 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
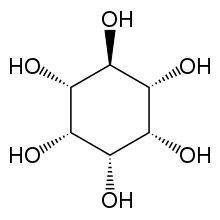
| IUPAC name
epi-Inositol[1] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,2R,3r,4S,5S,6s)-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.984 |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 180.156 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Epi-Inositol is one of the stereoisomers of inositol.[2]
Use in medicine
Epi-inositol has been found to regulate Yeast INO1 Gene Encoding (Inositol-1-P synthase) in animals. During the study with Epi-Inositol, Yeast INO1-expression was measured in northern blots.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 1415. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ "Inositols". ursula.chem.yale.edu. Retrieved 2022-06-17.
- ↑ A., Shaldubina; S., Ju; L., Vaden; D, Ding; Belmaker, R. H; Greenberg, M. L (February 13, 2002). "Epi-inositol regulates expression of the yeast INO1 gene encoding inositol-1-P synthase". Millipore Sigma. PMID 11840310. Archived from the original on June 17, 2022. Retrieved June 17, 2022.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.