Native name: Saaqqayaaq-Qikirtasiit | |
|---|---|
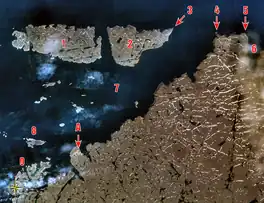 Digges Islands identified by No. 1 and 2. | |
 Digges Islands  Digges Islands | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Digges Sound, an arm of Hudson Bay |
| Coordinates | 62°34′59″N 77°49′59″W / 62.58306°N 77.83306°W |
| Archipelago | Arctic Archipelago |
| Area | 91 km2 (35 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
Canada | |
| Nunavut | Nunavut |
| Region | Qikiqtaaluk |
| Demographics | |
| Population | Uninhabited |
The Digges Islands[1] (Inuit: Saaqqayaaq-Qikirtasiit)[2] are members of the Arctic Archipelago in the territory of Nunavut. The two islands, West Digges and East Digges, are located in Digges Sound, an arm of Hudson Bay, where the strong currents of the bay meet Hudson Strait.
The hamlet of Ivujivik, on the Ungava Peninsula, is south of the islands. East Digges Island is closer to the northern tip of the Ungava Peninsula than West Digges. Mansel Island is to the southwest, while Nottingham Island is to the north.
The islands' rocky cliffs topography is ideal for seabirds; thick-billed murre colonies are abundant.
Arctic exploration
In 1610, the first recorded encounter between Europeans and Nunavik Inuit occurred on Digges Islands during Henry Hudson's last expedition.[3] Hudson named many Arctic points after patrons who financed the voyage, including Dudley Digges, the namesake of the Digges Islands. In 1611 four of Hudson's mutineers were killed here by Inuit and in 1612 Thomas Button had five of his crew killed somewhere near the Islands.
The area was explored again soon after by Jens Munk during his 1619 voyage.[4]
References
- ↑ "285 - Digges Islands, Nunavut". Atlas of Canada. Archived from the original on 2012-07-01. Retrieved 2008-06-10.
- ↑ Issenman, Betty. Sinews of Survival: The living legacy of Inuit clothing. UBC Press, 1997. pp252-254
- ↑ "ATTRACTIONS". nunavik-tourism.com. Archived from the original on 2015-05-22. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ↑ "MUNK (Munck), JENS ERIKSEN, Danish". Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
External links