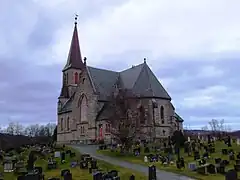| Melhus Church | |
|---|---|
| Melhus kirke | |
| Gauldal Cathedral (Gauldalskatedralen) | |
 View of the church | |
| 63°16′25″N 10°17′33″E / 63.273655036°N 10.2924647927°E | |
| Location | Melhus, Trøndelag |
| Country | Norway |
| Denomination | Church of Norway |
| Churchmanship | Evangelical Lutheran |
| Website | http://kirken.no/melhus |
| History | |
| Status | Parish church |
| Founded | 12th century |
| Consecrated | 10 Nov 1892 |
| Architecture | |
| Functional status | Active |
| Architect(s) | Carl Julius Bergstrøm |
| Architectural type | Cruciform |
| Style | Neo-Gothic |
| Completed | 1892 |
| Specifications | |
| Capacity | 500 |
| Materials | Stone |
| Administration | |
| Diocese | Nidaros bispedømme |
| Deanery | Gauldal prosti |
| Parish | Melhus |
| Type | Church |
| Status | Listed |
| ID | 84936 |
Melhus Church (Norwegian: Melhus kirke), also known as "the Gauldal Cathedral", is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Melhus municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. It is located in the village of Storsand, about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) south of the village of Melhus. It is the church for the Melhus parish which is part of the Gauldal prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Nidaros. The gray, stone church was built in a cruciform design in 1892 using plans drawn up by the architect Carl Julius Bergstrøm. The church seats about 500 people. The churchyard contains a cemetery.[1][2]
The church contains a controversial oil painting, which has been thought to be a portrait of Petter Dass.
History


The earliest existing historical records of the church date back to the year 1533, but the church was built much earlier. The first church in Melhus was a medieval stone church that was constructed in stages from about 1150 to 1190. Construction probably began shortly before the year 1150, and the chancel was probably completed around 1160. Based on stylistic features, the nave should have been completed around the year 1190. The church was originally dedicated to St. Andreas. It had a rectangular nave and a narrower, rectangular chancel with a lower roof line. There was a tall tower on the west end of the roof of the nave. There was also a small wooden entry porch on the west end of the church.[3][4]
In 1589, there were five churches in the Melhus prestegjeld (more or less equivalent to a parish), and Melhus Church was the main one. The annex chapels were scattered about the parish. Two of the five were located in Leinstrand and Flå and the remaining two churches were in Hølonda.[3][4]
In 1814, this church served as an election church (Norwegian: valgkirke).[5] Together with more than 300 other parish churches across Norway, it was a polling station for elections to the 1814 Norwegian Constituent Assembly which wrote the Constitution of Norway. This was Norway's first national elections. Each church parish was a constituency that elected people called "electors" who later met together in each county to elect the representatives for the assembly that was to meet in Eidsvoll later that year.[5][6]
In 1889, a Royal Decree was issued which ordered that the old medieval Melhus Church be demolished.[7] During this demolition in 1890, a perfectly preserved hatchet dating from about 1100 was discovered in a wall of the medieval church. This axe was identified as the country's only preserved tool for cutting stone (Norwegian: "steinhuggerøks") from that period, and it is now located in the Norwegian Museum of Science and Technology.[8] The new church was designed by Carl Julius Bergstrøm. The new building was consecrate on 10 November 1892. It is a neo-Gothic cruciform church in stone with around 500 seats.[4]
Although the old church was torn down, several architectural elements of the medieval building were saved and incorporated into the new building. Much woodwork from the old church was included in the newer one.[4][9] The old portal was also reused in the new church. Apparently, a few artifacts from the old church were not moved to the new church, and instead ended up in other places. When Gerhard Schøning visited the old medieval church he noted this: "At the southern side of the entrance to the choir, there is an epitaph that Karen and Anders Helkands have erected to their parents and children". When the medieval church was demolished in 1890, the epitaph was no longer there. Few people knew that the epitaph was hidden on Søndre Melhuus farm.[10]
The newer church building has been carefully maintained for over one hundred years; it has had several renovations.[11] In 1999, Medieval runic inscriptions were discovered on the medieval portal. These inscriptions were professionally examined in 2001.[12]
Media gallery
"Petter Dass" portrait

Melhus Church houses a collection of painted portraits, primarily of clergymen. The most well-known painting is one that has traditionally been considered to be a portrait of Petter Dass, a 17th-century Norwegian poet and hymn writer. The painting was thought to be the only existing portrait of the poet.
A few years ago, after some nearby churches were set on fire, there was a debate as to whether the portrait was secure enough.[13] Some historians, however, believe that the subject of this famous portrait is not Petter Dass at all, but the clergyman Oluf Mentzen Darre. For example, Kåre Hansen is absolutely certain that this portrait has nothing to do with Petter Dass.[14] (Kåre Hansen wrote a book about the poet, his power, and the myths surrounding him. In this book the author analyzed and investigated the painting, and came to the conclusion that the man depicted in this famous portrait is not Petter Dass.)
Subsequently the Petter Dass Museum became involved in the controversy. S. Gustavsen found it strange that the portrait is still shown on the Petter Dass Museum web site, commenting that to consider this painting to be a portrait of Petter Dass is the same as to still "believe that the earth is flat and the sun orbits the earth." The museum itself cannot prove whether the portrait is of Petter Dass or not, and so they feature the debate on their web site.[15]
See also
References
- ↑ "Melhus kirke". Kirkesøk: Kirkebyggdatabasen. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- ↑ "Oversikt over Nåværende Kirker" (in Norwegian). KirkeKonsulenten.no. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- 1 2 "Melhus kirkested" (in Norwegian). Norwegian Directorate for Cultural Heritage. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 "Melhus kirke". Norges-Kirker.no (in Norwegian). Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- 1 2 "Valgkirkene". LokalHistorieWiki.no (in Norwegian). Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ↑ "Om valgene". Valgene i 1814 (in Norwegian). Arkivverket. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ↑ "Genealogical resources in Norway" (in Norwegian). www.disnorge.no. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ Andreassen, Thorleif (16 October 2006). "På skattejakt". Oslopuls; Aftenposten (in Norwegian). oslopuls.aftenposten.no. Retrieved 31 May 2009.
- ↑ Norwegian Kgl. Utenriksdepartement. Presse- og kulturavdelingen. Norway handbook.
- ↑ "Epitafium i Melhus kirke" (in Norwegian). Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ "Melhus Kirke" (in Norwegian). Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ Knirk, James E. (2000). "Arbeidet ved Runearkivet, Oslo". Nytt om runer (in Norwegian). Runic Archives, Museum of Cultural History at the University of Oslo. 15: 16–20. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ Vårvik, Anette (20 March 2009). ""Petter Dass" henger usikret i Melhus kirke". Trønderbladet (in Norwegian). www.tronderbladet.no. Archived from the original on 8 June 2009. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ Stautland, Helge Johan (20 December 2004). "Dette er ikke Petter Dass". Kristelig Pressekontor (in Norwegian). Archived from the original on 8 June 2009. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ↑ Hansen, Ivar Roger. "Petter Dass-portrettet i Melhus kirke — myte og mysterium" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Petter Dass Museum. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 June 2009. Retrieved 29 May 2009.