 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
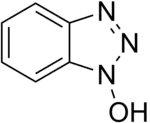
1H-1,2,3-Benzotriazol-1-ol | |
| Other names
N-Hydroxybenzotriazole HOBt | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.173 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5N3O | |
| Molar mass | 135.1234 g mol−1 (anhydrous) |
| Melting point | 156 to 159 °C (313 to 318 °F; 429 to 432 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Danger | |
| H203 | |
| P210, P230, P240, P250, P280, P370+P380, P372, P373, P401, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Hydroxybenzotriazole (abbreviated HOBt) is an organic compound that is a derivative of benzotriazole. It is a white crystalline powder, which as a commercial product contains some water (~11.7% wt as the HOBt monohydrate crystal). Anhydrous HOBt is explosive.
It is mainly used to suppress the racemization of single-enantiomer chiral molecules and to improve the efficiency of peptide synthesis.
Use in peptide synthesis

Automated peptide synthesis involves the condensation of the amino group of protected amino acids with the activated ester. HOBt is used to produce such activated esters. These esters are insoluble (like the N-hydroxysuccinimide esters) and react with amines at ambient temperature to give amides.[1]
HOBt is also used for the synthesis of amides from carboxylic acids aside from amino acids. These substrates may not be convertible to the acyl chlorides.[2] For instance amide derivatives of ionophoric antibiotics have been prepared in this way.[3]
Safety
Due to reclassification as UN0508, a class 1.3C explosive, hydroxybenzotriazole and its monohydrate crystal are no longer allowed to be transported by sea or air as per 49CFR (USDOT hazardous materials regulations). However, UNECE draft proposal ECE/TRANS/WP.15/AC.1/HAR/2009/1 has been circulated to UN delegates and, if implemented, would amend current regulations thus allowing for the monohydrate crystal to be shipped under the less-stringent code of UN3474 as a class 4.1 desensitized explosive.
References
- ↑ W. König, R. Geiger (1970). "Eine neue Methode zur Synthese von Peptiden: Aktivierung der Carboxylgruppe mit Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid unter Zusatz von 1-Hydroxy-benzotriazolen". Chem. Ber. 103 (3): 788–798. doi:10.1002/cber.19701030319. PMID 5436656.
- ↑ Andrew G. Myers, Bryant H. Yang, and Hou Chen TRANSFORMATION OF PSEUDOEPHEDRINE AMIDES INTO HIGHLY ENANTIOMERICALLY ENRICHED ALDEHYDES, ALCOHOLS, AND KETONES Organic Syntheses, Vol. 77, p. 29 (2000); Coll. Vol. 10, p.509 (2004).
- ↑ Łowicki, Daniel; A. Huczyński; M. Ratajczak-Sitarz; A. Katrusiak; J. Stefańska; B. Brzezinski; F. Bartl (2009). "Structural and antimicrobial studies of a new N-phenylamide of monensin A complex with sodium chloride". Journal of Molecular Structure. 923 (1–3): 53–59. Bibcode:2009JMoSt.923...53L. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2009.01.056.