Strawtown, Indiana | |
|---|---|
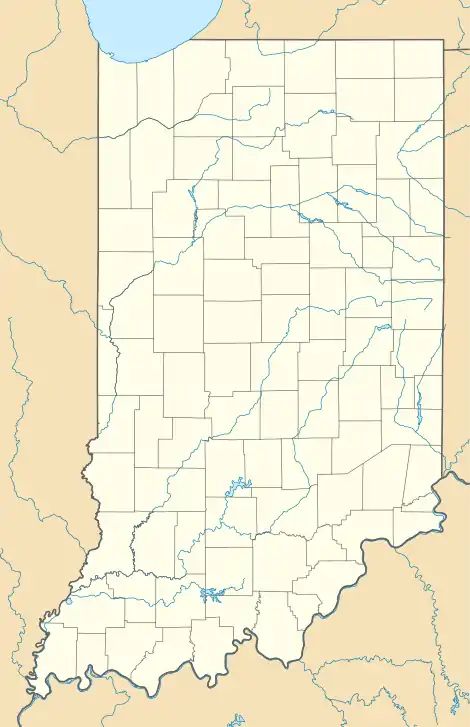 Strawtown  Strawtown | |
| Coordinates: 40°07′24″N 85°56′40″W / 40.12333°N 85.94444°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Indiana |
| County | Hamilton |
| Township | White River |
| Elevation | 794 ft (242 m) |
| ZIP code | 46060 |
| FIPS code | 18-73682[2] |
| GNIS feature ID | 444266[1] |
Strawtown is an unincorporated community in White River Township, Hamilton County, Indiana.
History
Strawtown was once an Indian village, but was laid out by white settlers in 1819 to serve travelers. Situated on the Conner Trail which connected the cities of Cincinnati and Indianapolis, it served as the halfway point between Anderson and Indianapolis. Strawtown was officially platted by Bicknell Cole and William Conner in 1836.
The area was possibly named after a native Delaware chief named Straw or Strawbridge.[3] Indian Strawtown was located across the river 1.5 miles (2.4 km) to the east and north of present-day Strawtown. Miami and Shawnee tribes invited the Delaware to settle in the White River basin after a 1795 treaty. Indian Strawtown was one of 14 Delaware villages established along the West Fork of the river.[4]
In 1821, a minimum purchase of 80 acres (320,000 m2) per speculator was offered at a price of $1.25 per acre. The following year, five Strawtown settlers went to the Brookville land office and purchased tracts at that price. By 1836, roughly 30 families had purchased land in this area.[5]
A post office was opened in 1834 and closed in 1902.[6] It was originally established upstream in Stevensburg on October 13, 1829, as one of the earliest posts in the territory.[7]
William Foster’s saw mill was established two miles (3 km) downstream in what is now Clare. Lumber was bound and floated like a raft down towards Noblesville and Indianapolis.[8]
Doctor Amos Palmer organized and taught the first school in Strawtown during the winter of 1822-23. The county was separated into two equal townships in 1823, White River to the north and Delaware to the south. Rapid growth, spurred partly by the state’s plans to run the Central Canal through Strawtown, caused the creation of seven additional townships. The canal in that area never materialized and growth stagnated, thanks in part to the location of the nearest railway four miles to the west.[9]
Archaeology
Strawtown is the site of a current archaeological dig, funded through Indiana University – Purdue University Fort Wayne (IPFW) by the National Science Foundation. The Archaeological Survey of IPFW received a $10,000 grant for a two-week educational archaeology program at the Strawtown Koteewi Park[10] near Noblesville in Hamilton County. The project will also result in a National Register nomination for a site near the Strawtown enclosure. During the past six years, IPFW has worked with the Hamilton County Parks Department to assess and explore the unique archaeological heritage of the 750-acre (3.0 km2) park. The goals of this project are to clarify the Late Prehistoric population dynamics of central Indiana, create a cultural and educational resource at the park for central Indiana, and develop the archaeological resources of the park as a destination for regional tourism.[11]
Geography
Strawtown is located east of Cicero and northeast of Noblesville at the intersection of State Road 37 and Strawtown Avenue. It is bounded to the north and west by the White River.
References
- 1 2 U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Strawtown, Indiana
- ↑ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ↑ (http://www.epodunk.com/cgi-bin/genInfo.php?locIndex=5736)
- ↑ (Early History of Strawtown: 1787-1861 by Cloe Morris, 1988, p. 3)
- ↑ (Early History of Strawtown: 1787-1861 by Cloe Morris, 1988, p. 10)
- ↑ "Hamilton County". Jim Forte Postal History. Retrieved September 17, 2014.
- ↑ (Sons of the Wilderness: John and William Conner by Charles N. Thompson, 1937, p. 202)
- ↑ (Early History of Strawtown: 1787-1861 by Cloe Morris, 1988, p. 16)
- ↑ (Early History of Strawtown: 1787-1861 by Cloe Morris, 1988, pp. 22-35)
- ↑ Strawtown Koteewi Park
- ↑ ("IPFW Archaeological Survey Homepage". Archived from the original on May 28, 2010. Retrieved February 25, 2010.)