| 9th century–1168 | |||||||||||
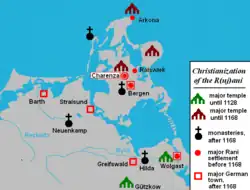 Christianization of the Rani; Slavic settlements, German towns with pagan temples and Christian monasteries | |||||||||||
| Status | Slavic tribe of the Lutician federation | ||||||||||
| Capital | Arkona (seat of pagan high priests, political and religious centre) Charenza (princely seat and formal capital) | ||||||||||
| Common languages | West Lechitic (Rani) | ||||||||||
| Religion | Polabian Slavic paganism, the known cults:
| ||||||||||
| Government | de facto pagan theocracy, formally hereditary monarchy (principality) | ||||||||||
| Prince | |||||||||||
• c. 955 (first) | Vitzlav | ||||||||||
• c. 1170 (last) | Jaromar I | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Formed | 9th century | ||||||||||
| 1168 | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Germany | ||||||||||
The Rani or Rujani (German: Ranen, Rujanen) were a West Slavic tribe based on the island of Rugia (Rügen) and the southwestern mainland across the Strelasund in what is today northeastern Germany.
The Rani tribe emerged after the Slavic settlement of the region in the ninth century,[1] and ranked among the most powerful of several small Slav tribes between the Elbe and lower Vistula rivers before the thirteenth century. They were among the last tribes to hold to Slavic paganism, and the influence of their religious center at Arkona reached far beyond their tribal borders.[2]
In 1168, the Rani were defeated by King Valdemar I of Denmark, and his adviser Absalon, Bishop of Roskilde, resulting in the conversion of the region to Christianity.[3][4][5][6] In the course of the Ostsiedlung of the thirteenth century, the tribe was assimilated by German and Danish settlers and the Rani were gradually Germanised. The Principality of Rugia remained Danish until 1325.[7][8]
Settlement
In the late migration period, areas that had previously been settled by Germanic tribes became settled by Slavs. In Rugia and the adjacent mainland, where the Rugii were recorded before the migration period, Slavs first appeared in the ninth century;[1] continuous settlement from the pre-Slavic era is suggested based on pollen analyses and name transitions,[9] so a Rugian remnant seems to have been assimilated.
The tribal name of the former inhabitants, the Rugii, may be the root of both the medieval name of Rugia and the tribal name of the Slavic R(uj)ani, though this hypothesis is not generally accepted.[10]
Religion

The Rani believed in multiple gods, all of which had several faces and were worshipped as tall wooden statues in their respective temples. They were worshipped in temples, holy groves, at home and in ritual meals. The most powerful of their gods was Svantevit, a four-headed god whose temple stood at Cape Arkona on the northernmost shore of Wittow, at that time still an island immediately to the north of Rügen. This temple was worshipped and collected tributes not only from the Rani, but from all Baltic Wends after their earlier main religious centre, Rethra, was destroyed in by Germanic raiders in 1068/9.[11]
Other gods were Tjarnaglofi, whose temple was on Jasmund near modern Sagard, and Rugievit, Porevit and Porenut, to whom there were temples in the capital, Charenza. Temples to other gods were found throughout Rani territories.
After the forced Christianization, monasteries and churches replaced the temples. Built into the church of Altenkirchen is a large stone from Arkona with a relief showing a Svantevit priest.
Administration and culture
Medieval chronicler Helmold of Bosau described the Rani as the only Wendish tribe ruled by a king and reports them as having subdued many other tribes, while not tolerating subordinance themselves. Common decisions of the Wendish tribes were made only with the approval of the Rani. The highest-ranking position was in fact that of the High Priest, who stood above the king. The oracle decided whether and where campaigns were to be mounted, and after a victory the money and precious metals of any bounty were given to the temple before the rest was partitioned. Subdued tribes were made subordinate to the temple.[11]
The Rani political capital was Charenza (then Korenitza, today an unsettled site called Venzer Burgwall). Rani dukes also resided at Rugard castle, a precursor of the modern city of Bergen. Throughout the Rani lands there were castles (burghs), all having a ring-like wall of wood and clay, protecting villages and/or religious sites, and functioned as strategic strongholds or seats of the gentry.
The Rani also established a main, mixed Slavic and Viking, trading center in Ralswiek. In the 11th and 12th centuries, they also conducted Viking-style raids on their neighbors.
Language
The Rani spoke a West Lechitic language, one of the Lechitic group of West Slavic languages. In the course of the 12th to 15th centuries, it was replaced by Low German as politics and ethnic structure had changed due to Ostsiedlung. The Rani language went extinct when the last Rujani-speaking woman died on the Jasmund peninsula in 1404.[12]
History
In 955, Rani took part in the Battle of Recknitz, assisting German Otto I in defeating the Obotrites at the Recknitz (Raxa) River.
As the Obodrite state expanded in the late 11th century, the Rani were also pressed and in 1093 had to pay tribute to Obodrite prince Henry.[13] They launched a naval expedition in 1100, in the course of which they sieged Liubice, a predecessor of modern Lübeck and then the major Obodrite stronghold.[14] This attack was however repulsed.[14] In 1123, the Rani struck again and killed Henry's son Waldemar. When in 1123/24 an Obodrite army led by Henry reached Rani territory, the Svantevit priests were forced to sue for peace.[14] Henry's army consisted of 2,000–6,000 men, devastated the coastal settlements, and the terms of the subsequent agreement were that the island would only be spared in return for an immense sum which had to be collected from the continental Slavs further east. Regrouping after Henry's death (1127), the Rani again assaulted and this time destroyed Liubice in 1128.[14] At this time they seem to have been devoted pagans, with their priests holding theocratic powers.

In 1136, the Danes defeated the Rani, who in turn had to promise to adopt Christian faith — yet returned to their pagan beliefs as the Danish headed back.[14]
A force of Rani attacked the Danish fleet during the 1147 Wendish Crusade. Saxon armies repeatedly managed to raid Rugia.
The Danes, who had attacked the Rani already in 1136 and 1160, finally conquered the Rani stronghold of Arkona in 1168, forced the Slavs to become vassals of Denmark and to convert to Christianity.[14] The wooden statues of their gods were burned and monasteries and churches were built throughout Rani territories.
The former Rani realm henceforth became the Danish Principality of Rugia.
List of rulers
Reported names of Rani tribal leaders ("kings" or "princes") were:
- Ráni were one of the Lutici tribes who were often described as a "tribe without a ruler", meaning political power was asserted via discourse in an assembly. [15][16]
- c. 1066 Kruto (according to some disputed theories a grandfather of Ratislav, considered to be a ruler of Rujána as the ruler of Lutici after the death of Gotšalk)
- c. 1092 Vartislav
- c. 1105 Ratislav (the 1st ruler of Rujána that's known for sure)
- c. 1164 Tetislav (the last ruler of pagan Rujána, became Danish Prince of Rugia in 1168)
- c. 1170 Jaromar I
- 1218 Barnuta
- 1221 Vislav I. (after resignation of his brother Barnuta)
- 1249 Jaromar II.
- 1260 Vislav II.
- 1302 Vislav III. (his only son died before him)
- 1325 Vartislav IV. (nephew of Vitslav III., the last ruler of Rani blood. His death led to the Rügen wars of succession and in 1354 the former principality went to Pomerania-Wolgast)
Sources
- Thompson, James Westfall (1928). Feudal Germany, Volume II. New York: Frederick Ungar Publishing.
- Herrmann, Joachim (1970). Die Slawen in Deutschland (in German). Berlin: Akademie-Verlag GmbH. p. 530.
See also
Notes
- 1 2 Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.15, ISBN 3-515-07671-9
- ↑ Sebastian Brather, Archäologie der westlichen Slawen: Siedlung, Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft im früh- und hochmittelalterlichen Ostmitteleuropa, Walter de Gruyter, 2001, p.331, ISBN 3-11-017061-2
- ↑ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Gerhard Krause, Horst Robert Balz, Gerhard Müller, Theologische Realenzyklopädie, Walter de Gruyter, 1997, pp.40ff, ISBN 3-11-015435-8
- ↑ Werner Buchholz, Pommern, Siedler, 1999, p.34, ISBN 3-88680-272-8
- ↑ Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.43, ISBN 83-906184-8-6 OCLC 43087092
- ↑ Werner Buchholz, Pommern, Siedler, 1999, pp.46-52,pp.61-63 ISBN 3-88680-272-8
- ↑ Klaus Herbers, Nikolas Jaspert, Grenzräume und Grenzüberschreitungen im Vergleich: Der Osten und der Westen des mittelalterlichen Lateineuropa, 2007, pp. 76ff, ISBN 3-05-004155-2, ISBN 978-3-05-004155-1
- ↑ Joachim Herrmann, Die Slawen in Deutschland, Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.27, pp.33ff
- ↑ Johannes Hoops, Hans-Peter Naumann, Franziska Lanter, Oliver Szokody, Heinrich Beck, Rudolf Simek, Sebastian Brather, Detlev Ellmers, Kurt Schier, Ulrike Sprenger, Else Ebel, Klaus Düwel, Wilhelm Heizmann, Heiko Uecker, Jürgen Udolph, Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde, Walter de Gruyter, pp.419ff, ISBN 3-11-017733-1
- 1 2 Kyra T. Inachin, Die Geschichte Pommerns, Hinstorff Rostock, 2008, p.14, ISBN 978-3-356-01044-2
- ↑ Werner Besch, Sprachgeschichte: Ein Handbuch zur Geschichte der deutschen Sprache und ihrer Erforschung2nd edition, Walter de Gruyter, 1998, p.2707, ISBN 3-11-015883-3
- ↑ Joachim Herrmann, Die Slawen in Deutschland, Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.367
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Joachim Herrmann, Die Slawen in Deutschland, Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.268
- ↑ Lübke, Christian: Lutizen. Historisches. In Beck, Heinrich; et al. (eds.). RGA XIX, 19 (2 ed.). de Gruyter, 2001, p. 51, ISBN 3-11-017163-5
- ↑ Garipzanov, Ildar H. Franks, Northmen, and Slavs. Identities and state formation in early medieval Europe. Cursor mundi. 5. Geary, Patrick J.; Urbańczyk, Przemysław. Brepols, 2008, p. 198, ISBN 978-2-503-52615-7