 | |
 | |
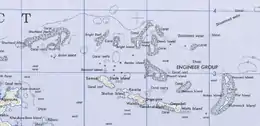
 Engineer Islands | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Oceania |
| Coordinates | 10°34′48″S 151°14′32″E / 10.58000°S 151.24222°E[1] |
| Archipelago | Louisiade Archipelago |
| Adjacent to | Solomon Sea |
| Total islands | 15 |
| Major islands | |
| Area | 11.12 km2 (4.29 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 198 m (650 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Slade |
| Administration | |
| Province | |
| District | Samarai-Murua District |
| LLG[2] | Bwanabwana Rural Local Level Government Area |
| Island Group | Engineer Islands |
| Largest settlement | Gegadali (pop. ~270) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 1200 (2014) |
| Pop. density | 108/km2 (280/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Papauans, Austronesians, Melanesians. |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
| ISO code | PG-MBA |
| Official website | www |
The Engineer Islands are an archipelago in the Solomon Sea belonging to Papua New-Guinea.
Geography
The Engineer Islands belong to Milne Bay Province, and are one of the groups forming the Louisiade Archipelago. They are located on the western edge of Louisiade archipelago, east of Basilaki and south of Normanby . The islands form an unusual group consisting of high islands, low coral islands, atolls and underwater reefs, which are located in a radius of 24 km to 14 km away. The three largest islands lie on the southwestern part of the group. They are: Tubetube (Slade Island), Naruaruari (Skelton Island ) and Kwaraiwa (Watts island), each about 3.5 km long and about 0.75 km wide. The islands are hilly with elevations of up to 150 m (at Slade Island). The eastern boundary of the Engineer group is marked by a crescent-shaped reef, on which the four low islands Hummock, Haszard, Button and Flat are located.[3] In the center of the archipelago there is a reef with a semi-enclosed lagoon. on it, the islands Powell and Pender lying on the western side while Messum Island is on the eastern side.
Climate
Engineer islands have a tropical rainforest climate (Af) with heavy to very heavy rainfall year-round. The following climate data is for Slade island.
| Climate data for Slade island (Kasapae village) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.8 (87.4) |
31.3 (88.3) |
30.6 (87.1) |
29.4 (84.9) |
28.4 (83.1) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.6 (87.1) |
29.1 (84.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.0 (80.6) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.5 (76.1) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.0 (78.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23.3 (73.9) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.2 (73.8) |
22.8 (73.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 216 (8.5) |
229 (9.0) |
244 (9.6) |
350 (13.8) |
354 (13.9) |
312 (12.3) |
292 (11.5) |
308 (12.1) |
304 (12.0) |
286 (11.3) |
180 (7.1) |
197 (7.8) |
3,272 (128.9) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[4] | |||||||||||||
Administration
There are several more island groups that belong to the Engineer Islands Ward:
- The Shortland Islands are located 2 km to the northwest.
- Laseinie Islands (with Koyagaugau (Dawson Island)) are located 20 km to the north.
- Kegawam Islands are located 25 km to the north.
History
John Moresby discovered the islands in 1873 and named them in honor of the English Engineers of his steamboat HMS Basilisk.[5] The islands were named after the individual crew members from the engine room: Slade, Skelton, Watts, Butchart, Bright, among others.
Population
There are 4 inhabited islands, with the main village Gegadali located on Watts Island.[6] The inhabitants of the archipelago speak Bwanabwana Language.[7]
References
- ↑ Prostar Sailing Directions 2004 New Guinea Enroute, p. 168
- ↑ "LLG map" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-08-11. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- ↑ Patricia May, Margaret Tuckson The traditional pottery of Papua New Guinea
- ↑ "Climate: Kasapae". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
- ↑ Arthur Wichman (Hrsg.): Entdeckungsgeschichte von Neu-Guinea (bis 1828). Bd. 1, E. J. Brill, Leiden 1909, S. 187
- ↑ "Papua New Guinea WWW Virtual Library – Google Maps version". Archived from the original on June 9, 2007. Retrieved 2016-03-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ Ethnologue, Languages of the World: Bwanabwana, A language of Papua New Guinea