| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[1,1′-Biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
2,2'-dibenzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.889 |
| EC Number |
|
| 536420 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 242.230 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.2917 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 235.5 °C (455.9 °F; 508.6 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
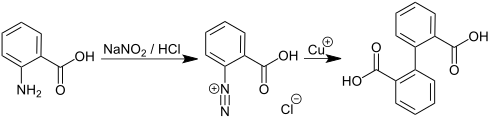
Diphenic acid, also known as Dibenzoic acid, is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4CO2H)2. It is the most studied of several isomeric dicarboxylic acids of biphenyl. It is a white solid that can be prepared in the laboratory from anthranilic acid via the diazonium salt.[1] It is the product of the microbial action on phenanthrene.[2]
The compound forms a variety of coordination polymers.[3] It also exhibits atropisomerism. It can form an internal anhydride featuring a seven-membered ring fused to the two benzene rings.
Preparation
Diphenic acid is prepared from anthranilic acid by diazotization, followed by reduction with copper(I).[4]
It can also be synthesized from the oxidation of phenanthrene by peracetic acid, which is first prepared from acetic acid and 90% hydrogen peroxide:[5]
- CH3COOH + H2O2 ⇌ CH3COOOH + H2O
- 4 CH3COOOH + C14H10 → 4 CH3COOH + C14H10O4
Phenanthrene can also be treated with other oxidizing agents (such as hydrogen peroxide, chromium trioxide, potassium dichromate, or potassium permanganate), which first yields phenanthrenequinone and gives diphenic acid on further oxidation.[6][7] Similarly, phenanthrenequinone can be boiled in alcoholic potash (potassium hydroxide in alcohol) to give the potassium salt of diphenic acid,[8] and can alternatively be photo-oxidized to diphenic acid.[9]
References
- ↑ Atkinson, E. R.; Lawler, H. J. (1927). "Diphenic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 7: 30. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.007.0030.
- ↑ Moody, J. D.; Freeman, J. P.; Doerge, D. R.; Cerniglia, C. E. (2001). "Degradation of Phenanthrene and Anthracene by Cell Suspensions of Mycobacterium sp. Strain PYR-1". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 67 (4): 1476–1483. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.4.1476-1483.2001. PMC 92757. PMID 11282593.
- ↑ Yang, Jin; Ma, Jian-Fang; Liu, Ying-Ying; Ma, Ji-Cheng; Batten, Stuart R. (2009). "A Series of Lead(II) Complexes with π−π Stackings: Structural Diversities by Varying the Ligands". Crystal Growth & Design. 9 (4): 1894–1911. doi:10.1021/cg801085d.
- ↑ "DIPHENIC ACID". Organic Syntheses. 7: 30. 1927. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.007.0030.
- ↑ O'Connor, William F.; Moriconi, Emil J. (1953). "2,2′-Diphenic Acid from Phenanthrene". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. 45 (2): 277–281. doi:10.1021/ie50518a020. ISSN 0019-7866.
- ↑ Noller, Carl R. (1960), "Kondensierte aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffe und ihre Derivate", Lehrbuch der Organischen Chemie (in German), Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 614–639, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-87324-9_28, ISBN 978-3-642-87325-6, retrieved 2023-03-27
- ↑ Meyer, Hans (1938). Synthese der Kohlenstoffverbindungen : Erster Teil: Offene Ketten und Isocyclen (in German). Vienna. p. 1170. ISBN 978-3-7091-3245-6. OCLC 913683350.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ Gustav, Schultz (1886). Die Chemie des Steinkohlentheers: Bd. Die Rohmaterialen. Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn.
- ↑ Coehn, A.; Jung, G.; Daimer, J., eds. (1926). Photochemie und Photographische Chemikalienkunde (in German). Vienna: Springer Vienna. p. 136. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-5403-8. ISBN 978-3-7091-5255-3.