Henri Alphonse Barnoin (7 July 1882 – 17 March 1940) was a French painter born in Paris in 1882.[1]
Biography

Barnoin's father was an artist as were two of his uncles, and he studied art at the École des Beaux Arts in Paris. Although Barnoin initially studied with Luc-Olivier Merson, it was his second teacher, Émile Dameron, who became a more significant influence on his artistic style, attracting Barnoin to Impressionism.[1] His work was part of the painting event in the art competition at the 1928 Summer Olympics.[2]
He first exhibited his paintings at the Salon des Artistes de Paris in 1909. He continued to exhibit regularly at this annual Salon, winning a silver medal in 1921 and a gold medal in 1935. He chose to live in Concarneau in 1919, having been a frequent visitor to the port before the 1914–1918 war. There he opened a studio on the "Quai Pénéroff" which became a favourite meeting place for fellow artists all inspired by the light and animated scenes of fishing boats, village markets, and the sea. In 1926, Barnoin became official Artist to the French Navy. In addition to his oil paintings, he was a renowned pastellist, enjoying playing with the effect of light on a variety of scenes in a Post-Impressionist style. He died in Paris in 1940.[3] Among Barnoin's favored subjects were marine, harbour, and coastal scenes, mostly painted in the rich settings of Brittany. This is exemplified in his painting Fishing Harbour, Concarneau, Brittany.[1]
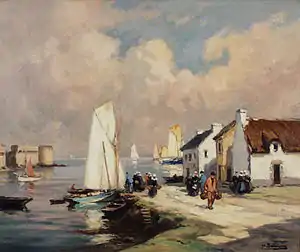
Some of Barnoin's most famous works are A Brittany harbour, La promenade en barque, Pardon de St. Fiacre, Bretagne, and Debarqument de la pêche au Passage-Lanriec. See also gallery below. His work can be seen in the Musée du Faouet and the Musée des beaux-arts in Quimper, and at the Musée des beaux-arts in Brest.[1]
The Musée de Faouët, a museum dedicated to showing the paintings of artists who had worked in Brittany, had a major retrospective of Henri Barnoin’s paintings in 2006.
Gallery
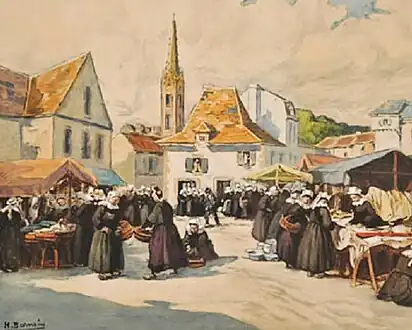 A market scene in Brittany
A market scene in Brittany
 Market day scene in Quimper's Place Saint-Corentin.
Market day scene in Quimper's Place Saint-Corentin.
 Breton women at the Sainte-Barbe fountain in Le Faouët.
Breton women at the Sainte-Barbe fountain in Le Faouët. The fabric market in Faouët. This painting is in the Musée du Faouët.
The fabric market in Faouët. This painting is in the Musée du Faouët.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Further biographical notes". Retrieved 30 December 2015.
- ↑ "Henri Barnoin". Olympedia. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- ↑ "Biographical notes". Retrieved 30 December 2015.
Further reading
- René Maurice, Trois artistes morbihannais: Arthur Midy, Henri Barnoin, Henri Moret, Imprimerie du Nouvelliste, Lorient, 1937
- Camille de Montergon, Histoire de Concarneau, Librairie E. Le Tendre, Concarneau, 1953
- Gérald Schurr and Pierre Cabanne, Dictionnaire des petits maîtres de la peinture, 2003 (ISBN 2859173781)
- Henri Belbeoch (preface by Jacques Foucart), Les peintres de Concarneau, Éditions Palantines, 1993 (ISBN 2950468551)
- Gérald Schurr, Le Guidargus de la peinture, Les Éditions de l'Amateur, 1996 (ISBN 2859172084)
- Emmanuel Bénézit, Dictionnaire des peintres, sculpteurs, dessinateurs, graveurs, vol. 1, Gründ, 1999
- André Cariou, Les peintres de Pont-Aven, Éditions Ouest-France, 1999 (ISBN 273732517X)
- Jean-Marc Michaud, Henri Barnoin, Éditions Le Télégramme, Brest (Finistère), 2006 (ISBN 9782848331683)
- Bernard Frélaut, La merveilleuse Bretagne des peintres, Georges Nael Éditeur, 2006 (ISBN 2831303877)