| Foster graph | |
|---|---|
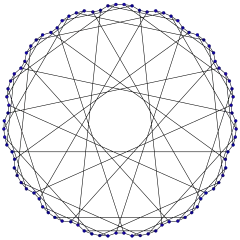 The Foster graph | |
| Named after | Ronald Martin Foster |
| Vertices | 90 |
| Edges | 135 |
| Radius | 8 |
| Diameter | 8 |
| Girth | 10 |
| Automorphisms | 4320 |
| Chromatic number | 2 |
| Chromatic index | 3 |
| Queue number | 2 |
| Properties | Cubic Bipartite Symmetric Hamiltonian Distance-transitive |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Foster graph is a bipartite 3-regular graph with 90 vertices and 135 edges.[1]
The Foster graph is Hamiltonian and has chromatic number 2, chromatic index 3, radius 8, diameter 8 and girth 10. It is also a 3-vertex-connected and 3-edge-connected graph. It has queue number 2 and the upper bound on the book thickness is 4.[2]
All the cubic distance-regular graphs are known.[3] The Foster graph is one of the 13 such graphs. It is the unique distance-transitive graph with intersection array {3,2,2,2,2,1,1,1;1,1,1,1,2,2,2,3}.[4] It can be constructed as the incidence graph of the partial linear space which is the unique triple cover with no 8-gons of the generalized quadrangle GQ(2,2). It is named after R. M. Foster, whose Foster census of cubic symmetric graphs included this graph.
The bipartite half of the Foster graph is a distance-regular graph and a locally linear graph. It is one of a finite number of such graphs with degree six.[5]
Algebraic properties
The automorphism group of the Foster graph is a group of order 4320.[6] It acts transitively on the vertices, on the edges and on the arcs of the graph. Therefore, the Foster graph is a symmetric graph. It has automorphisms that take any vertex to any other vertex and any edge to any other edge. According to the Foster census, the Foster graph, referenced as F90A, is the only cubic symmetric graph on 90 vertices.[7]
The characteristic polynomial of the Foster graph is equal to .
Gallery
 Foster graph colored to highlight various cycles.
Foster graph colored to highlight various cycles. The chromatic number of the Foster graph is 2.
The chromatic number of the Foster graph is 2. The chromatic index of the Foster graph is 3.
The chromatic index of the Foster graph is 3.
References
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Foster Graph". MathWorld.
- ↑ Wolz, Jessica; Engineering Linear Layouts with SAT. Master Thesis, University of Tübingen, 2018
- ↑ Brouwer, A. E.; Cohen, A. M.; and Neumaier, A. Distance-Regular Graphs. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
- ↑ Cubic distance-regular graphs, A. Brouwer.
- ↑ Hiraki, Akira; Nomura, Kazumasa; Suzuki, Hiroshi (2000), "Distance-regular graphs of valency 6 and ", Journal of Algebraic Combinatorics, 11 (2): 101–134, doi:10.1023/A:1008776031839, MR 1761910
- ↑ Royle, G. F090A data
- ↑ Conder, M. and Dobcsányi, P. "Trivalent Symmetric Graphs Up to 768 Vertices." J. Combin. Math. Combin. Comput. 40, 41-63, 2002.
- Biggs, N. L.; Boshier, A. G.; Shawe-Taylor, J. (1986), "Cubic distance-regular graphs", Journal of the London Mathematical Society, 33 (3): 385–394, doi:10.1112/jlms/s2-33.3.385, MR 0850954.
- Van Dam, Edwin R.; Haemers, Willem H. (2002), "Spectral characterizations of some distance-regular graphs", Journal of Algebraic Combinatorics, 15 (2): 189–202, doi:10.1023/A:1013847004932, MR 1887234.
- Van Maldeghem, Hendrik (2002), "Ten exceptional geometries from trivalent distance regular graphs", Annals of Combinatorics, 6 (2): 209–228, doi:10.1007/PL00012587, MR 1955521, S2CID 195315348.