| Polydesmidae | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Polydesmus collaris in central Italy | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | Polydesmidae Leach, 1815 |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
Polydesmidae is a family of millipedes in the order Polydesmida.[1] These millipedes range from 4 mm to 30 mm in length.[2] This family includes species notable for featuring sexual dimorphism in segment number: Adult females in the genus Perapolydesmus have the usual 20 segments (counting the collum as the first segment and the telson as the last), but the adult males have only 19.[3]
Genera
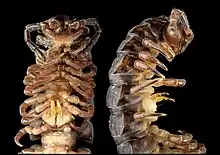
Male Nipponesmus shirinensis from Taiwan in ventral and lateral view
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Polydesmidae.
- Antrochodus
- Archipolydesmus
- Basicentrus
- Bhutanodesmus
- Bidentogon
- Bosniodesmus
- Bosporodesmus
- Brachydesmus
- Brembosoma
- Calianotus
- Chromobrachydesmus
- Cookia
- Cretodesmus
- Dixidesmus
- Epanerchodus
- Eumastigonodesmus
- Goniodesmus
- Haplobrachidesmus
- Haplocookia
- Heterocookia
- Himalodesmus
- Hispaniodesmus
- Huzichodus
- Jaxartes
- Kirgisdesmus
- Leptobrachydesmus
- Lophobrachydesmus
- Mastigonodesmus
- Mastuchus
- Merioceratium
- Niponchodus
- Nipponesmus
- Nomarchus
- Pacidesmus
- Peltogonopus
- Perapolydesmus
- Polydesmus
- Prionomatis
- Propolydesmus
- Pseudopolydesmus
- Retrorsia
- Riuerchodus
- Sardodesmus
- Schedoleiodesmus
- Schizobrachydesmus
- Schizomeritius
- Schizoturanius
- Scytonotus
- Serradium
- Spanobrachium
- Speodesmus
- Stylobrachydesmus
- Telopoditius
- Tolosanius
- Trachynotus
- Troglobrachydesmus
- Turanodesmus
- Uniramidesmus
- Usbekodesmus
- Utadesmus
References
- ↑ "Polydesmidae". Catalogue of Life. 29 October 2014. Retrieved 7 November 2014.
- ↑ Enghoff, Henrik; Golovatch, Sergei; Short, Megan; Stoev, Pavel; Wesener, Thomas (2015). "Diplopoda — Taxanomic Overview". In Minelli, Alessandro (ed.). The Myriapoda. Vol. 2. Leiden, The Netherlands: Koninklijke Brill NV. p. 402. ISBN 978-90-04-15612-8.
- ↑ Enghoff, Henrik; Dohle, Wolfgang; Blower, J. Gordon (1993). "Anamorphosis in Millipedes (Diplopoda) — The Present State of Knowledge with Some Developmental and Phylogenetic Considerations". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 109 (2): 103–234. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1993.tb00305.x.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.