 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
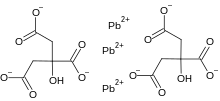
| IUPAC name
2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate; lead(2+); trihydrate | |
| Other names
Lead citrate trihydrate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.402 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10O14Pb3 | |
| Molar mass | 999.8 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White odorless powder or crystals |
| Density | 4.63 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 309.6 °C (589.3 °F; 582.8 K) |
| Soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H302, H332, H360, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P301+P312, P304+P312, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P314, P330, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Lead citrate is a compound of lead and citrate that is primarily used as an enhancer for heavy metal staining in electron microscopy.[2] This salt binds to osmium and uranyl acetate and enhances contrast in many cellular structures. Lead citrate is highly reactive with carbon dioxide.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.