| Sabbinge Castle | |
|---|---|
Huis te Sabbinge | |
| Kasteelstraat 2 4471 PV Oud-Sabbinge, the Netherlands | |
 Sabbinge Castle from the north in 2010 | |
 Sabbinge Castle | |
| Coordinates | 51°31′56″N 3°47′58″E / 51.532180°N 3.799381°E |
| Type | Water castle |
| Site information | |
| Open to the public | No |
| Site history | |
| Built | c. 1250 |
| Materials | brick |
Sabbinge Castle is a small castle in Oud-Sabbinge, on the former island Wolphaartsdijk
Castle characteristics
The tower house

It seems that Sabbinge Castle is an example of a tower house. A tower house is a type of tower-like house which was designed from the start to function as a defendable habitation all by itself. An old photograph of Sabbinge Castle from before the restoration shows it as such. The wide windows on the left make it seems like a very small building. The closed façade on the right, with its low gate gives a better impression of the building.
Up till 1832, there was a moat around the castle. The tower house might have been part of a bigger structure, because there were reports of foundations found in the area in the 19th century.[1]
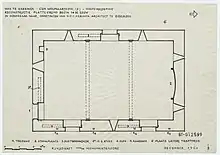
The tower house had a vaulted basement. On top of that was the old hall where the owners lived. In 1962 the walls at the level of the hall were said to be one meter thick on all sides.[2] According to the floor plan this is more like 80 cm, or three stone. On the northern wall, the main floor had a fireplace.
A very special feature of the main floor were the safety measures near the four large windows. There were wooden shafts in the walls on both sides of these windows. It seems that these were used to shift big bars into the window opening in times of danger. See floor plan and pictures.
Second construction phase

Before restoration, the foundations of an eight sided stair tower were found along the northern part of the western wall of the tower house. This did not belong to the original design of the tower house, because it decreased the defensive capabilities.
The stair tower points to a second phase in the construction history of Sabbinge Castle. It's tempting to place the construction of the large windows to the same time, but a professional investigation of the building's history has not been done yet. During the renovation, a short western wing was added to the castle. Its relation to the original castle is unknown.
Location and Name
Location
The hamlet Oud-Sabbinge is on the former island Wolphaartsdijk, which was situated between Noord-Beveland and Zuid-Beveland. It was part of the oldest of the three ambachten (lordships) of the island.[3] The castle is on the western fringe of Oud-Sabbinge.
The original name of Oud-Sabbinge is simply Sabbinge, for the polder Sabbinge. Later a new polder 'Nieuw Sabbinge' was made to the south. The name of the old polder then changed to Oud-Sabbinge.[3]
Name
The castle is known by two names: "Hoge Huis", and "Huis te Sabbinge". In medieval times, the Dutch word huis meant castle, but the first name uses it in the modern Dutch meaning of house.
History
Van Sabbinge
The Van Sabbinge family was mentioned in the 13th century. The castle, which might have started as a Motte-and-bailey castle was probably founded at this time.[1]
Van Schenge
The Van Schenge family was closely related to the Van Sabbinges. In about 1300 a Jan van Schenge lived at Sabbinge Castle.[1] The Schenge was the water between Wolphaartsdijk and Zuid-Beveland.
A knight lord Jan van Schenge is in a 1315 charter.[4] In 1321 the count ordered a reconciliation, where the Van Schenges / Sabbinges were involved as: Jan, son of Lord Jan of Sabbinge; Jan, son of Lord Gilles of Sabbinge; Jan son of Lord Willem of Schenge. These three replaced Willem, son of Jan of Schenge. The charter also refers to bloodshed and damage in Sabbinge, when Looper son of Jan had been ordered by the count to break the house of Claes van Schenge.[5]
In 1334 most of Wolphaartsdijk island was flooded. Oud-Sabbinge polder probably stayed dry, but a marine sediment layer on top of agricultural land indicates that it must have been flooded at least once before 1953. The castle was probably damaged at the time.[6]
Van Cats
In 1457 an heiress of Sabbinge Castle married Wolfert van Cats.[6] He was lord of Oostkerke, which was the name for the village Wolphaartsdijk up till 1960. It led to a union of the two closeby lordships. As a consequence the lords left Sabbinge Castle, which was converted to serve as a farm.[1] On the early 19th century cadaster map, the house is indeed shown with a large attached barn.
Renovation
Lenshoek
After the house ceased to function as a farm, it went into decline. In 1959, the Lenshoek family planned to demolish the ruinous house. However, it sold it to Wolphaartsdijk municipality for one guilder.[7]
In 1962 Wolphaartsdijk's mayor Barend ter Haar Romeny arranged that the castle was renovated.[7] The Rijksdienst voor de Monumentenzorg gave architect de Lussanet de la Sablonière from Middelburg the order to make a high over renovation plan. Architect Heringa from Zierikzee made a more detailed plan. The new inhabitant would be the insurerer Van Dam from Rotterdam.[8]
References
- Kuipers, J.J.B. (1999), "Huis, Hoge", Kastelenlexicon, Nederlandse Kastelen Stichting (NKS)
- Van Mieris, Frans (1754), Groot charterboek der graaven van Holland, van Zeeland, en heeren van Vriesland, vol. II, Pieter vander Eyk, Leyden
- Stenvert, Ronald; Van Cruyningen, Piet (2003), Monumenten in Nederland. Zeeland, Rijksdienst voor de Monumentenzorg, Waanders, p. 270
- Wilderom, M.H. (1968), Tussen Afsluitdammen en Deltadijken, vol. III, Rijkswaterstaat
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 Kuipers 1999, p. Bezits- en bouwgeschiedenis.
- ↑ "Het Hoge Huis". Provincial Zeeuwse Courant. 8 November 1962.
- 1 2 Wilderom 1968, p. 121.
- ↑ Van Mieris 1754, p. 153.
- ↑ Van Mieris 1754, p. 252.
- 1 2 Wilderom 1968, p. 122.
- 1 2 Wilderom 1968, p. 324.
- ↑ "'t Ooghe Uus van Sabbingen". Gereformeerd gezinsblad. 2 May 1964.