| Demographics of Vilnius | |
|---|---|
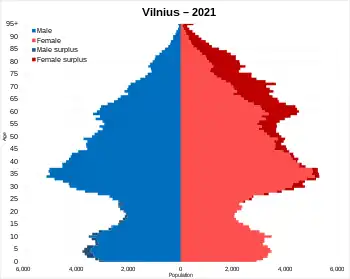 Population pyramid of the Vilnius City in 2021 | |
| Population | 633,481 (2023) |
After the Russian invasion of Ukraine and an influx of Ukrainian refugees to Lithuania, who were granted a refugee status[1] the number of inhabitants of Vilnius rose to 633,481 as of November 2023 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The number of inhabitants of Vilnius, born in Ukraine rose from 10 thousand to 29 thousand between 2021 and 2023. The number of persons born in Belarus rose from 25 thousand to 37 thousand during the same period mostly as a consequence of 2020–2021 Belarusian protests and intensified fleeing abroad of its citizens. Also, numbers of persons, who settle in Vilnius, coming from Central Asia, Caucasus, African, Asian (most notably - India) countries are on the rise.[2]
As of late 2023, 73 thousand foreigners lived in Vilnius, up from 38 thousand a year and a half earlier. In January 2022, there were also 5 000 foreign minors living in Vilnius, but the number had risen to 13 000 in January 2023.[3]
Before these dramatic changes, what led to the sharp rise of the number of inhabitants, the city of Vilnius as of early 2021 had a population between 569,729[4][5] (according to Statistics Lithuania) and 588,412[6] (according to the State Enterprise Centre of Registers). According to the municipality of Vilnius, the city had a population of 597,610[2] as of May 2022 – the figure includes Grigiškės, a formally separate town within the municipality of the capital, but without a separate body of a town government except that of a Vilnius city district (seniūnija). The actual number of city inhabitants could be higher as according to the Vilnius territorial health insurance fund, there were 732,815 permanent inhabitants as of January 2021 in Vilnius city and Vilnius district municipalities combined[7][note 1].
According to the predictions, made by the municipality specialists of the city planning department of Vilnius, the number of inhabitants of Vilnius in 2030 could be between 630,3 thousand (pessimistic scenario) and 685 thousand (optimistic scenario) with the basic scenario of 651,6 thousand inhabitants within the city borders.[9]
Evolution
Demographic evolution of Vilnius between 1766 and 2023:
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: [11][12]: 214, 303 [13][14] ¹ Sharp decline after the Vilnius uprising (1794); ² Decline of population due to Napoleonic wars and the aftermath; ³ Sharp decline of population of Vilnius because of World War I and the aftermath during the clashes around Vilnius. These resulted in evacuation of Russian military, bureaucracy and the majority of its Russian inhabitants from Vilnius in 1915, as well as fleeing or evacuation of other Vilnius inhabitants of various communities (mostly Jewish and Lithuanian) to Russia and rural parts of Lithuania;[15][16] ⁴ Rise of population due to influx of Polish and Jewish war refugees[17] and migration of Lithuanian bureaucracy, students from temporary capital Kaunas and other localities in Lithuania; ⁵ Sharp decline of population after atrocities of World War II and The Holocaust | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vilnius inhabitants by ethnicity
| Year | Lithuanians | Poles | Russians | Jews | Others | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1897[18] | 3,131 | 2% | 47,795 | 31% | 30,967 | 20% | 61,847 | 40% | 10,792 | 7% | 154,532 |
| 1916[19] | 2.6% | 50.1% | 1.5% | 43.5% | 2.3% | ||||||
| 1917[20] | 2.1% | 53.65% | 1.6% | 41.44% | 0.77% | ||||||
| 1919[19] | 2.3% | 56.1% | 3.2% | 36.2% | 2.3% | ||||||
| 1923[19] | 0.9% | 60.2% | 2.8% | 33.5% | 2.6% | ||||||
| 1931[21] | 0.8% | 65.9% | 3.8% | 28% | 0.6% | ||||||
| 1941[22] | 28.1% | 50.7% | 3.6% | 16.2% | 1.4% | ||||||
| 1942[19] | 20.5% | 71.9% | 2% | - | - | 0.4% | |||||
| 1951[19] | 30.8% | 21% | 33.3% | 3.1% | 11.8% | ||||||
| 1959[23] | 33.6% | 20% | 29.4% | 6.9% | 10% | ||||||
| 1970[19] | 42.8% | 18.6% | 24.5% | 4.4% | 10% | ||||||
| 1979[19] | 47.3% | 18% | 22.2% | 2.3% | 10.3% | ||||||
| 1989[19] | 50.5% | 18.8% | 20.2% | 1.6% | 8.9% | ||||||
| 2001[24] | 57.5% | 18.9% | 14.1% | 0.5% | 9.1% | ||||||
| 2011[25] | 63.2% | 16.5% | 12% | 0.4% | 8.6% | ||||||
| 2021[26] | 67.1% | 15.4% | 9.7% | N/A | 7.8% | ||||||
| Number of inhabitants | |
|---|---|
| Lithuanians | 338,758 |
| Poles | 88,408 |
| Russians | 63,991 |
| Belarusians | 18,924 |
| Ukrainians | 5,338 |
| Jews | 2,026 |
| Tatars | 934 |
| Roma | 619 |
| Armenians | 435 |
| Latvians | 360 |
| Germans | 341 |
| Other | 2,065 |
| Refused to answer | 13,432 |
| Total | 535,631 |
| Number of inhabitants | |
|---|---|
| Lithuanians | 373,513 |
| Poles | 85,436 |
| Russians | 53,887 |
| Belarusians | 15,156 |
| Ukrainians | 4,687 |
| Other | 5,705 |
| Refused to answer | 18,112 |
| Total | 556,490 |
Vilnius inhabitants by the country of birth
| Country of birth | Number of inhabitants |
|---|---|
| 517,936 | |
| 25,591 | |
| 18,731 | |
| 10,158 | |
| 2,239 | |
| 1,598 | |
| 1,335 | |
| 954 | |
| 752 | |
| 618 | |
| 578 | |
| 496 | |
| 474 | |
| 470 | |
| 408 | |
| 384 | |
| 378 | |
| 373 | |
| 364 | |
| 341 | |
| 329 | |
| 316 | |
| 297 | |
| 283 | |
| 254 | |
| 209 | |
| 189 | |
| 187 | |
| 153 | |
| 149 | |
| 140 | |
| 122 | |
| 120 | |
| 114 | |
| 109 | |
| 98 | |
| 97 | |
| 91 | |
| 87 | |
| 79 | |
| 79 | |
| 77 | |
| 73 | |
| 70 | |
| 70 | |
| 67 | |
| 67 | |
| 64 | |
| 51 | |
| 51 | |
| 50 | |
| 49 | |
| 46 | |
| 45 | |
| 44 | |
| 44 | |
| 41 | |
| 40 | |
| 36 | |
| 31 | |
| 28 | |
| 27 | |
| 27 | |
| 26 | |
| 26 | |
| 24 | |
| 23 | |
| 23 | |
| 22 | |
| Other countries | 500 |
Elderships of Vilnius
| Eldership | Area km²[28] | Inhabitants[29] | Density per km² |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verkiai | 56 | 50,881 | 909 |
| Žirmūnai | 5.7 | 43,880 | 7698 |
| Pašilaičiai | 7.9 | 41,218 | 5217 |
| Antakalnis | 77.2 | 40,875 | 530 |
| Naujoji Vilnia | 38.6 | 39,102 | 1013 |
| Fabijoniškės | 5.9 | 38,027 | 9275 |
| Naujamiestis | 4.9 | 33,206 | 6777 |
| Lazdynai | 9.9 | 32,410 | 3274 |
| Naujininkai | 37.6 | 31,697 | 843 |
| Šeškinė | 4.6 | 29,809 | 6480 |
| Pilaitė | 13.9 | 28,335 | 2038 |
| Justiniškės | 3.0 | 26,684 | 8895 |
| Karoliniškės | 3.7 | 25,250 | 6824 |
| Senamiestis | 4.4 | 22,411 | 5093 |
| Vilkpėdė | 10.8 | 19,519 | 1807 |
| Šnipiškės | 3.1 | 15,750 | 5081 |
| Viršuliškės | 2.6 | 14,096 | 5422 |
| Žvėrynas | 2.6 | 13,703 | 5270 |
| Rasos | 16.3 | 11,666 | 716 |
| Grigiškės | 7.0 | 11,246 | 1607 |
| Paneriai | 84.8 | 10,537 | 124 |
| Undeclared inhabitants | 9,123 | ||
| Total | 400.5 | 589,425 | 1472 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Some inhabitants of Vilnius district were registered at Vilnius city healthcare facilities – the actual number of permanent city inhabitants within the city administrative borders must have been higher than official figures of 569, 588 or 589 thousand, but smaller than 643,965 (as of 31 December 2020)[8]
References
- ↑ WAR REFUGEES FROM UKRAINE, Statistics of Lithuania
- 1 2 3 4 5 Statistics of Vilnius
- ↑ Number of foreigners living in Lithuania surpasses 200,000
- ↑ "Nuolatinių gyventojų skaičius apskrityse ir savivaldybėse metų pradžioje". osp.stat.gov.lt. Archived from the original on 2020-02-03. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- ↑ "Vilniaus istorija". vle.lt. Retrieved 15 January 2020.
- ↑ State Enterprise Centre of Registers of Lithuania
- ↑ Health Insurance Fund under the Ministry of Health
- ↑ Inhabitants, registered at Vilnius city primary healthcare facilities
- ↑ Vilniaus miesto darnaus judumo plano santrauka, Vilniaus planas, page 48
- ↑ "Resident population by city / town at the middle of the year". Vilnius. Statistics Department of Lithuania. 1 July 2023. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- ↑ "Gyventoju skaicius pagal savivaldybes 2023" (PDF). Registrucentras.lt. 2023-01-05.
- ↑ Juozas Jurginis; Vytautas Merkys; Adolfas Tautavičius (1968). Vilniaus miesto istorija [Vilnius city history] (in Lithuanian). Vilnius.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ Lexykon geograficzny, dla gruntownego poięcia gazet i historyi z różnych autorów zebrany, przetłumaczony i napisany przez x. Hilaryona Karpińskiego, Z. S. Bazylego w prowincyi litewskiey kapłana i teologa. Po śmierci iego, z przydatkiem odmian, które zaszły, z wykładem na początku terminów geograficznych, i słownikiem nazwisk łacińskich na końcu położonym, do druku podany [A geographic Lexicon, for the thorough help of newspapers and histories from various authors collected, translated and written by x. Hilaryon Karpiński, Z. S. Bazyli in the provinces and a Lithuanian priest and theologian. After the death of iego, with the advent of variations that have occurred, with a lecture at the beginning of geographical terms, and a dictionary of Latin names at the end, printed for publication] (in Polish). Vilnius. 1766. p. 602.
- ↑
Słownik geograficzny Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich, Tom XIII [Geographical dictionary of the Kingdom of Poland and other Slavic countries, Volume XIII] (in Polish). Warsaw. 1893. p. 493. Retrieved 10 March 2018.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ "The Great War in Lithuania 1914–1918".
- ↑ Pukienė, Vida. "Voronežas – lietuvių švietimo židinys Rusijoje Pirmojo pasaulinio karo metais". Istorija (in Lithuanian).
- ↑ Iš nežinios į nežinią: Antrojo pasaulinio karo atbėgėliai Lietuvoje [From one uncertainty to another uncertainty: World War II refugees in Lithuania] (in Lithuanian). Kaunas: National M.K. Čiurlionis Art Museum. 2015. ISBN 978-9955-471-55-4.
- ↑ Первая всеобщая перепись населения Российской Империи 1897 г. – Вильна [First general census of the Russian Empire in 1897 – Vilna] (in Russian).
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Srebrakowski 2000, p. 129.
- ↑ Brensztejn 1919, p. 24.
- ↑ "Drugi powszechny spis ludności z dn. 9.XII.1931 r. Miasto Wilno" [Second general population census of 9.12.1931. Vilnius city] (in Polish).
- ↑ Srebrakowski 2020, p. 47.
- ↑ Snyder, Timothy (2003). The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999. Yale University Press. pp. 92–93. ISBN 978-0-300-10586-5.
- ↑ "Gyventojai [Population]" (PDF). Statistics Department of Lithuania. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 April 2012.
- ↑ Lietuvos gyventojai 2011 metais (2011 m. gyventojų surašymo rezultatai / Lithuanian 2011 Population Census in Brief) [Population of Lithuania in 2011 (Population Census 2011 results)]. Statistics Department of Lithuania. ISBN 978-9955-797-17-3. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ↑ "Rodiklių duomenų bazė - Oficialiosios statistikos portalas". Osp.stat.gov.lt. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ↑ Lietuvos Respublikos 2011 m. gyventojų surašymo rezultatai, 162-163 p.
- ↑ Vilnius city elderships by the area
- ↑ Vilnius elderships by the number of inhabitants
Works cited
- Brensztejn, Michał (1919). Spisy ludności m. Wilna za okupacji niemieckiej od d. 1 listopada 1915 r. (in Polish). Warsaw.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Srebrakowski, Aleksander (2000). Polacy w Litewskiej SRR 1944-1989. Toruń.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Srebrakowski, Aleksander (2020). "The nationality panorama of Vilnius". Studia z Dziejów Rosji i Europy Środkowo-Wschodniej. LV (3).