
Srivijaya archaeological park (Indonesian: Taman Purbakala Kerajaan Sriwijaya), formerly known as Karanganyar archaeological site, is the ancient remnants of a garden and habitation area near the northern bank of Musi river within Palembang vicinity, South Sumatra, Indonesia.[1] Remnants of ancient man-made canals, moats, ponds and artificial islands discovered in this area suggests the site was related with a 9th-century settlement related to the Srivijaya empire.[2] Several artifacts, such as Buddhist statues, beads, pottery and Chinese ceramics were found in this area, confirming the area was once a dense human habitation.
Archaeological site
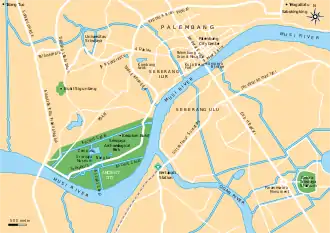
The archaeological park is located in Jalan Syakhyakirti, Kelurahan Karanganyar, Kecamatan Gandus, Palembang,[1] on an alluvial plain of the Musi River near its junction with the Ogan and Kramasan rivers.[3] Before the archeological excavation of the site in the late 1980s, the site of Karanganyar was thought to be a potential site for a Srivijayan political power center. However, immediately after the first excavations, the site, with its waterways, reservoirs, and "floating islands" (balai kambang) was thought to be more related with the site of Sultan Mahmud Badaruddin II, early 19th-century leader of the Palembang Sultanate. Mahmud Badaruddin II had acquired the land and had started developing the area, probably to prepare his own burial ground, following a Palembang tradition in which the burial of the members of the royal family were to be done on site surrounded by water flowing into the Musi River.[4] Karanganyar site had indeed been occupied in Srivijayan times, mainly in the 9th-century, however the only traces left of this period are a scatter of surface finds of contemporary artifacts e.g. Chinese ceramics, a few layers of ancient brick wall, and possibly one ancient canal. So far, archaeologists has found nothing in the site that can legitimately assign the Karanganyar site to the Srivijayan dynasty instead of to the Palembang Sultanate.[4] Other archaeological sites to Karanganyar that is related with the 7th - 15th centuries Srivijayan dynasty are the Kambang Unglen, Padang Kapas, Ladang Sirap and Bukit Seguntang, and still for a variety of reasons, identification of confirmed archaeological sites of the Srivijayan period remains ambiguous.[5]
The Karanganyar site elevation is less than 2 meters (6 ft 7 in) from the surface of Musi river. Located around 4 kilometers (2.5 mi) southwest from Palembang city center or south from Seguntang hill, the site can be accessed with public transportation heading to Tangga Batu.
The site consists of three sub-sites: Karanganyar 1, 2, and 3. The largest site, Karanganyar 1, takes the plan of a rectangular pond measuring 623 by 325 meters (2,044 ft × 1,066 ft). In the center of the pond are two artificial islands: Nangka (462 by 325 meters (1,516 ft × 1,066 ft)) and Cempaka (40 by 40 meters (130 ft × 130 ft)). Moats measuring (15 by 1,190 meters (49 ft × 3,904 ft)) surround Nangka island. Sub-site Karanganyar 2, southwest of the main pond, takes the plan of a small pond with a small square artificial island measuring (40 by 40 meters (130 ft × 130 ft)). Sub-site Karanganyar 3 is a pond located east of Karanganyar 1 measuring 60 by 60 meters (200 ft × 200 ft).
Seven canals connected the three sub-sites. Canal 1, identified by locals as Parit Suak Bujang, is the largest and longest, measuring 3 kilometers (1.9 mi) long and 25–30 meters (82–98 ft) wide with both ends connected to the Musi river. The 1.6-kilometer (0.99 mi) long canal 2 is parallel with canal 1, located south of the Karanganyar 1 and 3 sites. The west end of canal 2 ends in the Karanganyar 2 site, while the east end connects to the Musi river. Canal 1 and Canal 2 are connected by the 700-meter (2,300 ft) long canal 3 that runs along the north–south axis located between sub-sites 1 and 3. Parallel to canal 3 are canal 4 and 5 located west of sub-site 1 with their south ends connecting to canal 2. There are two canals, canal 6 and 7, that connect canal 2 with the Musi river in the south side.
History

Aerial photographs taken in 1984 revealed the canal network span in the Karanganyar site, confirming some ancient landscape modifications and man-made water structures. The canals compound is located not far from the location where the Kedukan Bukit Inscription was discovered. Moreover, the Karanganyar site is located not far from Bukit Seguntang, the highest point of Palembang, which is also an important archaeological site containing some archaeological fragments; inscriptions, ancient tombs, as well as an Amaravati-style statue of Buddha.
The government of South Sumatra province renovated the site to create an archaeological park, and the completion of the park construction was overseen on 22 December 1994 by Indonesian president Suharto.[1] The archaeological park also hosts the Sriwijaya Museum, which serves as the information center of Srivijayan history and sites in Palembang.[6][7] In the center of this site there is a pavilion constructed in Limasan Palembang traditional architecture that contains the replica of the Kedukan Bukit inscription placed in a glass case. The inscription tells the Siddhayatra journey of Dapunta Hyang Sri Jayanasa, considered as the establishment of Srivijayan empire. After having been established for more than a decade, the Srivijaya archaeological park has not fulfilled its expected function as the center of information and education as well as tourist attraction. Because of the lack of information and promotion and poor maintenance, most of the Palembang citizen are unaware of its existence and its function as the center of information about Srivijayan sites in Palembang. All this time both the local government and the people have paid little attention to this archaeological park.[6] Today, the archaeological park is poorly maintained and only attract a few of visitors.[8]
Archaeological findings

Artifact findings discovered in this area revealed the everyday life of its inhabitants, such as colorful beads, amber, ropes made from arenga pinnata fibers, brick structure, Chinese ceramics, pottery, and the remnant of a wooden ship. Most of these findings were discovered during the construction of the archaeological park. Reconstruction of pottery and ceramics fragments revealed daily domestic objects such as a vase, water vessel, bowl, plate, stove, clay pot, and roof. These domestic artifacts suggest the area was once a dense human habitation.
The water structures such as canals, ponds and artificial islands also confirm human habitation for long periods. The people that once inhabited the area probably built these canals for water drainage to prevent flooding as well as water transportation to connect the Musi River with inland areas.
Between 1985 and 1989 archaeological excavation was conducted and discovered fragments of pottery, ceramics, beads, and brick structure. The Chinese ceramics discovered here are dated from Tang, Sung, Yuan and Qing dynasties, spanning the 7th to 19th centuries. Excavation in Cempaka island revealed a brick structure buried 30 centimetres (12 in) deep with east–west axis. Other than canals and the small brick structure, there are no significant building or temple ruins discovered on this site. Archaeology experts suggest the lack of building ruins is because the site is located near a large river surrounded by tropical rainforest with no stone quarry near the area. As the result the temple, palace, and houses were probably built from wood and bricks, organic materials that easily decay and were destroyed by frequent flooding of the river and humidity in less than 200 years.[9]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Indonesia Travel. "Taman Purbakala Kerajaan Sriwijaya" (in Indonesian). Kementerian Pariwisata dan Ekonomi Kreatif Republik Indonesia. Retrieved 2011-12-02.
- ↑ "S. Sumatra to hold Sriwijaya Festival". The Jakarta Post. Palembang. June 14, 2014.
- ↑ "UTILIZATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF HISTORICAL SITES FOR IMPROVING THE ECONOMY OF THE REGION".
- 1 2 Manguin 2008, p. 4.
- ↑ Manguin 2001, p. 55.
- 1 2 Nurhadi Rangkuti (2009-10-24). "Taman Purbakala Kerajaan Sriwijaya Sebagai Pusat Informasi Sriwijaya" (in Indonesian). Balai Pelestarian Peninggalan Purbakala (BP3) Jambi Wilayah Kerja Propinsi Jambi, Sumatera Selatan, Bengkulu, dan Kepulauan Bangka-Belitung. Retrieved 2011-12-02.
- ↑ palembangnews.com. "Taman Purbakala Kerajaan Sriwijaya" (in Indonesian). Media Center Dinas Komunikasi dan Informatika Kota Palembang. Retrieved 2011-12-02.
- ↑ "Taman Purbakala Kerajaan Sriwijaya Palembang Sepi Pengunjung". Sriwijaya Post (in Indonesian). 3 May 2016.
- ↑ Ilham Khoiri. "Mengais Jejak Kebesaran Sriwijaya" (in Indonesian). Sumsel News Online. Retrieved 2011-12-02.
Cited works
- Ahmad Rapanie, Cahyo Sulistianingsih, Ribuan Nata, "Kerajaan Sriwijaya, Beberapa Situs dan Temuannya", Museum Negeri Sumatera Selatan, Dinas Pendidikan Provinsi Sumatera Selatan.
- Manguin, Pierre-Yves (2001). Miksic, John (ed.). Ancient History. Indonesian Heritage. Singapore: Archipelago Press. ISBN 9813018267.
- Manguin, Pierre-Yves (2008). "'Welcome to Bumi Sriwijaya' or the Building of a Provincial Identity in Contemporary Indonesia" (PDF). Asia Research Institute. Working Paper Series (102). Retrieved May 14, 2017.