 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1′-(1,3-Phenylene)di(methanamine) | |
| Other names
m-Xylene-α,α'-diamine 1,3-Benzenedimethanamine MXDA m-Phenylenebis(methylamine) 1,3-Bis(aminomethyl)benzene 1,3-Phenylenedimethanamine 1,3-Xylylenediamine m-Xylylenediamine 1,3-Xylenediamine m-Xylenediamine 1,3-Bis(aminomethyl)benzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.575 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2735 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.198 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Amine[1] |
| Density | 1.032 g/cm3 (20°C)[2] |
| Melting point | 14 °C; 58 °F; 288 K[2] |
| Boiling point | 247 °C; 477 °F; 520 K[2] |
| Miscible (20°C)[2] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.03 mmHg (25°C)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 117 °C; 243 °F; 390 K[2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
700 ppm/1 hour (rat, inhalation)[3] 930 mg/kg (rat, oral)[3] 2 g/kg (rabbit, skin)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
REL (Recommended) |
C 0.1 mg/m3 [skin][2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
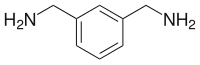
m-Xylylenediamine is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CH2NH2)2. A colorless oily liquid, it is produced by hydrogenation of isophthalonitrile.[4]
Uses and reactions
m-Xylylenediamine (MXDA) is used in a variety of industrial applications including amine based curing agents for epoxy resins[5] which may then be formulated into coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers.[1]
m-Xylylenediamine undergoes to Sommelet reaction to give isophthalaldehyde.[6]
Hazards
Exposure to m-xylylenediamine may occur by inhalation, skin contact, eye exposure, or ingestion. It can cause chemical burns, tissue damage, delayed pulmonary edema, shock, and skin sensitization. Symptoms of inhalation include a burning sensation in the respiratory tract, cough, sore throat, labored breathing, and dyspnea (shortness of breath). It is also flammable and produces toxic fumes when burned. m-Xylylenediamine reacts with acids, acid chlorides, and acid anhydrides.[1][7]
References
- 1 2 3 "M-Xylylenediamine". PubChem.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0671". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 3 "RTECS PF88DF10". NIOSH.
- ↑ Pollak, Peter; Romeder, Gérard; Hagedorn, Ferdinand; Gelbke, Heinz-Peter (2000). "Nitriles". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_363. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ "MXDA│Epoxy Resin Curing Agents│MITSUBISHI GAS CHEMICAL CO.,INC". www.aromaticchemicals.com. Retrieved 2018-08-19.
- ↑ Ackerman, J. H.; Surrey, A. R. (1967). "Isophthalaldehyde". Organic Syntheses. 47: 76. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.047.0076.
- ↑ "1,3-BIS(AMINOMETHYL)BENZENE". International Chemical Safety Cards.