| Lost Creek Lake | |
|---|---|
 The lake behind William L. Jess Dam | |
 Lost Creek Lake  Lost Creek Lake | |
| Location | Jackson County, Oregon |
| Coordinates | 42°40′59″N 122°39′17″W / 42.68306°N 122.65472°W |
| Type | reservoir |
| Primary inflows | Rogue River |
| Primary outflows | Rogue River |
| Catchment area | 674 sq mi (1,750 km2) |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 10 mi (16 km) |
| Surface area | 3,430 acres (13.9 km2) (full pool) |
| Water volume | 315,000 acre⋅ft (389×106 m3) |
| Shore length1 | 30 mi (48 km) |
| Surface elevation | 1,751 to 1,872 ft (534 to 571 m)[1] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lost Creek Lake is a reservoir located on the Rogue River in Jackson County, Oregon, United States. The lake is impounded by William L. Jess Dam which was constructed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers in 1977 for flood control and fisheries enhancement. The lake and dam were the first completed elements of the multi-purpose Rogue River Basin Project, consisting of Lost Creek Lake, Applegate Lake and the Elk Creek project. The lake is located approximately 27 miles (43 km) (straight line) northeast of Medford.[1]
History
Construction of Lost Creek Dam began in 1972 and was completed in 1977. In 1996, the Congress renamed Lost Creek Dam, along with the adjoining intake structure, in honor of William L. Jess, one of the founders of the Rogue Basin Association, which was established in 1955. Jess was a strong advocate for the construction and multiple use of the impounded waters.

The primary purpose of the dam is flood control and is operated in conjunction with Applegate Dam to regulate water flows down the river as well as to impound water for summer use. The dam is an earthfill structure with a gated spillway and contains two hydroelectric generating units with a total capacity of 49 megawatts. The hydroelectric plant has a rated flow capacity of 2,600 cubic feet per second (74 m3/s).[1] The technologically advanced and unusual intake tower regulates water temperature by combining lake water from different depths in a mixing chamber before releasing it downstream. This serves to cool the normally warm summer water of the Rogue River, which improves conditions for fish migration and survival. The dam is 3,750 feet (1,140 m) long, 327 feet (100 m) high, with the top of the dam at an elevation of 1,882 feet (574 m) above mean sea level (MSL).The river below the dam is a popular area for easy rafting and tubing in the summer when the water is relatively warm. Joseph H. Stewart State Recreation Area is located along the southern shore of the lake. Casey State Park is located on the Rogue River below the dam.
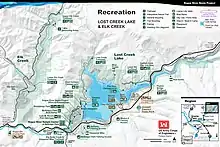
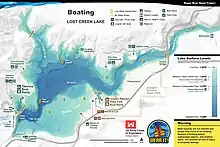
Recreation
Lost Creek Lake is located 37 miles northeast of Medford, OR, off of highway 62. The lake has been a popular recreational site for southern Oregonians since its construction in the 70's. Outdoor enthusiasts of all kinds find amusement in the lake and on its surrounding land. With average rainfall the lake is around 3,430 acres and 280 feet in depth, providing plenty of area for summertime watersports such as boating, skiing, wake boarding, tubing, and jet-skiing. The Lost Creek Lake is a popular year round spot for trout and small mouth bass fishing. A 20-mile trail along the lakeshore can be used by hikers or mountain bikers. This trail runs through the Joseph H. Stewart State Park, which is a popular camping destination, offering 150+ sites with electrical hookups for RVs and Campers, as well as 50 tent sites with water. Public bathrooms and showers are also available in the campground, as well as a RV dump station.[2] Two boat landings are located off of the lakes shores, one of which is part of the Joseph H. Stewart State Park. The state park boat landing is located next to the Lost Creek Marina. In addition to boat storage and rentals, the marina features on water fueling, a bait and tackle shop, and a small store and restaurant.[3]
Applicable fishing regulations and information can be found at the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife website.
Photo gallery
 Storm clouds build near Crater Lake in the distance, and reflect in the waters of Lost Creek Lake, Oregon.
Storm clouds build near Crater Lake in the distance, and reflect in the waters of Lost Creek Lake, Oregon. Rafters start their float down the Rogue River from McGregor Park boat ramp.
Rafters start their float down the Rogue River from McGregor Park boat ramp. North Shore Lost Creek Lake.
North Shore Lost Creek Lake. Lost Creek Lake in fall.
Lost Creek Lake in fall. Stewart State Park marina.
Stewart State Park marina. McGregor Park nature trails.
McGregor Park nature trails. Walkway on Lost Creek Lake.
Walkway on Lost Creek Lake. Rogue Nature Center at McGregor Park in fall.
Rogue Nature Center at McGregor Park in fall. Takelma Day Use Area picnic shelters.
Takelma Day Use Area picnic shelters. The Rogue River bends around McGregor Park.
The Rogue River bends around McGregor Park. Feeding fish at the Cole M. Rivers fish hatchery.
Feeding fish at the Cole M. Rivers fish hatchery. Rogue River Trail and lake.
Rogue River Trail and lake. Intake tower at low water.
Intake tower at low water..jpg.webp) Fall fly fishing downstream of Lost Creek Lake
Fall fly fishing downstream of Lost Creek Lake.jpg.webp) A fly fisherman downstream of Lost Creek Lake
A fly fisherman downstream of Lost Creek Lake Spring at the Lost Creek Lake powerhouse.
Spring at the Lost Creek Lake powerhouse. Snow falls at the Lost Creek powerhouse on the Rogue River.
Snow falls at the Lost Creek powerhouse on the Rogue River.
Fish hatchery
Cole Rivers Hatchery is located on the Rogue River, 30 miles northeast of Medford, Oregon, on Highway 62, about 1⁄2 mile downstream of Lost Creek Dam. The site is at an elevation of 1,545 feet above sea level at 42°39′49″N 122°41′06″W / 42.6635°N 122.6849°W. The hatchery land covers 58 acres (23 ha).
The US Army Corps of Engineers constructed the hatchery in 1973 to mitigate impacts to salmon spawning and rearing areas blocked by the construction of the Lost Creek, Applegate, and Elk Creek Dams (the latter was never constructed). The Hatchery was named in honor of Cole M. Rivers, a biologist on the Rogue River for 20 years. The facility is used for adult collection, spawning, egg incubation and rearing of spring chinook, coho, summer steelhead, and winter steelhead, and egg incubation and rearing of fall chinook and rainbow trout.[4]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Lost Creek Dam and Lake". www.nwd-wc.usace.army.mil. Columbia Basin Water Management Division. 2009-05-31. Archived from the original on 2009-05-12. Retrieved 2009-05-10.
- ↑ "Oregon State Parks". oregonstateparks.org.
- ↑ "Home". lost-creek-marina.com. Archived from the original on 2015-03-27. Retrieved 2015-03-23.
- ↑ "Cole Rivers Hatchery - Program Management Plan 2018" (PDF). www.dfw.state.or.us. Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 4, 2010. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
External links
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Corps Lake Gateway – Lost Creek Lake
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Lost Creek Lake
- Recreation.gov: Lost Creek Lake
- Rogue-Umpqua Scenic Byway
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Lost Creek Lake
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Lost Creek Dam and Lake Water Management data
- Bonneville Power Administration: Dams photo gallery