| Qiang | |
|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Qiang people |
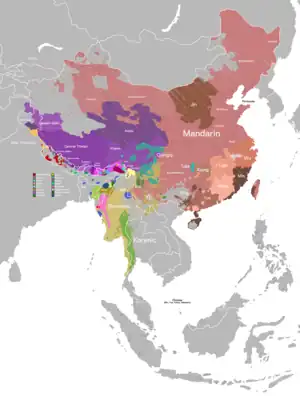
| Geographic distribution | Sichuan Province |
| Linguistic classification | Sino-Tibetan
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | qian1264 |
Qiang language, called Rma (尔玛) or Rme [1] by its speakers, is a Sino-Tibetan language cluster of the Qiangic branch spoken by approximately 140,000 people in north-central Sichuan Province, China.
Qiang consists of:
- Northern Qiang language (a non-tonal language)
- Southern Qiang language (a tonal language)
Writing system

In 2017, the Rma script, invented by Wei Jiuqiao (魏久乔), was officially finalized and has been accepted by many Qiang people as the first ever official writing system for their language.[2] There is no published information as to whether the script is compatible with both the Northern Qiang language and the Southern Qiang language or if it is only compatible with one of the languages. The writing system has also been given a preliminary proposal to encode it to the Universal Character Set of Unicode.[3]
Consonants
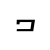 b /p/ |
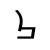 p /pʰ/ |
 bb /b/ |
 m /m/ |
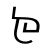 f /f/ |
 w /w/ |
 wf /v/ |
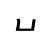 d /t/ |
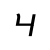 t /tʰ/ |
 dd /d/ |
 n /n/ |
 lh /ɬ/ |
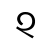 l /l/ |
 lr /lʴ/ |
 g /k/ |
 k /kʰ/ |
 gg /ɡ/ |
 ng /ŋ/ |
 h /h/ |
 hh /ɣ/ |
— |
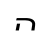 j /tɕ/ |
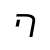 q /tɕʰ/ |
 jj /dʑ/ |
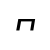 x /ɕ/ |
 xx /ʑ/ |
 y /j/ |
— |
 gv /q/ |
 kv /qʰ/ |
 v /χ/ |
 vh /ɦ/ |
 vv /ʁ/ |
— | — |
 z /ts/ |
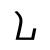 c /tsʰ/ |
 zz /dz/ |
 s /s/ |
 ss /z/ |
— | — |
 zh /tʂ/ |
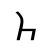 ch /tʂʰ/ |
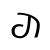 dh /dʐ/ |
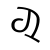 sh /ʂ/ |
 rr /ʐ/ |
— | — |
Vowels
 a /a/ |
 ae /æ/ |
 ea /e/ |
 u /u/ |
 e /ə/ |
 nn /◌̃/ |
 i /i/ |
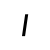 ü /y/ |
 o /o/ |
 /ʔ/ |
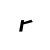 r /ʴ/ |
— |
Classification
Sims (2016)[4] gives the following classification for the "Qiangish" (or "Rma") languages, which include Northern Qiang and Southern Qiang. Individual dialects are highlighted in italics.
- Qiangish
- Northern Qiang ('upstream' *nu- innovation group)
- NW Heishui: Luhua 芦花镇
- Central Heishui
- Qinglang 晴朗乡
- Zhawo 扎窝乡
- Ciba 慈坝乡
- Shuangliusuo 双溜索乡
- uvular V's innovation group: Zhimulin 知木林乡, Hongyan 红岩乡, Mawo 麻窝乡
- SE Heishui: Luoduo 洛多乡, Longba 龙坝乡, Musu 木苏乡, Shidiaolou 石碉楼乡
- North Maoxian: Taiping 太平乡, Songpinggou 松坪沟乡
- South Songpan: Xiaoxing 小姓乡, Zhenjiangguan 镇江关乡, Zhenping 镇坪乡
- West Maoxian / South Heishui: Weigu 维古乡, Waboliangzi 瓦钵乡梁子, Se'ergu 色尔古镇, Ekou, Weicheng 维城乡, Ronghong, Chibusu, Qugu 曲谷乡 [basis for written language], Wadi 洼底乡, Baixi 白溪乡, Huilong 回龙乡, Sanlong 三龙乡
- Central Maoxian: Heihu 黑虎乡
- SE Maoxian (reflexive marker innovation): Goukou 沟口乡, Yonghe 永和乡
- Southern Qiang (perfective agreement suffixes innovation group)
Reconstruction
Sims (2017)[5] reconstructs tones for Proto-Rma (alternatively called Proto-Qiangish), proposing that the lack of tones in Northern Qiang is due to Tibetan influence. High tones and low tones are reconstructed for Proto-Rma, as well as for Proto-Prinmi.
References
- ↑ Wen, Maotao (2014). The Creation of the Qiang Ethnicity, its Relation to the Rme People and the Preservation of Rme Language (Master's thesis). Duke University.
- ↑ 传承羌语,支持尔玛文 Support the Rma Script of the Qiang (Rma) Language. Archived from the original on 2021-12-21. Retrieved 2019-10-28 – via Youtube.
- ↑ Chan, Eiso; Jiuqiao, Wei; Sims, Nathaniel (June 6, 2022). "Preliminary proposal to encode Rma script to UCS" (PDF). Unicode.org. International Organization for Standardization. Retrieved November 13, 2022.
- ↑ Sims, Nathaniel (2016). "Towards a More Comprehensive Understanding of Qiang Dialectology" (PDF). Language and Linguistics. 17 (3): 351–381. doi:10.1177/1606822X15586685.
- ↑ Sims, Nathaniel (2017). The Suprasegmental Phonology of Proto-Rma (Qiang) in Comparative Perspective. Presented at the 50th International Conference on Sino-Tibetan Languages and Linguistics, Beijing, November 26, 2017.
Bibliography
- Bradley, David (1997). "Tibeto-Burman Languages and Classification" (PDF). In Bradley, D. (ed.). Papers in South East Asian Linguistics No. 14: Tibeto-Burman Languages of the Himalayas. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. pp. 1–72. ISBN 0-85883-456-1.
- Evans, Jonathan P. (2006). "Vowel Quality in Hongyan Qiang" (PDF). Language and Linguistics. 7 (4): 731–754.
- LaPolla, Randy J. (2003). A Grammar of Qiang: With Annotated Texts and Glossary. with Chenglong Huang. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. doi:10.1515/9783110197273. ISBN 3-11-017829-X.