| Trolleybuses in Lviv | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Owner | Lviv city council |
| Locale | Lviv, Ukraine |
| Transit type | Trolleybus |
| Number of lines | 10 (11) |
| Website | www.let.org.ua |
| Operation | |
| Began operation | 27 November 1952 |
| Operator(s) | Lvivelectrotrans |
| Number of vehicles | 72 of 115 |
| Technical | |
| System length | 136 km (2022) |
| Electrification | 600V DC |
| Average speed | 13 km/h |
The Lviv trolleybus (Ukrainian: Львівський тролейбус, translit.: L’vivs’kyi troleibus) is a trolleybus system in Lviv, Ukraine. The trolleybus network is operated by Lvivelectrotrans - a municipal enterprise, that is the operator of trams and trolleybuses in the city. LET is owned by the Lviv city council. The length of the contact network is 136 km (01.2023), and the length of the route network is 169 km (01.2021).[1] As of 2021, 24,678,300 paid passengers (including 2,785,623 students) used trams and trolleybuses. In 2021, trolleybuses performed 3.29 million kilometers of transportation work (vehicle-km).
History
The first idea of introducing trolleybus traffic in Lviv dates back to April 1909. It is connected with the construction of a tram line to the High Castle. In cause of the complex topography of the route of the future line, the head of the Lviv Tramway, Józef Tomicki, proposed to build a "railless electric omnibus" line instead of a tram line, that is, a trolleybus.
On November 27, 1952, regular trolleybus traffic on route No. 1 (Railway Station — Mickiewicz Square) was opened. At that time, the rolling stock consisted of five MTB-82D vehicles that ran on the line at intervals of every 20 minutes.
In 1953, trolleybus route No. 2 (Mickievicz Square — Bohdanivka) was opened, with a length of 3.3 km. In 1954, this route was extended to Sknyliv railway station. In the same year, a line was laid from Mickiewicz Square along Shota Rustaveli and Stryiska to modern Hasheka Street (stop "7's km"), in three years - from Mickiewicz Square to Novyi Lviv, and in another year - to Holosko.
In June 1963, the first LAZ 695T trolleybus, assembled at the Lviv Bus Plant, on the basis of a bus body with electrical equipment from decommissioned old MTB-82D trolleybuses, drove onto the streets of Lviv.
On March 1, 2019, the Lviv City Council signed.[2] a guarantee agreement with the EBRD regarding the purchase of 50 new trolleybuses manufactured by "Electron-trans" and the partial renewal of the trolleybus depot.[3]
On November 4, 2019, the first 10 Electron T19102 trolleybuses were presented at the trolleybus depot. The new trolleybuses have video surveillance cameras, USB ports for recharging phones and gadgets. Trolleybuses are equipped with two air conditioners for the interior and for the driver's cabin.
In 2020-2021, LET and the authorities of Lviv intended to purchase 70-100 battery trolleybuses (with in-motion charging) with IFC loan funds, but city council members did not support[4] this decision, citing too high interest rates. This project is now suspended.
Lviv is the first city in Ukraine that started to use modern trolleybus catenary and spare parts (forks and crossings) of Elektroline[5] company (Czech Republic). It was installed in 2021 during the reconstruction of the trolleybus catenary network on Kulparkivska[6] street. The project was implemented with EBRD loan funds.
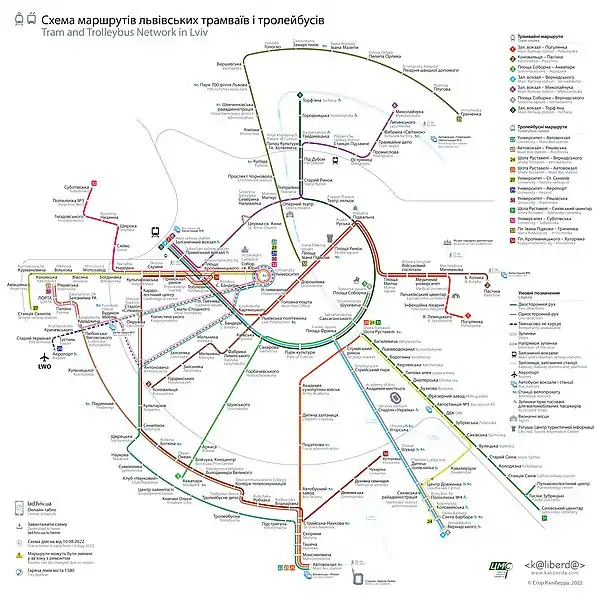
List of existing routes
As of 08.2022 Lviv trolleybus system consists of 11 routes:
| No. | Departure point | Point of arrival | Vehicles in service | Intervals (min) | Route length (km) | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weekday | Weekend | Weekday | Weekend | Full lap | ||||
| 22 | Lviv University | Avtovokzal (Main bus station) | 10 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 10,4 | |
| 23 | Riashivska str. | Avtovokzal (Main bus station) | 7 | 6 | 10 | 12 | 8,6 | |
| 24 | Shota Rustaveli str. | Santa Barbara | 8 | 6 | 10 | 12 | 8,4 | |
| 25 | Shota Rustaveli str. | Avtovokzal (Main bus station) | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 6,2 | |
| 27 | Lviv University | Sknyliv train station | 1 | 0 | 50 | - | 7,4 | |
| 29 | Lviv University | Lviv Airport | - | - | 8 | 8 | Temporarily out of service | |
| 30 | Lviv University | Riashivska str. | 8 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 6,4 | |
| 31 | Shota Rustaveli str. | Pulmonology Center | 3 | 2 | 40 | 60 | 11,7 | |
| 32 | Lviv University | Subotivska str. | 8 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 6,6 | |
| 33 | Ivan Pidkova square | Hrinchenka str. | 10 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 6,1 | |
| 38 | Kropyvnytskoho square | Khutorivka str. | 8 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 9,5 | |
| 11 | Total | 70 | 55 | 81,3 | ||||
From July 1, 2019, a new numbering[7] of trolleybus lines (routes) was introduced to avoid duplication in the numbering of different types of transport (especially with trams). Each route, regardless of whether it is operated by buses, trams or trolleybuses, has its own unique number, as the first stage of the transition to uniform numbering of routes for all types of public transport. Numbers 1 to 19 are reserved for tram routes, numbers 20 to 39 are reserved for trolleybus routes. For decades before this change tram and trolleybus routes in Lviv had the same numbering of lines (2 and 2, 3 and 3, etc.). The problem still exists with bus routes that also starts from No. 1A to 63, and duplicate all tram and trolleybus route numbers.
.png.webp)
Rolling stock
Rolling stock of trolleybuses in operation as of August 2022:
| Brand | Model | Year of procurement | Number of vehicles | Low floor | Air conditioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skoda | 14Tr | 1988-2013 | 21 | No | No |
| LAZ | E183 | 2006, 2008 | 7 | Yes | No |
| Electron | T19101 | 2014, 2016 | 2 | Yes | No |
| Electron | T19102 | 2015, 2016, 2019 | 58 | Yes | Yes (50) |
| Electron | E19 | 2015 | 1 | ||
| 4 | Total | 89 | 68 LF | 50 with AC | |
Other brands and models of trolleybuses (of total 115) are withdrawn from operation.
70 trolleybuses were in operation[8] on the routes (morning rush hour) on August 10, 2022.
List of rolling stock over past decades
| Years | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of vehicles | 243 | 119 | 85 | 122 |
| Prevailing models | Skoda 9Tr, | Skoda 14Tr,
LAZ 52522 |
Skoda 14Tr,
LAZ E183, LAZ 52522 |
Skoda 14Tr, |
| Network length, km | 122 | 117 | 117 | 132 |
Fares
The fare in Lviv city electric transport (as well as in urban buses) is established on the basis of the decision of the executive committee of the Lviv City Council.
Passengers can pay the fare by buying a paper one-time ticket for cash at kiosks or from the driver. Another option is to buy a monthly pass at the kiosks. Passes are divided into types: joint tram and trolleybus pass, and separate tram or trolleybus.
Since 2017, electronic fare payment has been introduced in trams and trolleybuses. Passengers can pay using smartphone by scanning a QR code or via bluetooth. The service is provided by private companies, in particular, the country's largest bank PrivatBank through its Privat24[9] mobile application.
Preferential categories of passengers, pensioners, children under 7 years of age, as well as school students are exempt from paying for travel during the academic year. A discount of 50% of the fare is provided for university students.
Coverage of expenses (cost recovery) by passengers (who are obliged to pay the fare) of Lviveleсtrotrans, including users of trams and trolleybuses, varies between 25 and 33%[10] in the last 10 years. The rest of the sum is compensated from the city budget for the transportation of privileged categories of passengers. However, there is no system for clearing these passengers, neither at the local nor at the national level. From time to time, a sample count is made, and they are submitted to the state statistics service of the Lviv region. On the basis of a special formula, the ratio of the number of privileged passengers relative to paid passengers is derived. Based on this coefficient, the amount of necessary compensation to the carrier is calculated. Such a system is extremely imperfect. Since 1993, by a resolution of the Government of Ukraine from May 17, 1993 No. 354,[11] free travel in urban electric transport has been introduced for pensioners. According to the Constitution of Ukraine, these expenses should be compensated from the state budget, but in all years the amount of necessary funds did not exceed 60% of the need. Since 2016, the Government has stopped[12] providing such compensation, and the provision of it has completely switched to local budgets.
Images
 Škoda 14Tr on route 13 (now route 33)
Škoda 14Tr on route 13 (now route 33) Škoda 14Tr on route 24
Škoda 14Tr on route 24 LAZ 52522 on route 9 (now route 29)
LAZ 52522 on route 9 (now route 29) LAZ 52522 on route 11 (now route 31)
LAZ 52522 on route 11 (now route 31) LAZ E183
LAZ E183 LAZ E183 #106 on route 24
LAZ E183 #106 on route 24 LAZ E183 #109 on route 24
LAZ E183 #109 on route 24 Electron T19101
Electron T19101 Electron T19102 on route 3 (now route 23)
Electron T19102 on route 3 (now route 23)
References
- ↑ "Public transport in Lviv. History and statistics 2022 » TUMI". TUMI. Retrieved 2023-10-06.
- ↑ "EBRD finances new trolleybuses in Lviv". www.ebrd.com. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
- ↑ "RECONSTRUCTION OF THE TROLLEYBUS DEPOT "BE"!". Communal Enterprise Lvivelectrotrans. June 22, 2022.
- ↑ "Депутати не підтримали закупівлю 100 тролейбусів в українського виробника — Львівська міська рада". city-adm.lviv.ua (in Ukrainian). 2021-07-08. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
- ↑ "Elektroline Inc". www.elektroline.cz. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
- ↑ Portal, On Kulparkivska Street, the reconstruction of the trolleybus line at the EBRD expense is ongoing | Lvivelectrotrans-City Transport (2022-08-30). "On Kulparkivska Street, the reconstruction of the trolleybus line at the EBRD expense is ongoing | Lvivelectrotrans - City Transport Portal". Lvivelectrotrans. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "З 1 липня 2019 року змінюється нумерація маршрутів міських тролейбусів — Львівська міська рада". city-adm.lviv.ua (in Ukrainian). 2019-06-11. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
- ↑ "Статистика транспорту Львова". kstat.pp.ua. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
- ↑ "100,000th transport e-ticket bought in Lviv". en.PrivatBank.ua. June 8, 2017.
- ↑ "Рейтингові показники ефективності роботи підприємств – корпорація "Укрелектротранс"". www.korpmet.org.ua. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
- ↑ "Про безплатний проїзд пенсіонерів на транспорті загального користування". Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 2022-08-30.
- ↑ "Мери обласних центрів заявляють про те, що уряд змушує їх підняти ціни на проїзд". LB.ua. Retrieved 2022-08-30.
Links
- Lvivelectrotrans official web-site.
- Interactive map of Lviv public transport routes (lines).
- Communal transport operators of Lviv reported on their work in 2020.
- The city plans to purchase 92 new buses and 60 trolleybuses for hosting UEFA EURO 2012[1]
- Lviv E-Buses - IFC Disclosure.
- Lviv continues to renovate trolleybus network.
- Public transport in Lviv. History and statistics 2022. Transformative Urban Mobility Initiative (2022)
- ↑ Interview of the mayor of Lviv Andriy Sadovyi on February 24, 2011.
