Ectopic calcification is a pathologic deposition of calcium salts in tissues or bone growth in soft tissues. This can be a symptom of hyperphosphatemia. Formation of osseous tissue in soft tissues such as the lungs, eyes, arteries, or other organs is known as ectopic calcification, dystrophic calcification, or ectopic ossification.[1]
Causes
Absorption of calcium salts normally occurs in bony tissues and is facilitated by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D. However, increased amounts of parathyroid hormone in the blood result in the deposit of calcium in soft tissues. This can be an indication of hyperparathyroidism, arteriosclerosis, or trauma to tissues.
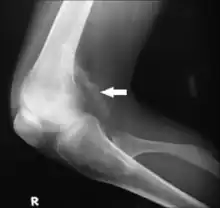
Calcification of muscle can occur after traumatic injury and is known as myositis ossificans. It can be recognized by muscle tenderness and loss of stretch in the affected area. To reduce the risk of calcification after an injury, initiate what is commonly known as "RICE" (rest, ice, compression, and elevation).[2]
Diagnosis
Typically, the diagnosis of extra-skeletal ectopic calcification is quite straightforward. A physical examination of a suspected area with calcified deposits palpates as hard and rough. To confirm, the calcified tissues can be seen on an x-ray.
Prognosis
Ectopic ossification of the heart valves is an indicator of future heart problems, hyperparathyroidism, and necrosis of tissues.
See also
References
- ↑ Giachelli CM (1999). "Ectopic Calcification: Gathering Hard Facts about Soft Tissue Mineralization". Am. J. Pathol. 154 (3): 671–5. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65313-8. PMC 1866412. PMID 10079244.
- ↑ "Post-traumatic ectopic calcification in the muscles of athletes: a review" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-06-18.