 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
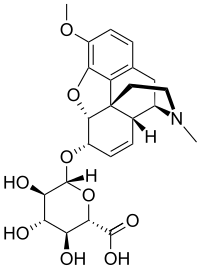
| IUPAC name
(5α,6α)-3-methoxy-17-methyl-7,8-didehydro-4,5-epoxymorphinan-6-yl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-{[(4R,4aR,7S,7aR,12bS)-9-methoxy-3-methyl-2,3,4,4a,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-4,12-methano[1]benzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-yl]oxy}oxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H29NO9 | |
| Molar mass | 475.494 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Codeine-6-glucuronide (C6G) is a major active metabolite of codeine and may be responsible for as much as 60% of the analgesic effects of codeine. C6G exhibits decreased immunosuppressive effects compared to codeine.[1] During its metabolism, codeine is conjugated with glucuronic acid by the enzyme UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase-2B7 (UGT2B7) to form codeine-6-glucuronide.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ Srinivasan, V.; Wielbo, D.; Tebbett, I. R. (1997). "Analgesic effects of codeine-6-glucuronide after intravenous administration". European Journal of Pain. 1 (3): 185–190. doi:10.1016/S1090-3801(97)90103-8. PMID 15102399. S2CID 23099329.
- ↑ Vree, T. B.; Van Dongen, R. T.; Koopman-Kimenai, P. M. (2000). "Codeine analgesia is due to codeine-6-glucuronide, not morphine". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 54 (6): 395–398. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2000.tb11929.x. PMID 11092114. S2CID 8281493.
- ↑ Armstrong, S. C.; Cozza, K. L. (2003). "Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions of Morphine, Codeine, and Their Derivatives: Theory and Clinical Reality, Part II". Psychosomatics. 44 (6): 515–520. doi:10.1176/appi.psy.44.6.515. PMID 14597688.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.