 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
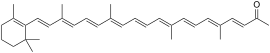
| IUPAC name
5′-Apo-β,χ-caroten-6(5H)-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E,19E)-5,9,14,18-Tetramethyl-20-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)icosa-3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19-nonaen-2-one | |
| Other names
E161i | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.693 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E161i (colours) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C33H44O | |
| Molar mass | 456.714 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Deep violet crystals |
| Insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Citranaxanthin is a carotenoid pigment used as a food additive under the E number E161i as a food coloring. There are natural sources of citranaxanthin, but it is generally prepared synthetically.[1] It is used as an animal feed additive to impart a yellow color to chicken fat and egg yolks.[2]
References
- ↑ Citranaxanthin Archived 2012-10-17 at the Wayback Machine, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
- ↑ Citranaxanthin, International Programme on Chemical Safety
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.