| RNASE4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | RNASE4, RAB1, RNS4, Ribonuclease 4, ribonuclease A family member 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 601030 MGI: 1926217 HomoloGene: 10576 GeneCards: RNASE4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ribonuclease 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASE4 gene.[5][6]

Function
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the pancreatic ribonuclease family. Secreted ribonucleases are the only enzyme family that is vertebrate-specific. Among the 13 members of this superfamily, ribonuclease 4 (RNase 4), is the most conserved gene across different vertebrate species.[7] The human form of RNase 4 is an intracellular and plasma enzyme which was first isolated from colon adenocarcinoma cell line HT-29.[8] It can be found in the pancreas, saliva, and the liver, displaying a similar distribution pattern to that of angiogenin (ANG). It plays an important role in mRNA cleavage and has marked specificity towards the 3' side of uridine nucleotides.
Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding the same protein. RNase 4 is co-expressed and shares the same promoter with angiogenin (ANG), another member of this superfamily.[7] Each gene splices to a unique downstream exon that contains its complete coding region.[6] RNase 4 has also been studied in its involvement with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a nervous system disease, due to its similarity with ANG which has been associated with ALS pathogenesis.[7]
Structure

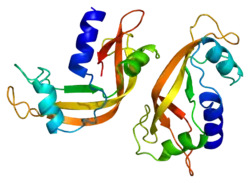
RNase 4 features a unique structure compared to its homologous enzymes in the superfamily. It contains 119 amino acid residues making it the shortest known human RNase and contains no N-glycosylation sites. RNase 4 displays an α + β type polypeptide chain folding and a V-shape with the active site cleft in the middle.[8] It contains three α-helices and four β -strands while the secondary structures are connected by six loops. There are four disulfide bridges located throughout the structure that connect the α-helices, β -strands, and loops.[8] The overall structure of RNase 4 is similar to its homologous enzyme RNase A, EDN, and angiogenin.
A shorter C terminus is a unique feature of RNase 4 which places the carboxy terminus in the pyrimidine recognition site which results in RNase 4 unique specificity. The pyrimidine recognition site is where there are major difference compared to its homologous enzymes. It contains an arginine residue at position 101, a phenylalanine reside at 42, and a threonine residue at 44.[8] These residues contribute to the ribonuclease 4 specificity and are adapted to recognize a uridine-type base over cytidine-containing substrates.
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000258818 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021876 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Rosenberg HF, Dyer KD (November 1995). "Human ribonuclease 4 (RNase 4): coding sequence, chromosomal localization and identification of two distinct transcripts in human somatic tissues". Nucleic Acids Research. 23 (21): 4290–4295. doi:10.1093/nar/23.21.4290. PMC 307382. PMID 7501448.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: RNASE4 ribonuclease, RNase A family, 4".
- 1 2 3 Li S, Sheng J, Hu JK, Yu W, Kishikawa H, Hu MG, et al. (April 2013). "Ribonuclease 4 protects neuron degeneration by promoting angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and neuronal survival under stress". Angiogenesis. 16 (2): 387–404. doi:10.1007/s10456-012-9322-9. PMC 3582744. PMID 23143660.
- 1 2 3 4 Terzyan SS, Peracaula R, de Llorens R, Tsushima Y, Yamada H, Seno M, et al. (January 1999). "The three-dimensional structure of human RNase 4, unliganded and complexed with d(Up), reveals the basis for its uridine selectivity". Journal of Molecular Biology. 285 (1): 205–214. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2288. PMID 9878400.
Further reading
- Shapiro R, Fett JW, Strydom DJ, Vallee BL (November 1986). "Isolation and characterization of a human colon carcinoma-secreted enzyme with pancreatic ribonuclease-like activity". Biochemistry. 25 (23): 7255–7264. doi:10.1021/bi00371a002. PMID 3467790.
- Seno M, Futami J, Tsushima Y, Akutagawa K, Kosaka M, Tada H, Yamada H (April 1995). "Molecular cloning and expression of human ribonuclease 4 cDNA". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression. 1261 (3): 424–426. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(95)00040-n. PMID 7742370.
- Zhou HM, Strydom DJ (October 1993). "The amino acid sequence of human ribonuclease 4, a highly conserved ribonuclease that cleaves specifically on the 3' side of uridine". European Journal of Biochemistry. 217 (1): 401–410. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18259.x. PMID 8223579.
- Egesten A, Dyer KD, Batten D, Domachowske JB, Rosenberg HF (October 1997). "Ribonucleases and host defense: identification, localization and gene expression in adherent monocytes in vitro". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 1358 (3): 255–260. doi:10.1016/S0167-4889(97)00081-5. PMID 9366257.
- Terzyan SS, Peracaula R, de Llorens R, Tsushima Y, Yamada H, Seno M, et al. (January 1999). "The three-dimensional structure of human RNase 4, unliganded and complexed with d(Up), reveals the basis for its uridine selectivity". Journal of Molecular Biology. 285 (1): 205–214. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2288. PMID 9878400.
- Xu XR, Huang J, Xu ZG, Qian BZ, Zhu ZD, Yan Q, et al. (December 2001). "Insight into hepatocellular carcinogenesis at transcriptome level by comparing gene expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma with those of corresponding noncancerous liver". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (26): 15089–15094. Bibcode:2001PNAS...9815089X. doi:10.1073/pnas.241522398. PMC 64988. PMID 11752456.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, et al. (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–1178. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.