.jpg.webp) | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | HMS Lark |
| Ordered | 24 March 1761 |
| Builder | Elias Bird, Rotherhithe |
| Laid down | 5 May 1761 |
| Launched | 10 May 1762 |
| Completed | 9 July 1762 at Deptford Dockyard |
| Commissioned | May 1762 |
| Fate | Burnt to avoid capture at Newport, Rhode Island, 5 August 1778 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Richmond-class fifth-rate frigate |
| Tons burthen | 680 61⁄94 bm |
| Length |
|
| Beam | 34 ft 5 in (10.49 m) |
| Depth of hold | 12 ft 0+1⁄2 in (3.670 m) |
| Sail plan | Full-rigged ship |
| Complement | 210 officers and men |
| Armament | |
HMS Lark was a 32-gun Richmond-class frigate fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1762[1] and destroyed in Narragansett Bay in 1778, during the American Revolutionary War.[2]
On 11` January, 1778, under command of Captain Richard Smith, she chased ashore a vessel, probably schooner Sally, near the Providence River and burned it.[3] Between 29 May and 18 July, the British captured a number of vessels: the sloops Sally and Fancy, snow Baron D'Ozell, Olive Branch, sloop Betsey, and schooner Sally. Lark shared the prize money with Kingfisher, Hope, Sphinx, and the Pigot galley.[4]
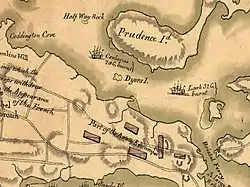
French Admiral d'Estaing's squadron arrived in Narragansett Bay on 29 July 1778 to support the American army under General George Washington during the battle of Rhode Island. On 30 July, four French ships of the line entered Narrangansett Bay and positioned themselves north of Conanicut Island to support the American and French forces in the battle of Rhode Island.[5] The arrival of the French vessels trapped several British vessels, Lark among them. On 5 August 1778, as Lark lay off Newport, Captain Richard Smith had her set on fire and her cables cut. She then drifted on to shore.[6] The Royal Navy ended up having to destroy ten of their own vessels in all.[6]
The remains of Lark are now part of a site listed on the National Register of Historic Places, the "Wreck Sites of HMS Cerberus and HMS Lark."
Citations
- ↑ "Archaeological Sites Under Investigation at AUVfest 2008". Archived from the original on 31 May 2008. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- ↑ Marx, Robert F. (1987). Shipwrecks in the Americas. Dover Publications. p. 152. ISBN 0-486-25514-X.
- ↑ "Naval Documents of The American Revolution Volume 11 AMERICAN THEATRE: Jan. 1, 1778–Mar. 31, 1778 EUROPEAN THEATRE: Jan. 1, 1778–Mar. 31, 1778" (PDF). U.S. Government printing office via Imbiblio. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- ↑ "No. 12460". The London Gazette. 22 July 1783. p. 4.
- ↑ "No. 11921". The London Gazette. 24 October 1778. p. 1.
- 1 2 Hepper (1994), p. 52.
References
- Robert Gardiner, The First Frigates, Conway Maritime Press, London 1992. ISBN 0-85177-601-9.
- Hepper, David J. (1994). British Warship Losses in the Age of Sail, 1650–1859. Rotherfield: Jean Boudriot. ISBN 0-948864-30-3.
- David Lyon, The Sailing Navy List, Conway Maritime Press, London 1993. ISBN 0-85177-617-5.
- Rif Winfield, British Warships in the Age of Sail, 1714 to 1792, Seaforth Publishing, London 2007. ISBN 978-1-84415-700-6.
41°31′12″N 71°19′49″W / 41.5201°N 71.3303°W