The Ferret armoured car, also commonly called the Ferret scout car, is a British armoured fighting vehicle designed and built for reconnaissance purposes. The Ferret was produced between 1952 and 1971 by the UK company Daimler. It was widely used by regiments in the British Army, as well as the RAF Regiment and Commonwealth countries throughout the period.
History
The Ferret was developed in 1949 as a result of a British Army requirement issued in 1947. 'Light reconnaissance cars' existed during the Second World War, notably the Daimler Dingo.
Given its experience with the successful Dingo (6,626 produced and one of two British AFVs produced throughout WWII) Daimler was awarded a development contract in October 1948, and in June 1950 the first prototype of the Car, Scout, 4×4, Liaison (Ferret) Mark 1 was delivered.
Designated the FV 701(C), it was one of several versions resembling the original Daimler scout cars, and represented the basic model Ferret. This shared many similar design features with the Dingo, notably the H form drive train in which a central differential eliminates loss of traction due to wheel-slip, and parallel drive shafts considerably reduced the height of the vehicle (roughly equivalent to that of a tracked AFV) compared to conventional armoured car designs.[4]
Like the Daimler scout car, the Ferret suspension consisted of pairs of transverse links and single coil springs, the wheels driven by Tracta constant-velocity joints, but the Ferret benefited from epicyclic reduction gears reducing transmission torque loads, essential with the six cylinder 4.26 litre water-cooled Rolls-Royce B.60 petrol engine. Connected by a fluid coupling to a pre-selector five speed epicyclic gearbox, all gears available in reverse, in its original form, the Ferret produced 116 bhp (87 kW) at 3,300 rpm and 129 bhp (96 kW) at 3,750 in its final form.
This improved power-to-weight ratio, longer wheelbase (2.29 m (7.5 ft) compared with the Dingo's 1.98 metres (6.5 feet)) and the fitting of larger 9.00×16 run flat tyres increased speed and mobility over broken ground.
Compared with the Daimler Dingo and Canadian Ford Lynx, the Ferret featured a larger cabin, directly mounted to the hull (the Ferret is much noisier than Dingo, lacking a monocoque body).
6–16 mm (0.24–0.63 in) steel plate protects the crew from shell splinters at most angles except directly overhead because the basic vehicle was open-topped and unarmed, with the exception of six forward-firing grenade launchers fitted to the hull over the front wheels (normally carrying smoke grenades), a feature found on all subsequent marks and models.
However, the Ferret normally carried a .303" (7.7 mm) Bren light machine gun or a pintle-mounted .30" (7.62 mm) Browning light machine gun[4] in addition to the crew's personal weapons.
Ferret Mark 2

Compared to the lightly armed and protected Mark 1, the Mark 2 was designed from the outset to mount a .30" (7.62 mm) Browning in a one-person traversable turret, at the cost of one crew member. While this offered better crew protection and protected the exposed gunner, the turret raised the height of the vehicle.
Service
Mark 1 and Mark 2 Ferrets were used by Australian Military 1953-70, at which time Australian military forces disposed of them at public auction.
The Sri Lanka Army used Mark 1 and Mark 2 Ferrets from 1955 to 1999, with the last decade in a non-front line role. The Sri Lanka Armoured Corps still retains a few operational Ferret Mark 1 for ceremonial use, while some Mark 2s are gate guardians or in museums.[5]
According to the US Military, 20 national armies were operating the Ferret in 1996.[6]
Production
A total of 4,409 Ferrets, including 16 sub-models under various Mark numbers, were manufactured between 1952 and 1962, when production ceased. It is possible to upgrade the engine using the more powerful FB60 version from the Austin Princess 4-Litre-R; this upgrade providing a 55 bhp (41 kW) gain over the standard B60 engine.
Operators
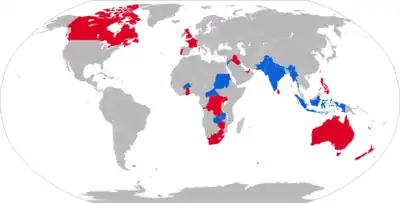

Current operators
 Abu Dhabi: 65[7]
Abu Dhabi: 65[7] Bahrain: 8[7]
Bahrain: 8[7] Burkina Faso: 30[8]
Burkina Faso: 30[8] Brunei[9]
Brunei[9] Cameroon: 15[10]
Cameroon: 15[10] Central African Republic: 8[11]
Central African Republic: 8[11] Gambia: 8[7]
Gambia: 8[7] Indonesia: 55[7]
Indonesia: 55[7] Jamaica: 15; Mk 4 variant[7]
Jamaica: 15; Mk 4 variant[7] Jordan: 180[7]
Jordan: 180[7] Kenya: 12[12]
Kenya: 12[12] India: 320[7]
India: 320[7] Madagascar: 10[7]
Madagascar: 10[7] Malawi: some donated by South Africa[13][9]
Malawi: some donated by South Africa[13][9] Nepal: 40; Mk 4 variant[7]
Nepal: 40; Mk 4 variant[7] Nigeria: 40[7]
Nigeria: 40[7] Oman: 15[7]
Oman: 15[7] Pakistan: 90 [7][14]
Pakistan: 90 [7][14] Qatar: 10[7]
Qatar: 10[7] Saint Kitts and Nevis: 3
Saint Kitts and Nevis: 3 Sudan: 40–50[7][15]
Sudan: 40–50[7][15] Uganda: 15[7]
Uganda: 15[7] Ukraine: At least one Mk1 purchased privately.[16][17]
Ukraine: At least one Mk1 purchased privately.[16][17] Zambia: 28[7]
Zambia: 28[7]
Former operators

.svg.png.webp) Australia: 265[7]
Australia: 265[7] Biafra: 1[18]
Biafra: 1[18].svg.png.webp) Canada: 124[19]
Canada: 124[19] France: 200;[7] likely replaced by the Panhard AML[20]
France: 200;[7] likely replaced by the Panhard AML[20] Ghana: 30[7]
Ghana: 30[7].svg.png.webp) Hong Kong: Used by the Royal Hong Kong Regiment.[21]
Hong Kong: Used by the Royal Hong Kong Regiment.[21] Iran: 50[7]
Iran: 50[7] Iraq: 20[7]
Iraq: 20[7] Lebanon: 5; possibly donated by Jordan[22]
Lebanon: 5; possibly donated by Jordan[22].svg.png.webp) Libya: 15[7]
Libya: 15[7] Malaysia: 92; Mk 2 variant[7] (Some still active in Royal Malaysian Police)
Malaysia: 92; Mk 2 variant[7] (Some still active in Royal Malaysian Police) Burma: 45[7]
Burma: 45[7] New Zealand: 9; Mk 2 variant[7]
New Zealand: 9; Mk 2 variant[7] Netherlands: 6 Mk 2, 1 Mk 1, operated by 11 Infantry Recce Company[23]
Netherlands: 6 Mk 2, 1 Mk 1, operated by 11 Infantry Recce Company[23] North Yemen[9]
North Yemen[9] Portugal: 32; Mk 4 variant[24]
Portugal: 32; Mk 4 variant[24].svg.png.webp) Rhodesia
Rhodesia Saudi Arabia: 30[7]
Saudi Arabia: 30[7] Somalia: 18[7]
Somalia: 18[7].svg.png.webp) South Africa: 231[25]
South Africa: 231[25] South Yemen: 15[7]
South Yemen: 15[7] Sri Lanka: 42[7]
Sri Lanka: 42[7] United Kingdom[22]
United Kingdom[22].svg.png.webp) Zaire: 30[7][9]
Zaire: 30[7][9] Zimbabwe: 10[26]
Zimbabwe: 10[26]
Variants

There are several Marks of Ferret, including those with varying equipment, turret or no turret and armed with Swingfire anti-tank missiles. Including all the marks and experimental variants, there have probably been over 60 different vehicles.
- Mk 1
- FV701C
- Liaison duties
- No turret
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG
- MK 1/1
- Fitted with thicker side and rear hull plates during manufacture
- Sealed hull for fording
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG
- Mk 1/2
- As Mk 1/1 but fitted with fixed turret with hinged roof door
- Crew of three
- Armament Bren LMG, later GPMG
- Mk 1/2
- As Mk 1/1 but fitted with flotation screen
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG

- Mk 2
- Original reconnaissance vehicle with 2-door turret from Alvis Saracen APC
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG
- Mk 2/1
- Original Mk 1 with 2-door turret from Alvis Saracen APC
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG with Bren LMG stowage
- Mk 2/2
- Original Mk 1 with extension collar and 3-door turret
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG
- Mk 2/3
- As original Mk 2 but fitted with thicker side and rear hull plates during manufacture
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG
- Mk 2/4
- Original Mk 2 but fitted with welded-on appliqué on side and rear of hull and turret
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG
- Mk 2/5
- As Mk 1 fitted with appliqué plates as the Mk 2/4
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG with Bren LMG stowage
- MK 2/6
- FV703
- As Mk 2/3 converted as carrier for *Vigilant antitank missile
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG and four missiles mounted in boxes, two on each side of turret
- Used by British Army and Abu Dhabi
- Mk 2/7
- FV701
- As Mk 2/6 stripped of anti-tank missiles after Vigilant withdrawn from service
- Mk 3
- Basic hull for Mk 4 and 5
- Larger wheels
- Heavier armour
- Stronger suspension
- Flotation screen
- Mk 4
- FV711
- Reconnaissance vehicle with 2-door turret from Alvis Saracen APC
- Also Mk 2/3 rebuilt to new specification
- Armament .30" (7.62 mm) Browning MG

- Mk 5
- Ferret 80[27]
- A new light reconnaissance vehicle proposed by Alvis in 1982, with only one non-operational mock up produced.
- New armoured aluminium hull with a 155 horsepower (116 kW) Perkins T6 diesel engine but incorporating many existing Mk 4 and Mk 5 components.
- 2-door turret from Alvis Saracen or Helio FVT900 turret.
- Armament: L37 7.62mm machine gun (2-door turret) or 20 mm autocannon with 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun (FVT900 turret).
References
- ↑ "Images de TENES :: Les BLINDES :: Auto_Mitrailleuse_AM_20_dans_le_Constantinois".
- ↑ Abbott, Peter; Rodrigues, Manuel (1998). Modern African Wars 2: Angola and Mozambique 1961-74. Osprey Publishing. p. 11.
- ↑ Staff Writer, "Alvis FV107 Scimitar: Armed Reconnaissance Vehicle (1971)", Military Factory, retrieved 11 October 2021
- 1 2 Ogorkiewicz, R.M. (1972). AFV Profiles 44 Ferrets and Fox. Profile Publications.
- ↑ "History Of the Armoured Corps". Sri Lanka Army. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
- ↑ "Anti-Armor Weapons Subcourse" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 December 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 "Trade Registers". Armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 3 November 2015.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2021, p. 452.
- 1 2 3 4 Christopher F. Foss (1976). Jane's World Armoured Fighting Vehicles (1976 ed.). Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Ltd. pp. 156–157. ISBN 0-354-01022-0.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2021, p. 455.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2021, p. 456.
- ↑ The Military Balance 2021, p. 472.
- ↑ Christopher F. Foss (16 May 2000). Jane's Tanks and Combat Vehicles Recognition Guide (2000 ed.). Harper Collins Publishers. pp. 386–391. ISBN 978-0-00-472452-2.
- ↑ "Pakistan Land Forces military equipment and vehicles of Pakistani Army".
- ↑ Richard Lobban Jr. (2010). Global Security Watch: Sudan (2010 ed.). Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 182. ISBN 978-0-313-35332-1.
- ↑ 🇺🇦 Ukraine Weapons Tracker [@UAWeapons] (16 August 2022). "#Ukraine: British 🇬🇧 military equipment in service with the Ukrainian army - here we see 14 Snatch Land Rover armored SUVs, 3 Vector Pinzgauer 718 6x6 armored patrol vehicles and a classic Ferret Mk 1 scout car! Note that these vehicles were mostly purchased using private funds. https://twitter.com/UAWeapons/status/1559532999523409920" (Tweet). Archived from the original on 16 August 2022. Retrieved 5 August 2022 – via Twitter.
- ↑ Newdick, Thomas (17 August 2022). "Antique Ferret Armored Car Shows Up In Ukraine". The Drive. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ↑ Jowett, Philip (2016). Modern African Wars (5): The Nigerian-Biafran War 1967–70. Oxford: Osprey Publishing Press. pp. 24–46. ISBN 978-1472816092.
- ↑ "Canadian Ferrets – All 124 listed by CAR / CFR – www.captainstevens.com". Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ↑ Defence Update (International). Defence Update G.m.b.H., 1984, 1984–85 Volume Collected Issues 48–58.
- ↑ "RHKR Equipment - Vehicle". www.rhkr.org. The Royal Hong Kong Regiment (The Volunteers) Association. Archived from the original on 16 June 2021. Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- 1 2 Christopher F. Foss (2001). Jane's Armour and Artillery (2002 ed.). Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Ltd. p. 260. ISBN 978-0710623096.
- ↑ Fabrique - Daimler Ferret Mk.II. "Daimler Ferret Mk.II - Zoeken in de collectie - Nationaal Militair Museum". NNM. Archived from the original on 5 November 2020. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- ↑ Keegan, John (1983). World Armies (Second ed.). Basingstoke: Palgrave-Macmillan. ISBN 978-0333340790.
- ↑ "Lesakeng". South African Armour Museum. 6 December 2012. Archived from the original on 3 July 2013. Retrieved 2013-06-18.
- ↑ Simon Baynham (1992). Zimbabwe in transition (October 1992 ed.). Almqvist & Wiksell International. p. 240. ISBN 978-9122015086.
- ↑ Jane's Armour and Artillery. Jane's Information Group. 1991. p. 253. ISBN 0710609647.
Bibliography
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (February 2021). The Military Balance 2021. Vol. 121. Routledge. ISBN 9781032012278.
External links
- Ferret Scout Car in Canadian Service
- Warwheels.net
- Ferret Walk Arounds on Prime Portal
- The Ontario Regiment (RCAC) Ferret Club, Oshawa, Ontario, Canada
- King's Own Royal Border Regiment Museum, Carlisle Castle, Cumbria, England has an example on display
