Loxstedt
Loxstedt (German) Lox (Low Saxon) | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Loxstedt within Cuxhaven district 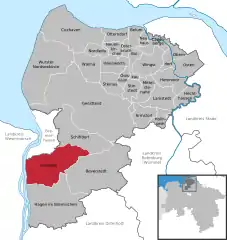 | |
 Loxstedt 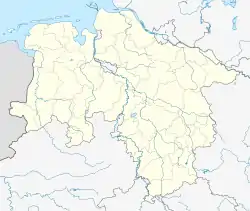 Loxstedt | |
| Coordinates: 53°28′N 08°39′E / 53.467°N 8.650°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Lower Saxony |
| District | Cuxhaven |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2021–26) | Detlef Wellbrock[1] (Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 141.24 km2 (54.53 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1 m (3 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 16,441 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 27612 |
| Dialling codes | 04703, 0471, 04740, 04744 |
| Vehicle registration | CUX |
| Website | www.loxstedt.de |
Loxstedt (in High German, in Low Saxon: Lox) is a municipality in the district of Cuxhaven in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated south of Bremerhaven.
History
Lacstidi (literally in lake stead), first mentioned in 1059, belonged to the Duchy of Saxony. At the carve-up of Saxony it became a part of the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen, newly raised to imperial immediacy in 1180. In the mid-16th century the inhabitants adopted Lutheranism. During the Leaguist occupation under Tilly (1628–1630), they suffered from attempts at re-Catholicisation.
In 1648 the prince-archbishopric was transformed into the Duchy of Bremen, which was first ruled in personal union by the Swedish – interrupted by a Danish occupation (1712–1715) – and from 1715 on by the Hanoverian Crown. In 1807 the ephemeric Kingdom of Westphalia annexed the duchy, before France annexed it in 1810. In 1813 the duchy was restored to the Electorate of Hanover, which – after its upgrade to the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814 – incorporated the duchy in a real union and the ducal territory, including Loxstedt, became part of the Stade Region, established in 1823.
In 1974 Loxstedt incorporated a number of smaller municipalities in its environs, among them Büttel, Dedesdorf, Eidewarden, Maihausen, Overwarfe, Ueterlande, and Wiemsdorf, which all had never been part of the Hanoveran state but had been part of the neighbouring state of Oldenburg, thus having a different history.
Villages in the municipality

The municipality consists of 21 villages, of which several include smaller settlements (number of inhabitants as of 28 February 2004) :
|
|
|
Transportation
Loxstedt has three exits on the Bundesautobahn 27. The Bundesstraße 437, connecting the Stotel A27 exit to the Weser tunnel, has been constructed so that it can be easily upgraded to an autobahn. The Bundesautobahn 22, the so-called Küstenautobahn, which currently is in planning stage, will replace the B 437 in the future. The Bundesstraße 71 runs through Bexhövede and Stinstedt, connecting the municipality to Bremerhaven and Beverstedt.
Public transport is mostly carried by buses within the public transport association Bremen/Lower Saxony (VBN). A minicab scheme, carried out by BremerhavenBus, offers hourly connections to Bremerhaven and to Loxstedt railway station, which is on the Bremen–Bremerhaven line and has been served since December 2010 by line RS 2 of the Bremen S-Bahn, running hourly between Bremerhaven-Lehe and Twistringen.[3]

Twin towns
Loxstedt's twin towns include:
 – Schwaan (Germany), since 1989
– Schwaan (Germany), since 1989
References
- ↑ "Direktwahlen in Niedersachsen vom 12. September 2021" (PDF). Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen. 13 October 2021.
- ↑ "LSN-Online Regionaldatenbank, Tabelle A100001G: Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes, Stand 31. Dezember 2021" (in German). Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen.
- ↑ Anruf-Sammeltaxi press release Archived 21 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine
External links
- Official website (in German)
- Local merchantmen organisation (in German)