
An Indian bead in Indiana gravel.
Indian bead is a colloquial American term for a fossilized stem segment of a columnal crinoid, a marine echinoderm of the class Crinoidea. The fossils, generally a centimeter or less in diameter, tend to be cylindrical with a small hole (either open or filled) along the axis and can resemble unstrung beads. The fossils are abundant in certain areas, including parts of the American Midwest where they are present in gravel. They are sometimes also referred to as "Indian money".[1]
The same item is known as Bonifatius pfennige in German ("Saint Boniface pennies") and St Cuthbert's beads in the United Kingdom.
Gallery
 Rare fossil of a crinoid completely intact
Rare fossil of a crinoid completely intact Calcified in limestone
Calcified in limestone Fossils from the Jurassic period
Fossils from the Jurassic period Intact stem of a crinoid, still embedded
Intact stem of a crinoid, still embedded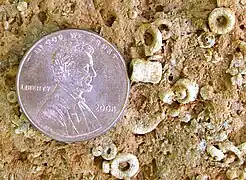 Small beads shown in comparison to a penny
Small beads shown in comparison to a penny
See also
- St. Cuthbert's beads, name for identical bead in Great Britain
References
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Indian beads.
- ↑ Weeden, William Babcock (1884). Indian Money as a Factor in New England Civilization. N. Murray, publication agent, Johns Hopkins university. p. 410. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.