Ulus Simsim | |
|---|---|
| fl. 1395–1470 | |
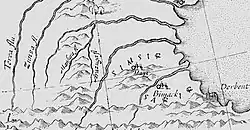 Medieval map of Simsim | |
| Religion | Sunni Islam[1] Vainakh religion |
• fl. 1395–1396 | Gayur-khan |
| Today part of | Russia |
Simsim (Persian: سیمسیم) was either a historical region or kingdom in the North Caucasus during the Middle Ages, existing in the 14th century. Predominantly localized roughly in Eastern Chechnya (Ichkeria), with some also connecting part of Kumyk Plain. Simsim is also localized in both Chechnya and Ingushetia. Its name may have been derived from the Chechen village of Simsir. However, according to folklore the King Gayur-khan was chosen as the leader of all Chechens by the Mehk-Khel (National Council). In its later years it allied itself with the Golden Horde before being destroyed in 1395 by Timurlane, which was recorded in Zafarnama by Nizam al-Din Shami and the Zafarnama by Sharaf ad-Din Ali Yazdi.
Name
The historical region or the kingdom is referred in the two Persian chronicles, Zafarnama (Shami) and Zafarnama (Yazdi), as Simsim.[2] Fasih Khwafi referred Simsim as "Ulus Simsim".[3]
Localization
Simsim is usually localized in Ichkeria, a region located in Eastern Chechnya,[4] with some authors localizing it both in the Ichkeria and Kumyk Plain.[5] It's also localized in both Chechnya and Ingushetia.[6][7][8][9]
Society
Simsir existed at a time when Chechens had a feudal system; in the early modern era, they overthrew their feudal rulers in a "revolutionary" event and established in its place a quasi-democratic taip system by which representatives of teips voted in a national council,[10] but while this differentiated Chechens from their neighbors more recently, it was not the case in the Middle Ages when Simsim existed.
In the Middle Ages, Chechen societies such as Simsir had a hierarchical and pyramidal structure. The Principality of Simsir's prince (the eela) sat at the top, followed by nobility and vassals (uzden), followed by free commoners (halxoi), followed by servants (yalxoi, including gharbashash, i.e. bond women), followed by serfs (lesh, lai in the singular), with only slaves and war captives (yiisarsh) beneath them; additionally, clerics were placed in the uzden nobility class. The wife of a prince was called a stuu and addressed as stulla.[11]
History
Alliance with the Golden Horde

In the 14th century, its rulers became tributaries of the Golden Horde, which brought Islamic influence with it, the ruler of Simsir was a powerful prince called Gayur Khan from the Sado-Orsoy clan. He was a Christian ruler who was very close to the Khan Khidir who at times used him as an ambassador to the Rus cities for negotiations and peace. After the death of Khan Khidir the Golden Horde fell into chaos for over 20 years. One of the main figures of this era was the warlord Mamai who was defeated by a Chechen army led by Gayur Khan in 1362.[12] This is believed to have resulted in an independent Simsir Kingdom ruled by Gayur Khan. He was also an important ally to Khan Tokhtamysh which is seen from the 18th century manuscript by the general Sultan Kazi-Girey which notes that the Chechens were in the vanguard of the Tokhtamysh against the Timurid empire during the Battle of the Terek river. The defeat of the Golden Horde led to disastrous consequences for the Simsir Kingdom as Timur decided to invade due to their alliance with Tokhtamysh.[13][12]
Timurid invasion
In the reign of its last ruler, Gayur Khan, the Principality of Simsir was destroyed by Timurlane in 1395 as part of his campaign against the Golden Horde. Its population fled south, into the mountains, in order to escape the attacks of the Mongols.[14] In the Zafarnama it states that Timurlane chased these escapers south into the mountains and subdued them.[13] Timur placed Makhama the son of Gayur Khan as Vassal and converted him to Islam. The fate of Makhama is described in Chechen folklore collected by the Sadoy clan historian Murtazaliev. Makhama was assassinated by the Chechens that replaced him with the previous Gayur Khan who continued to resist Timur until he was treacherously murdered during negotiations by the Timurids.[15]
See also
References
- ↑ Долгиева et al. 2013, p. 135: "Правитель области Симсим, вероятно, был представителем власти Золотой Орды, и, судя по тому, что его сын носил имя Мухаммед, часть населения этой области исповедовала ислам."
- ↑ Зафар-Намэ 1941.
- ↑ Фасих Хавафи 1980.
- ↑ Гадло 1994, p. 186 (whilst referring to Ртвеладзе 1976, pp. 118–119, Хизриев 1977a; Хизриев 1977b)
- ↑ Шнирельман 2006, p. 164.
- ↑ Тменов et al. 1987, p. 138: "Вслед за тем Тимур покорил область Симсим, расположенную, по-видимому, на территории современной Чечено-Ингушетии."
- ↑ Кузнецов 1992, p. 348: "(...) а правителем области Симсим в Чечено-Ингушетии был Гаюрхан."
- ↑ Гаджиев, Давудов & Шихсаидов 1996, p. 306: "Разорив земли Чечни и Ингушетии (“область Симсим”) (...)"
- ↑ История Дагестана 2004, p. 231: "Разорив земли Чечни и Ингушетии (область Симсим) (...)"
- ↑ Jaimoukha 2005, p. 89.
- ↑ Jaimoukha 2005, p. 276.
- 1 2 Tesaev, Amin (2018). "Симсим". РЕФЛЕКСИЯ. 2: 61–67.
- 1 2 Sharaf ad-Din Ali Yazdi (2008). Zafar Nama (Book of the victories of Amir Timur, translated from Persian to Uzbek by Muhammad Ali ibn Darvesh Ali Bukhari (16th century)). Tashkent: Academy of the Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan. "Abu Rayhan Beruni" Institute of Oriental Studies. SAN'AT. p. 203.
- ↑ Jaimoukha 2005, p. 35–36.
- ↑ Муртазалиев, В. К вопросу об истории государства и права чеченцев.
Bibliography
English sources
- Jaimoukha, Amjad (2005). The Chechens: A handbook (PDF). Psychology Press. pp. 1–343. ISBN 9780415323284.
Russian sources
- Анчабадзе, Ю. Д.; et al. (2007). Минц, Л. М.; et al. (eds.). Народы мира: энциклопедия [Peoples of the World: Encyclopedia] (in Russian). Москва: ОЛМА Медиа Групп. pp. 1–640. ISBN 978-5-373-01057-3.
- Долгиева, М. Б.; Картоев, М. М.; Кодзоев, Н. Д.; Матиев, Т. Х. (2013). Кодзоев, Н. Д.; et al. (eds.). История Ингушетии [History of Ingushetia] (4th ed.). Ростов-на-Дону: Южный издательский дом. pp. 1–600. ISBN 978-5-98864-056-1.
- Тменов, В. X.; Кузнецов, В. А.; Гутнов, Ф. Х.; Тотоев, Ф. В. (1987). "Глава IX: Северная Осетия в XIV —XV вв." [Chapter 9: North Ossetia in the 14th-15th centuries]. In Дзугаева, Э. X.; et al. (eds.). История Северо-Осетинской АССР: С древнейших времен до наших дней. В 2-х т. [History of the North Ossetian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic: From ancient times to the present day. In 2 volumes] (in Russian). Vol. 1 (2nd ed.). Орджоникидзе: Ир. pp. 133–150.
- Гадло, А. В. (1994). Этническая история Северного Кавказа X—XIII вв [Ethnic history of the North Caucasus 10th – 13th centuries] (in Russian). СПб.: Изд-во С.-Петербург. ун-та. pp. 1–236. ISBN 5-288-01010-2.
- Гаджиев, М. Г.; Давудов, О. М.; Шихсаидов, А. Р. (1996). Гаджиев, М. Г.; Гамзатов, Г. Г.; Давудов, О. М.; Османов, А. И.; Османов, М.-З. О.; Шихсаидов, А. Р. (eds.). История Дагестана с древнейших времен до конца XV в. [History of Dagestan from ancient times to the end of the 15th century] (PDF) (in Russian). Махачкала: ДНЦ РАН. pp. 1–460.
- Гаджиев, М. Г.; Давудов, О. М.; Каимаразов, Г. Ш.; Османов, А. И.; Рамазанов, Х. Х.; Шихсаидов, А. Р., eds. (2004). История Дагестана с древнейших времен до наших дней. Tom 1: История Дагестана с древнейших времен до XX века [History of Dagestan from ancient times to the present day. Vol. 1: History of Dagestan from ancient times to the 20th century] (PDF) (in Russian). Москва: Наука. pp. 1–627. ISBN 5-02-009852-3.
- Кузнецов, В. А. (1992). Майсурадзе, Л. Ш. (ed.). Очерки истории алан [Essays on the history of the Alans] (in Russian) (2nd ed.). Владикавказ: Ир. pp. 1–390.
- Низам Ад-Дин Шами (1941). "Зафар-Намэ" [Zafar-Name]. In Ромаскевич, А. А.; Волин, С. Л. (eds.). Сборник материалов, относящихся к истории Золотой Орды: Извлечения из персидских сочинений [Collection of materials relating to the history of the Golden Horde: Extracts from Persian writings] (in Russian). Vol. 2. Translated by Тизенгаузен, В. Г. Ленинград: Изд-во Академии Наук СССР.
- Фасих Хавафи (1980). "Семьсот девяносто седьмой (1394 — 1395) год" [Seven hundred ninety-seventh (1394 – 1395) year]. Фасихов свод (Муджмал-и Фасихи) [Fasihov code (Mujmal-i Fasihi)] (in Russian). Translated by Юсупова, Д. Ю. Ташкент: Фан.
- Ртвеладзе, Э. В. (1976). "О походе Тимура на Северный Кавказ" [About Timur's campaign in the North Caucasus]. In Виноградов, В. Б. (ed.). Археолого-этнографический сборник: вып. 4 [Archaeological and ethnographic collection: no. 4] (in Russian). pp. 103–128.
- Сборник материалов, относящихся к истории Золотой Орды: Извлечения из персидских сочинений [Collection of materials relating to the history of the Golden Horde: Extracts from Persian writings] (in Russian). Vol. 2. Translated by Тизенгаузен, В. Г. Ленинград: Изд-во Академии Наук СССР. 1941. pp. 1–.
- Хизриев, Х. (1977a). "Походы Тимура на Северо-Западный и Центральный Кавказ" [Timur's Campaigns in the North-Western and Central Caucasus]. Вопросы истории Чечено-Ингушетии (in Russian). Грозный: Чечено-Ингушское книжное изд-во. 11: 11–25.
- Хизриев, Х. (1977b). "Из истории борьбы народов Чечено-Ингушетии и Ставрополья против Тимура" [From the history of the struggle of the peoples of Chechen-Ingushetia and Stavropol against Timur]. Вопросы истории Чечено-Ингушетии [Issues of the history of Checheno-Ingushetia] (in Russian). Vol. 11. Грозный: Чеч.-Инг. кн. изд-во. pp. 25–40.
- Хизриев, Х. (1992). Ирисханов, И. А. (ed.). Кавказцы против Тимура (Борьба народов Северного Кавказа против экспансии Тимура) [Caucasians against Timur (The struggle of the peoples of the North Caucasus against the expansion of Timur)] (in Russian). Грозный: Книга. pp. 1–168. ISBN 5-7666-0320-7.
- Шараф ад-Дин Али Йазди (2008). Алимова, А. А.; et al. (eds.). Зафер-наме [Zafer-name] (in Russian). Translated by Ахмедов, А. Ташкент: Сан'ат. pp. 1–486. ISBN 978-9943-322-13-4.
- Шнирельман, В. А. (2006). Калинин, И. (ed.). Быть Аланами: Интеллектуалы и политика на Северном Кавказе в XX веке [To be Alans: Intellectuals and Politics in the North Caucasus in the 20th Century] (in Russian). Москва: Новое Литературное Обозрение. pp. 1–348. ISBN 5-86793-406-3. ISSN 1813-6583.