county was converted as a county-level city in 1987, later was elevated to prefecture status in 1996.[4]

Geography and climate
Suqian possesses the majority of Luoma Lake, which is a major lake in the Huai River basin.
| Climate data for Suqian (Suyu District, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.3 (63.1) |
26.1 (79.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
32.8 (91.0) |
36.6 (97.9) |
38.5 (101.3) |
38.5 (101.3) |
37.5 (99.5) |
35.2 (95.4) |
33.1 (91.6) |
27.8 (82.0) |
20.4 (68.7) |
38.5 (101.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 5.4 (41.7) |
8.6 (47.5) |
14.1 (57.4) |
20.6 (69.1) |
25.7 (78.3) |
29.5 (85.1) |
31.1 (88.0) |
30.4 (86.7) |
26.7 (80.1) |
21.6 (70.9) |
14.5 (58.1) |
7.7 (45.9) |
19.7 (67.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.1 (34.0) |
3.9 (39.0) |
9.0 (48.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
20.6 (69.1) |
24.8 (76.6) |
27.3 (81.1) |
26.5 (79.7) |
22.2 (72.0) |
16.5 (61.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
3.2 (37.8) |
15.0 (59.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −2.4 (27.7) |
0.1 (32.2) |
4.6 (40.3) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.8 (60.4) |
20.6 (69.1) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.4 (74.1) |
18.5 (65.3) |
12.2 (54.0) |
5.6 (42.1) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
11.0 (51.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −15.6 (3.9) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
3.4 (38.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
17.1 (62.8) |
14.2 (57.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
−16.5 (2.3) |
−16.5 (2.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 22.7 (0.89) |
26.5 (1.04) |
41.9 (1.65) |
46.9 (1.85) |
76.4 (3.01) |
127.9 (5.04) |
211.1 (8.31) |
180.1 (7.09) |
91.3 (3.59) |
41.8 (1.65) |
35.2 (1.39) |
20.2 (0.80) |
922 (36.31) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 4.8 | 5.9 | 6.4 | 7.2 | 7.5 | 8.3 | 12.9 | 11.4 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 4.9 | 88.2 |
| Average snowy days | 3.2 | 2.6 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 9.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 68 | 66 | 64 | 65 | 69 | 72 | 82 | 83 | 79 | 72 | 71 | 68 | 72 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 143.5 | 143.7 | 181.4 | 200.7 | 211.5 | 182.1 | 175.4 | 180.5 | 172.9 | 177.1 | 153.3 | 151.1 | 2,073.2 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 45 | 46 | 49 | 51 | 49 | 42 | 40 | 44 | 47 | 51 | 50 | 49 | 47 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[5][6] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
As of the 2020 Chinese census, Suqian had a recorded population of about 4,986,192 whom 1,622,912 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Sucheng and Suyu urban districts.
Economy
Local Yanghe along with Moutai and Wuliangye, are the three biggest manufacturers of baijiu.[7] Besides, several domestic companies followed JD.com to site their call centres in Suqian.
Transport
Roads
Expressways
Rail
Yanghe Station, known as Suqian Station on Suqian–Huai'an Railway is located in the south outskirt of Suqian.
Education
Suqian College is the single institution in Suqian providing bachelor's degree education.
Administration

The prefecture-level city of Suqian administers 5 county-level divisions, including 3 counties and 2 districts.
These are further divided into 115 township-level divisions, including 111 towns and township, and 4 subdistricts.
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdivision | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2020) | Area (km2) | Density (/km2) |
| City Proper | |||||
| Sucheng District | 宿城区 | Sùchéng Qū | 1,034,392 | 1,018 | 1,016 |
| Suburban | |||||
| Suyu District | 宿豫区 | Sùyù Qū | 588,520 | 1,146 | 513.5 |
| Rural | |||||
| Shuyang County | 沭阳县 | Shùyáng Xiàn | 1,674,978 | 2,300 | 728.3 |
| Siyang County | 泗阳县 | Sìyáng Xiàn | 829,562 | 1,389 | 597.2 |
| Sihong County | 泗洪县 | Sìhóng Xiàn | 858,740 | 2,719 | 315.8 |
| Total | 4,986,192 | 8,572 | 581.7 | ||
References
- ↑ "China: Jiāngsū (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- ↑ 中国历史大辞典·历史地理卷 [The Great Encyclopaedia of Chinese history, Volume on Historical Geography]. Shanghai Cishu Press. 1996. pp. 838–839. ISBN 7-5326-0299-0.
- ↑ John Pollock (December 2010). A Foreign Devil in China. World Wide Publications. pp. 45–46. ISBN 978-1-59328-277-6.
- ↑ "Historical Evolution". Suqian Official Website.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 25 June 2023.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 25 June 2023.
- ↑ "Proof positive". The Economist. Retrieved 2018-02-08.
External links
- Government Website of Suqian (in Simplified Chinese)
- Suqian comprehensive guide with open directory (Jiangsu.net)
