| Rhabdopleurida Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
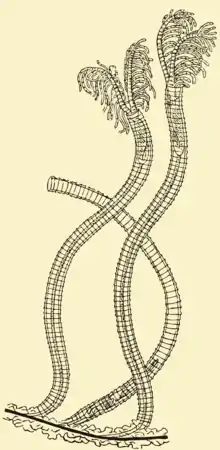 | |
| Rhabdopleura normani | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | Rhabdopleurida |
| Family: | Rhabdopleuridae Allman, 1869[1] |
| Genera | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Rhabdopleurida is one of three orders in the class Pterobranchia, which are small, worm-shaped animals, are the only surviving graptolites. Members belong to the hemichordates.[2][3] Species in this order are sessile, colonial, connected with a stolon, living in clear water and secrete tubes called tubarium. They have a single gonad, the gill slits are absent and the collar has two tentaculated arms.[4] Rhabdopleura is the best studied pterobranch in developmental biology.[5] Rhabdopleura is the only extant graptolite.[6][7]
Taxonomy
This small order is monotypic. It has only a single extant genus, containing four to six living species.
Order Rhabdopleurida Fowler, 1892
- Family Rhabdopleuridae Harmer, 1905
- Genus Rhabdopleura Allman, 1869
- Rhabdopleura annulata Norman, 1921 — Indo-Pacific region
- Rhabdopleura compacta Hincks, 1880 — Atlantic
- Rhabdopleura normani Allmann, 1869 — Atlantic and parts of the Pacific
- Rhabdopleura recondita Beli, Cameron and Piraino, 2018 — Mediterranean
- Rhabdopleura striata Schepotieff, 1909 — Pacific (Sri Lanka)
- Genus Rhabdopleura Allman, 1869
- Rhabdopleura grimaldi Julien, 1890
- Rhabdopleura manubialis Jullien & Calvet, 1903
Extinct species:
- †Rhabdopleura delmari Mortelmans 1955
- †Rhabdopleura graysoni Chapman, Durman & Rickards, 1995
- †Rhabdopleura hollandi Rickards, Chapman & Temple, 1984
- †Rhabdopleura kozlowskii Kulicki, 1969
- †Rhabdopleura obuti Durman & Sennikov, 1993
- †Rhabdopleura sinica Chapman, Durman & Rickards, 1995
- †Rhabdopleura vistulae Kozlowski, 1956
References
Wikispecies has information related to Rhabdopleurida.
- ↑ Maletz, Jörg (2014). "The classification of the Pterobranchia (Cephalodiscida and Graptolithina)". Bulletin of Geosciences. 89 (3): 477–540. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1465. ISSN 1214-1119.
- ↑ Animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu
- ↑ Eol.org
- ↑ Modern Text Book of Zoology: Invertebrates
- ↑ Sato, A; Bishop JDD; Holland PWH (2008). "Developmental biology of pterobranch hemichordates: history and perspectives". Genesis. 46 (11): 587–91. doi:10.1002/dvg.20395. PMID 18798243.
- ↑ Sato, A; Rickards, RB; Holland PWH (2008). "The origins of graptolites and other pterobranchs: a journey from 'Polyzoa'". Lethaia. 41 (4): 303–316. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.2008.00123.x.
- ↑ Mitchell, Charles E.; Michael J. Melchin; Chris B. Cameron; Jörg Maletz (2012). "Phylogenetic analysis reveals that Rhabdopleura is an extant graptolite". Lethaia. 46: 34–56. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.2012.00319.x. ISSN 0024-1164.
- Marinespecies.org
- ITIS.gov
- Hayward, P.J.; Ryland, J.S. (Ed.) (1990). The marine fauna of the British Isles and North-West Europe: 1. Introduction and protozoans to arthropods. Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK. ISBN 0-19-857356-1. 627 pp.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.