Rosina Widmann | |
|---|---|
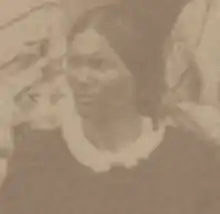 Rosina Widmann, c. 1860s | |
| Born | Rosina Binder 13 November 1826 |
| Died | 14 November 1908 (aged 82) |
| Nationality | German |
| Occupations | |
| Known for | Women's vocational education on the Gold Coast |
| Spouse |
Johann Georg Widmann
(m. 1847; died 1876) |
| Children | 12 |
Rosina Widmann, née Binder, (13 November 1826 – 14 November 1908) was a German educator and Basel missionary-wife who opened a girls’ school at Akropong in pre-colonial Ghana.[1][2][3][4] She was the first exemplar of a European missionary-wife who worked in Ghana for a long period.[1] Between 1847 and 1877, Widmann lived on the Gold Coast and was actively involved in both the Christian ministry and women's vocational education.[1][2] Her sojourn in Akropong was in three phases: January 1847 to April 1850; December 1851 to June 1867 and January 1869 to spring 1877.[1] Widmann was also a prolific writer, noted for her detailed diary entries of her thoughts and travels, everyday life as a missionary-wife, her interactions with her school pupils and with the Akan peoples of Akropong, providing a vivid narrative of nineteenth century European missionary activity in colonial Ghana, situated against the Akan culture.[1][2][4]
Early life
Childhood and education
Rosina Binder was born on 13 November 1826 in Korntal, a then newly founded Pietist village close to Stuttgart, Germany.[1][2][4][5] Some scholars have suggested that her grandparents may have been among the first settlers of Korntal.[1] The daughter of a farmer, Rosina Binder came from a large family and had ten other siblings, including half-brothers and sisters, with whom she grew up in southern Germany where the Württemberg Pietist lifestyle was commonplace.[1][2][4] Her mother was the second wife of her father.[1] She had a very basic education and later enrolled at a girls’ school where she learnt sewing and housekeeping.[2] In her records, she was described as “a simple Christian who had no higher education” but nonetheless gifted with an appreciable Biblical knowledge.[1] It is said that in nineteenth century Germany, Rosina Binder had “aspirations to rise socially but only knew ordinary cooking.”[1]
Marriage proposal
In 1845, when Rosina Widmann was nineteen years old, she received an unusual arranged marriage proposition from the Basel Mission: a thirty-one year-old German man, Johann Georg Widmann (1814 - 1876) who had attended the Basel Mission Seminary in Basel, Switzerland and had been working on the Gold Coast as missionary for three years was looking for a life partner.[6] Upon the recommendation of the Rev. Jakob Heinrich Staudt, the local Lutheran minister and a former lecturer at the Basel Mission Seminary, Binder had been chosen by the Basel Committee of Friends as a potential suitor for J. G. Widmann.[1] Like all Basel missionaries, Widmann had arrived in Ghana as a bachelor and had to prove himself in the field for a minimum of two years, before permission could be granted by the Home Committee to find a suitable wife or so-called mission bride on his behalf.[2][4] Due to the cost of travel, Johann Widmann could not physically go to Europe to find a bride.[2] Though Rosina Binder had never met her future husband, she was asked to marry him and join him at the mission station in Akropong in a tropical region known for its high missionary death toll.[2] By her own account, Johann Widmann did not even know her name.[4] The Basel Mission Inspector, Wilhelm Hoffmann who happened to be in her hometown met Binder and found her suitable.[1] He reported to the Home Committee that Rosina Binder would accept the proposal as soon as her grandmother gave her approval of the union, after which she would learn English and be trained in domestic skills.[1]
Rosina Binder accepted marriage proposal.[1][2] On 17 September 1846, at her commissioning service, the Lutheran pastor, the Rev. Staudt, selected Psalm 46 with emphasis on verses 1 and 7 as her Biblical verse for blessing: “God is our shelter and strength, always ready to help in times of trouble. The Lord Almighty is with us, the God of Jacob is our refuge.”[2] The pastor had wanted to bless her by laying on of hands but the church elders objected to it and the suggestion was shelved.[1] At the time of her departure from her hometown in Germany, her mother was gravely ill after giving birth to her youngest child. She noted in her diary, “Then I went to my beloved mother, who sat up in her bed and cried her heart out and couldn’t say more than: So you want to go now…Because of her weakness I did not speak many words and quickly rushed out of the room. Therefore, I forgot to say goodbye to my little two week-old sister, Sophie.”[2]
Voyage to London and the Gold Coast
On 19 September 1846, in Pietist fashion, she bade an emotional farewell to her grandmother, parents and siblings before leaving with four missionaries, Johann Dieterle, Joseph Mohr, Johannes Stanger and Friedrich Meischel who were also going to the Gold Coast.[1][2] When they were about thirty minutes outside Korntal, a group of young women with whom she had started a prayer fellowship six months earlier presented her with a token of grapes as “proof of their love” for her.[1] She entered a London-bound passenger steamship.[1][2] During the voyage, she and the missionaries often sang Lutheran hymns.[2]
Rosina Binder was in London for nearly two months, from 23 September to 20 November 1846.[1] During her stay in London, she wrote in her diary, “I looked at all the strangeness, strange people, strange language and strange customs with a heavy heart. Besides, I was very afraid of the long sea voyage.”[2] While in the British capital, she struggled to learn the English language.[1][2] The big city was strange to her as were the fashion style and Victorian version of pietism.[1]
She had not yet received a letter from her fiancé, Johann Widmann as normal ship connection was yet to be established and communication with the Gold Coast was spotty at best.[1] She worried even more when she learnt that her mother’s health was deteriorating.[1] She experienced desolation “illness and a spiritual crisis" – a lack of faith, feeling her calling to be a missionary had left her and neither Scripture nor prayer could lift her morale.[1]
She was hosted by an English couple, Mr. and Mrs. Young.[2] Per historical records, Mr. Young appeared to have made inappropriate advances towards her which she rejected.[2] Mrs. Young blamed her for her husband’s boorish behaviour.[2] In anguish and out of fear, she locked herself in her bedroom to pray, suppressing her cries with the room’s sofa.[2]
In time, she met several Moravian and other evangelical groups in London.[1] She also came into contact with a European missionary-wife based in Sierra Leone who coached her on her future life as a mission bride.[1] When she was about to leave London for the Gold Coast in November 1846, the husband of the missionary-wife commended her on her improved English skills.[1] A week before her departure, she also received her first letter from Johann Widmann which gave her hope in the sustenance of providence and restored her weakened faith –an asset for her future life in the mission field at Akropong.[1]
While on the first steamship she had even seen in her life, a twenty year-old Rosina Binder wrote a diary entry on New Year’s Eve in 1846, “Today seems to be a special and notable day. Exactly a year ago, I received the call to go to the Mission Field. How many difficulties have I gone through within this last year? And quite some pleasant experience too. Thanks be to God for everything.”[2]
On 6 January 1847, the ship sailed past Cape Three Points and by the afternoon, towards Cape Coast.[4] A day later, she arrived in Cape Coast after the seven-week passage.[2][4] She was transported to the shore via a landing boat.[4] Of her first impression, she penned, “The heat was pressing; I felt like being in a completely different world. People, animals, plant and houses everything was alien to me. My mind…and my body were very strained.”[2][4] Binder and the missionaries were received by one Mr. Freeman and an English couple, Mr. and Mrs. Allen.[4] As there was no vacancy at the mission house at Cape Coast, she was hosted by the Hatten family, a respected Euro-African mulatto family who lived a “newly built beautiful [stone] house”.[4] Mr. Hatten, a merchant in whose name the steamship was addressed, was away on a business trip.[4] Rosina Binder was therefore received by Mrs. Hatten.[4]
Marriage

Rosina Binder arrived in Christiansborg on 15 January 1847.[4] Johann Georg Widmann who had been waiting for her on the coast for two days, had by then returned to Akropong to attend to urgent mission work.[4] A few days after her arrival, Rosina Binder finally met her fiancé, Johann Widmann for the first time.[2][4] In her own account, their first meeting was full of nervous excitement.[2][4] Binder recalled, “Because I had not seen my dear groom before and would not be able to identify him, I asked that he should be pointed out to me to prevent any embarrassment. I cannot put into words the feelings that overcame my heart when I met with my dear husband. One has to experience something of this nature…We did not look at each other as if we are seeing each other for the first time, because even before we met, the Lord had tied our hearts deeply together. Before we left the room where we greeted each other for the first time, we fell on our knees and thanked the Lord, who had brought us together. We didn’t see each other as if we had seen ourselves for the first time. For the Lord, who has made the covenant – what we really believed joined our hearts in love before we knew each other. O how much would I have loved to share my joy with my beloved ones at home.”[2][4]
Widmann, Binder and the other missionaries departed from the Gold Coast on 19 January 1847 and arrived in Akropong the next day.[1] The wedding ceremony was on 21 January 1847.[1] The event was attended by West Indian and Basel missionary families.[1] Several Akropong indigenes peered through the chapel window to catch a glimpse of the bride.[1][2] The newlyweds deeply cared for each other, forging a strong bond and survivalist mindset due to the eternal fear of death from tropical disease.[1]
During her first pregnancy, Rosina Widmann fell ill to the extent she was unable to recognise her husband.[2] She gave birth to a boy.[2] Johann Winder and Rosina Binder had eleven more children, with four girls dying at an early age and were buried at the Akropong mission cemetery.[1][2][4] The rest were sent to Basel and lived in the missionary boarding house or in the missionary girls’ house.[1][4] Another son died in Korntal.[1][4]
Life on the Gold Coast
Missionary-wife in Akropong
On 19 January 1847, Rosina Widmann sat in a basket to acclimatise to the lush green of the tropical rainforest of the Akan inland.[2][4] Hammocks, stretchers, palanquins and baskets were most commonly used as means of transporting missionaries to the hinterlands during that period. After her wedding, she spent eighteen months trying to master the Twi language.[2] She became proficient in Twi to the point of saying, “In the evening, I prayed with my girls [from Akropong who lived and worked with them]. I asked the Lord in their own mother tongue. Thanks be to God that this is now possible.”[2] By mastering the language, she was able to make new friends among the Akuapem community.[1][2]
She also befriended the West Indian missionary families and shared wine and sweets with their children.[4] From her diaries, she mentioned that the West Indians became dissatisfied with the mission entreprise due to the failure of the Basel mission administration to fully honour their conditions of service.[4] A missionary living on the coast, Schiedt visited Akropong as a result.[4] There was a fracas between J. G. Widmann and Schiedt concerning the workplace grievances of the Jamaican families.[4] Schiedt left for the coast in late January 1847 only to return in July 1847 after Johann Widmann went to Christiansborg to settle his differences with Schiedt.[4] According to Rosina Widmann, the disagreement caused her anxiety.[4] Missionaries Schiedt, Widmann and Meischel then attended a mission conference in August 1847.[4]
She observed the marital fidelity issues between Liberian missionary, George Peter Thompson (1819 – 1889) and Angolan-born Moravian Jamaican educationist, Catherine Mulgrave (c.1827 – 1891). Furthermore, she witnessed the tension that existed among the Basel missionaries who quarrelled frequently with one another. She remarked, “I told Brother Mohr that it would be much better to be open with each other, because otherwise I am often under a heavy inward pressure.”[2] This situation depressed and distressed her, making her homesick, constantly worrying about her ageing parents in Germany.[2] She also experienced loneliness as her husband travelled for weeklong stays in neighbouring towns for mission work and to visit members of his congregation.[1][4] J. G. Widmann served as the resident minister of the Basel Mission Church at Akropong, later renamed the Christ Presbyterian Church from 1845 to 1876.[3] During this period, her school pupils who lived in her household kept her company. Rosina Widmann wrote in 1848 that one of her school girls, Amba comforted her tenderly during her illness, characterised by “headache and freezing [chills], dizziness and vomitting”.[4] She allowed Amba and another schoolgirl, Abena to sleep in her bedroom to alleviate her loneliness when her husband was away.[4] Another pupil, John slept in the hall.[4]
Once when her husband, J. G. Widmann was very ill, she lamented, “Since two weeks, he suffers from fever and O God, a lot of tears and thoughts about death are within me. My hand is shaking while I am writing this. He has just fallen asleep and looks utterly miserable. O Lord, do you want to take him already away from me? Don’t tempt me more than I could stand. O, you will not do it. And if you take this dear soul away. O God, my Saviour make me strong. God have mercy on me that I will not lose faith.”[2] Her husband eventually recovered from his illness and she nursed him back to full health over a long period.[2]
In an episode at Akropong, one of the Jamaicans, Ann Rochester, an unmarried woman, was writhing in abdominal pain, which could not be relieved with any medication available, herbal or otherwise.[2] Rosina Widmann was in the company Rochester's brother and sister; Mrs. Miller, the wife of Joseph Miller, a Jamaican missionary and a few other women from the village.[2][4] It turned out that she had been impregnated by a senior West Indian missionary.[2][4] Both the baby and Ann Rochester died during labour.[2][4] Cataloguing this tragedy in her diary, Rosina Widmann stated, “My pain was so great and still is. O what a high price she has to pay for her sin. O, may our dear Saviour hear her sights and receive her with grace.” The Basel mission refused to bury Ann Rochester in the mission cemetery because in their view, she was “guilty of sin.”[2] They accused the Widmanns of shielding the identity of the alleged father of the deceased baby.[4] The Basel missionaries at Akropong also sent letters of complaints to the Home Committee.[4]
In an attempt at evangelism in December 1848, she visited the tiny compound of an amiable old woman from the town of Davu.[4] Widmann initiated conversation with hint of conversion by talking about Christian concepts such original sin, repentance, redemption, salvation, life after death and heaven.[4] The old woman immediately walked away to the other end of the courtyard to sweep the floor and “put the chickens and goats in the stall.”[4] Indirectly, Widmann's message against “fetishes” had been rejected by the aged woman.[4] Rosina Widmann then proceeded to proselytize to the elderly lady's only daughter and several other women in the vicinity.[4] In another case, she had a philosophical conversation with an old Akuapem woman about the concept of a Supreme Being vis-à-vis Christian and native traditional beliefs.[1]
Rosina Widmann often visited the sick, especially women in Akropong, within both the mission and native communities.[1][2] This endeared her to the people who paid her visits in the “Christian village” or Salem quarters of Akropong. On one of such visits, an Akropong woman, out of curiosity, commented on her shawl, prompting Widmann to explain differences in textile production, as practised by her mother and sisters, using broad looms in Europe as compared the locally made Akropong stoles that were made by the method of strip-weaving.[1] The conversation lasted until almost midnight. From the tone of her writings, Rosina Widmann had not fully acculturated into Gold Coast society by 1849.[4]
Widmann also acted as an arbiter in disputes in Akropong.[1] In 1874, Widmann was an intermediary between the chieftain of Akropong, Okuapemhene, his council of elders and the elderly mother of a deceased king who lived on a plantation in a hamlet called Mamprobi, near a mausoleum where the kings were interred.[1] The old woman's self-imposed exile was due to feeling neglected by her sons and the then Okuapemhene, Nana Asa Kurofa. As a result, she refused to attend the traditional yearly yam festival, Odwira.[1] The palace courtiers therefore invited Rosina Widmann to mediate in the crisis between the senior woman and the chieftain.[1] Moreover, when one of the wives of the Akropong ruler - Gyebia, an Asante, had a dispute, her husband, the woman sought refuge at the mission station and was housed by Rosina Widmann.[1] Widmann intervened in the matter and helped the royal couple settle the matter.[1]
The Widmanns returned to Korntal for furlough twice during their long sojourn on the Gold Coast.[1][2]
Work in vocational education
The Basel Mission's vocational training for girls was instituted by Rosina Widmann in late January 1847, when she started classes in needlework for 12 girls at her home in Akropong where the Gold Coast mission headquarters was stationed.[7] Rosina Widmann had sought permission from the then, Okuapemhene, Nana Kwadade I for young girls in his chiefdom to be educated. Per the Basel Mission's newspaper in Akropong, the Station Chronicle, four female pupils enrolled at the new school almost immediately after the request.[1] This number rose to 17 girls two months later and to 24 students by August 1847.[1] It was later reported that the foundation class was made up of a few schoolgirls from the royal family, the ruling Asona clan of Akropong.[1] In 1848, there were 37 girls who attended the morning general lessons with 25 boys. In 1849, 30 girls and 30 boys attended the morning school. The Basel Mission gave each pupil a small sum of money, colloquially called “food money” (Kostgeld) for feeding expenses.[1] The Kostgeld was an incentive to keep enrollment afloat.[1]
The commencement of classes at Mrs. Widmann's school was shortly after her husband, J. G. Widmann and others had started teaching boys at Akropong.[1][7] In this period, weaving was the most common form of textile production in the Akan hinterland and the profession of seamstress or dressmaker as introduced by Widmann was a novel innovation there.[7] Previously, sewing and weaving the traditional cloth, “kente” were considered a man's domain in Akan society. Women were forbidden from touching the loom in Akuapem jurisdictions while their counterparts on the coasts could engage in commercial crafts.[1] Dressmaking, thus, became a source of employment and economic opportunity for women at Akropong.[1]
The vocational experimental model which also incorporated reading, writing, arithmetic, English and the basics of Christianity, evolved into the girls’ school at Akropong.[1][2] This education framework also included school children living with missionary families in their homes to be educated in a Christian way while employed as household staff or housemaids.[1][2][4] Rose Ann Miller (1836 – 1930), a Jamaican educator and the oldest of West Indian children who accompanied their parents to the Gold Coast in 1843, was Rosina Widmann's de facto interpreter.[1][3] Miller started assisting Widmann as early as 1848 when she was only twelve years old.[3]
Some apprehensive parents did not allow their daughters to attend the school in the mornings when academic subjects were taught but permitted them to go in the afternoon to learn sewing.[1] Later Widmann would add reading, arithmetic and Bible studies to the afternoon curriculum.[1] She began all her classes with a short prayer recited in the Twi language. School ended with a verse from Protestant hymn. Children were required to memorise the Lord's Prayer and English hymn verses. The teaching materials included a Twi language Primer and English textbooks.[1]
In one notable case, a girl named Adwoa Yirenkyiwa, born c. 1841 decided as a child that she wanted to attend Mrs. Widmann's school.[1] Her mother rejected her proposition initially. When Yirenkyiwa refused to eat food, her mother acceded to her wish and took her to Rosina Widmann.[1] The first two girls who lived in the Widmann household, though not yet baptised learned to recite the prayer, “Dear Saviour, give me a new heart! You died for us to redeem us, forgive my sins for the sake of your name.”[1]
The Akropong girls who lived with the Widmanns some faced dilemmas: food choices that were culturally forbidden by Akan society.[1] In 1849, mothers provided food for their wards in missionary care in accordance with their dietary prohibition.[1] This system changed in 1852 when the Rosina Widmann starting providing food to pupils under her tutelage.[1] An Akuapem girl living in her household refused chevon, fearing corporal punishment from her mother if she violated the cultural taboo.[1]
In April 1850, when the Widmanns went to Europe, pupils stopped attending the school and none had been baptised.[1] The school was later re-opened by Julie Mohr and Friederike Dieterle, spouses of missionaries, Joseph Mohr and Johann Dieterle.[1] The school's population once again increased.[1]
In 1851, the sister of William Yirenkyi, a local student catechist was sent to the school by their mother who was a princess.[1] Another royal member, Susanna Luise Anyama was one of Widmann's schoolgirls.[1] She was sent to Basel in 1858 for further training.[1] In 1864, she was considered a prospective bride for David Asante, the first native Akan Basel missionary on the Gold Coast.[1] Anyama, however declined the offer stating her desire to live in Europe.[1] A close relation Anyama, Ama Otwe attended the girls’ mission school in 1853. Otwe's half-sisters Susanna and Abenewa were also pupil of Widmann.[1] The first baptism of girls in training was on 8 August 1853.[1] These include Catherine Buruwa who married Paul Staudt Keteku, a catechist and translator.[1] Martha Korantemaa, who married Aburi catechist, Edward Samson, was baptised in 1856.[1] Keteku and Buruwa's daughter was christened in 1858 – the first of its kind in Akropong for native Christians.[1] In 1859, Yaa Krobea, fiancée of catechist, William Hoffmann Yirenkyi was baptised.[1] Krobea was a student of Rosina Widmann.[1] When Lydia, the baptised sister of Susanna Luise Anyama died in 1859, she became the first Akuapem Christian to be buried at the mission cemetery.[1] As Lydia was of royal lineage, her family initially opposed it but eventually acquiesced.[1]
Widmann also trained non-Christian brides of the mission's native catechists and teachers to know the rudiments of the Christian faith and housekeeping.[1] Ernestine Mader, missionary-wife of the School Inspector gave evening lessons in literacy to some of the prospective brides of teacher trainees.[1] Some catechists whose future wives became pregnant before marriage were dismissed, as the situation was at odds with Basel Mission's Pietist standards for monogamy and procreation while the polygamous traditional society, being more flexible, permitted it childbearing outside marriage.[1]
In 1869, Johann Georg Widmann wrote to the Basel Home Committee on return to the Gold Coast from furlough in Germany, to brief the mission's central administration on his wife's work: “She has taken over the running of the toddler school again and started a Sunday school for women and virgins, where she is supported by 5 monitors (assistant teachers) ... In our household, we have 15 people, some our former children, some young girls, of whom three are orphans, two girls and a little boy ...”[8][9] The number of girls who came to Rosina Widmann's school increased to 70 over time.[2] When the Basel Mission started distributing for the school children, enrollment climbed to 80 or 90 by the end of the 1840s.[1] Attrition was high as many students left within six to twelve months.[1] The school population dwindled further once the mission stopped proving cloth for the enrolled pupils.[1] In the end, only the pupils living in the missionary household remained in the school.[1]
Later years and death
Rosina Widmann stayed in Ghana, working for the Basel Mission for three decades and permanently returned to Korntal at the age of 50 in the spring of 1877, a few months after the passing of her husband.[1][2][4] The Rev. J. G. Widmann died on 27 November 1876 and his remains were buried in Akropong.[4] At Johann Widmann's funeral service, the chief of the town, the Krontihene attended the ceremony with his entourage of drummers though they remained outside the chapel, in silence, throughout the burial service.[1] The chief's delegation accompanied the funeral procession to the mission cemetery.[1]
Rosina Widmann died on 14 November 1908 in Korntal at the age of eighty-two.[1][4] Rosina's Widmann's near singular effort in the vocational education of girls at Akropong, without any instructional support from Basel, disproved an earlier assertion made by the Inspector of the Basel Mission, the Rev. Josenhans that “women were a burden for missionary work.”[2]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 Sill, Ulrike (2010). Encounters in Quest of Christian Womanhood: The Basel Mission in Pre- and Early Colonial Ghana. BRILL. ISBN 978-9004188884. Archived from the original on 30 March 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 Knispel, Martin and Kwakye, Nana Opare (2006). Pioneers of the Faith: Biographical Studies from Ghanaian Church History. Accra: Akuapem Presbytery Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - 1 2 3 4 Kwakye, Abraham Nana Opare (2018). "Returning African Christians in Mission to the Gold Coast". Studies in World Christianity. Edinburgh University Press. 24 (1): 25–45. doi:10.3366/swc.2018.0203.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 Missionary Practices on the Gold Coast, 1832-1895. Cambria Press. ISBN 9781621968733. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- ↑ "Rosina Widmann". geni_family_tree. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- ↑ Herppich, Birgit (31 October 2016). Pitfalls of Trained Incapacity: The Unintended Effects of Integral Missionary Training in the Basel Mission on its Early Work in Ghana (1828-1840). James Clarke Company, Limited. ISBN 9780227905883. Archived from the original on 11 June 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.
- 1 2 3 Schweizer, Peter Alexander (2000). Survivors on the Gold Coast: The Basel Missionaries in Colonial Ghana. Smartline Pub. ISBN 9789988600013.
- ↑ "Dimensionen der Erziehung und Bildung; Festschrift zum 60. Geburtstag von Margret Kraul". Hoffmann-Ocon, Andreas, Koch, Katja, Schmidtke, Adrian, Kraul, Margret. 2005. Archived from the original on 10 June 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: others (link) - ↑ Kraul, Margret (2005). Dimensionen der Erziehung und Bildung: Festschrift zum 60. Geburtstag von Margret Kraul (in German). Universitätsverlag Göttingen. ISBN 9783938616000. Archived from the original on 10 June 2018. Retrieved 3 September 2018.