| FAM178B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | FAM178B, family with sequence similarity 178 member B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 3026913 HomoloGene: 87288 GeneCards: FAM178B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
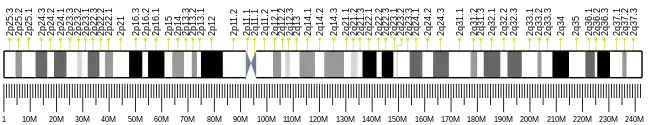
FAM178B is a protein coding that is located on the plus strand of chromosome 2.[5] The locus for the gene is 2q11.2. It is also known by the aliases Family with Sequence Similarity 178, Member B, and HSPC234.[6] In total there are 24 exons in the gene. FAM178B spans 110,720 base pairs, and contains 827 amino acids.
Forms
There are two isoforms of the gene transcript that exist by alternative splicing, and one gene precursor.[5]
| Isoform: | Identifier: | Length in Amino Acids: | Mass (daltons): |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q8IXR5-1 | 827 | 93,514 |
| 2 | Q8IXR5-2 | 119 | 13,809 |
| 3 | Q8IXR5-3 | 679 | 76,515 |
SLF2 (FAM178A) is an important paralog of FAM178B. SLF2 is predicted to play a role in the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway by regulating post-replication repair of UV-damaged DNA, and genomic stability maintenance.[7]
Protein structure
The molecular weight of the protein is 76.5 kilodaltons,[8] and the isoelectric point is 5.47.The gene has 6 transcript splice variants.[9] The protein has been phenotypically associated with bipolar disease due to its locus,[10] as well as body mass index (BMI), and cell adhesion.[11] A proposed structure for the protein can be found in the images for proposed structures.[12] The secondary structure for the FAM178B protein is predicted to be primarily alpha helices.[13] The tertiary structure of the protein may assume a coiled coil structure.[13]

Expression
FAM178B is most highly expressed in the skeletal muscle and brain tissues[14].The structure in which it is highly concentrated is in the corpus callosum of the brain.[14] Additionally, it is of high levels in the trigeminal nerve and spinal cord. Further, there is also high concentrations of the gene found near the heart, testes and olfactory regions.
According to the Allen Brain Atlas,[15] the olfactory regions, and the hippocampus of the mouse brain showed the greatest expressions of the gene when tested experimentally.

DNA Level Regulation
The proposed promoter region of FAM178B protein is below.[16] A table of relevant transcription factor binding sites that correspond to the sequence and colors highlighted in the promoter region is also included.


The promoter region of FAM178B is highly conserved across its most related orthologs, and is almost identical across the human, gorilla, chimp, bonobo and gibbon organisms.[17]
Protein Level Regulation
Below is a table that shows the protein modifications that could be potentially made to FAM178B, and the potential effects of these modifications on the protein itself:.[18]
Homology and Evolution
An important paralog of the gene is SLF2, which plays a role in the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway by regulating post replication repair of UV-damaged DNA. It also helps maintain genomic stability.[19] There are 74 known orthologs of the protein, and it can be traced back as far back as crustaceans.[5] FAM178B is heavily found in both vertebrates and invertebrates. The ortholog space for the protein FAM178B is quite large as it can be traced back 794 millions of years ago (mya) to mollusks with the apple snail, and Pacific Oyster. There are 134 known orthologs of FAM178B. However, the protein is not found in arthropods, or insects, which is interesting because those organisms also existed in that time period meaning that it was conserved across some taxa, but not others. The protein is most readily found in primates, and other non-primate mammals. The protein is also conserved across reptiles, some bony fish, and cartilaginous fish, and birds.
Below is a table illustrating some of the orthologs for FAM178B using BLAST[20] and BLAT.[21]
| Scientific Name: | Common Name: | Accession Number
from NCBI: |
Sequence Length:
(Amino Acids) |
Date of Divergence from Human Lineage:
(millions of years ago) |
Percent Identity: | Percent Similarity: |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo Sapiens | Human | Q8IXR5.2 | 827 | -- | -- | -- |
| Macaca Mulatta | Macque | XP_014968433 | 709 | 28.1 | 80 | 83 |
| Chlorocebus Sabaeus | Green Monkey | XP_008006245 | 724 | 28.1 | 91 | 94 |
| Cebus Capucinus | Capuchin | XP_017379417 | 808 | 42.6 | 88 | 91 |
| Otolemur Garnettii | Galago | XP_012666502 | 675 | 73.0 | 74 | 81 |
| Marmota Marmota | Marmot | XP_015355109 | 692 | 88.0 | 74 | 80 |
| Microtus Ochrogaster | Vole | XP_026641579 | 561 | 88.0 | 68 | 75 |
| Felis Catus | Cat | XP_019682636 | 720 | 94.0 | 71 | 77 |
| Equus Caballus | Horse | XP_023474395 | 659 | 94.0 | 78 | 84 |
| Panthera Tigris | Tiger | XP_007097881 | 674 | 94.0 | 75 | 80 |
| Miniopterus Natalensis | Bat | XP_016077151 | 649 | 94.0 | 73 | 81 |
| Bison Bison | Bison | XP_010828157 | 664 | 94.0 | 65 | 73 |
| Tursiops Truncatus | Dolphin | JH473473 | 827 | 94.0 | 61 | 68 |
| Alligator Mississippiensis | Alligator | XP_019343229 | 802 | 320.0 | 34 | 47 |
| Pogona Vitticeps | Bearded Dragon | XP_020635880 | 1003 | 320.0 | 41 | 56 |
| Apteryx Rowi | Kiwi | XP_025941058 | 512 | 320.0 | 42 | 58 |
| Gallus Gallus | Chicken | XP_024998603 | 547 | 320.0 | 37 | 50 |
| Rhincodon Typus | Whale Shark | XP_020388490 | 1155 | 465.0 | 34 | 53 |
| Callorhinchus Milii | Australian Ghostshark | XP_007910600 | 860 | 465.0 | 33 | 50 |
| Crassostrea Gigas | Pacific Oyser | EKC42969 | 1222 | 794.0 | 24 | 38 |
| Pomacea Canaliculta | Applesnail | PVD30455 | 1229 | 794.0 | 24 | 45 |
Timetree[22] for FAM178B
Interacting Proteins
There are 2 proteins that have high predicted values of interaction with FAM178B: LRSAM 1 and ZNF598.[23] LRSAM1[24] is also known as leucine rich repeat and sterile alpha motif protein 1. The value for the protein is .29 and the evidence is physical from hybrid pooling approaches. LRSAM1 was previously known as Tsg-associated ligase and is located on the LRSAM1 gene. Mutations have been associated with periphery neuropathy, and sensory disorders. It is highly expressed in the spinal cord, as is FAM178B. There is currently no known structure for the protein. ZNF598 is a zinc finger protein and the value is .13. It plays a key role in ribosome quality control. The predicted structures are below for both proteins.
 MENTHA[23] interacting proteins for FAM178B.
MENTHA[23] interacting proteins for FAM178B.
 STRING[25] interacting proteins for FAM178B.
STRING[25] interacting proteins for FAM178B.
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000168754 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000046337 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- 1 2 3 FAM178B - Protein FAM178B - Homo sapiens (Human) - FAM178B gene & protein. (n.d.). Retrieved February 25, 2019, from https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8IXR5
- ↑ RecName: Full=Protein FAM178B - Protein - NCBI. (n.d.). Retrieved February 25, 2019, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/Q8IXR5.2
- ↑ Räschle M, Smeenk G, Hansen RK, Temu T, Oka Y, Hein MY, Nagaraj N, Long DT, Walter JC, Hofmann K, Storchova Z, Cox J, Bekker-Jensen S, Mailand N, Mann M (May 2015). "DNA repair. Proteomics reveals dynamic assembly of repair complexes during bypass of DNA cross-links". Science. 348 (6234): 1253671. doi:10.1126/science.1253671. PMC 5331883. PMID 25931565.
- ↑ "SAPS < Sequence Statistics < EMBL-EBI". www.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2019-04-21.
- ↑ Gene: FAM178B (ENSG00000168754) - Splice variants - Homo sapiens - Ensembl genome browser 95. (n.d.). Retrieved February 25, 2019, from http://useast.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Gene/Splice?db=core;g=ENSG00000168754;r=2:96875882-96986592
- ↑ Bipolar disorder lithium response (continuous) or schizophrenia - Loci associated with Bipolar disorder lithium response (continuous) or schizophrenia - Homo sapiens - Ensembl genome browser 95. (n.d.). Retrieved February 25, 2019, from http://useast.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Phenotype/Locations?db=core;g=ENSG00000168754;ph=70698;r=2:96875882-96986592
- ↑ Gene: FAM178B (ENSG00000168754) - Phenotypes - Homo sapiens - Ensembl genome browser 95. (n.d.). Retrieved February 25, 2019, from http://useast.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Gene/Phenotype?db=core;g=ENSG00000168754;r=2:96875882-96986592
- ↑ SWISS-MODEL Repository | Q8IXR5. (n.d.). Retrieved February 25, 2019, from https://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/uniprot//Q8IXR5
- 1 2 "PHYRE2 Protein Fold Recognition Server". www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk. Retrieved 2019-04-22.
- 1 2 "Gene2Promoter". ExPasy.
- ↑ "Allen Brain Atlas".
- ↑ "ElDorado Introduction". www.genomatix.de. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- ↑ "Clustal Omega < Multiple Sequence Alignment < EMBL-EBI". www.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- ↑ "ExPASy: SIB Bioinformatics Resource Portal - Categories". www.expasy.org. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- ↑ Räschle, M., Smeenk, G., Hansen, R. K., Temu, T., Oka, Y., Hein, M. Y., … Mann, M. (2015). DNA repair. Proteomics reveals dynamic assembly of repair complexes during bypass of DNA cross-links. Science, 348(6234), 1253671. doi:10.1126/science.1253671
- ↑ "BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool". blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-04-21.
- ↑ "Human BLAT Search". genome.ucsc.edu. Retrieved 2019-04-21.
- ↑ "TimeTree :: The Timescale of Life". www.timetree.org. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- 1 2 "mentha: the interactome browser". www.mentha.uniroma2.it. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- ↑ "LRSAM1 - E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase LRSAM1 - Homo sapiens (Human) - LRSAM1 gene & protein". www.uniprot.org. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- ↑ "FAM178B protein (human) - STRING interaction network". string-db.org. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
Further reading
- Hillier, Ladeana W.; Graves, Tina A.; Fulton, Robert S.; Fulton, Lucinda A.; Pepin, Kymberlie H.; Minx, Patrick; Wagner-McPherson, Caryn; Layman, Dan; Wylie, Kristine (2005-04-07). "Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4". Nature. 434 (7034): 724–731. Bibcode:2005Natur.434..724H. doi:10.1038/nature03466. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 15815621.
- Stelzl, Ulrich; Worm, Uwe; Lalowski, Maciej; Haenig, Christian; Brembeck, Felix H.; Goehler, Heike; Stroedicke, Martin; Zenkner, Martina; Schoenherr, Anke (2005-09-23). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–968. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 16169070. S2CID 8235923.
- Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells