| Chaetodactylus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Chaetodactylus Rondani, 1866 |
Chaetodactylus is a genus of parasitic mite primarily associated with solitary bees with over 20 species.[1]
These mites usually kill young bee larvae and feed on provisioned pollen and nectar. In nests with partitions (Osmia), bees that develop in the innermost cells chew their way out of the nest, and phoretic deutonymphs from the opened cells may attach to them. The mites in the innermost cell may die because of their inability to break through the partition. In nests without partitions (Lithurgus), some young bees may complete development and transform to adults that disperse the mites.[1]
In colonies of Osmia cornifrons managed for pollination of blueberries in the US, Ch. krombeini phoretic deutonymphs could disperse from a nest to nearby nests by walking through nest entrances and holes made by parasitic wasps. Cross-nest dispersal via blueberry flowers visited by multiple individuals of O. cornifrons was proven to be negligible.[2][1]
Life cycle
Feeding stages live in bee nests. They are mostly kleptoparasitic, but they may kill developing bee larvae via direct attack.
Phoretic deutonymphs (non-feeding stage) disperse from one nest to another on adult bees. They cause no direct harm, but large mite loads may affect the bee's flying abilities and survival. In managed and aggregated bee colonies, they may infect new nests by active dispersal (walking).
Non-phoretic deutonymphs (non-feeding stage) can survive in the nest cavity to infest new bee generations, if the same nest is reused.[1]
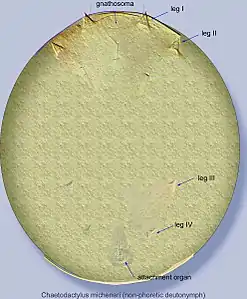 Chaetodactylus micheneri non-phoretic (immobile) deutonymph.
Chaetodactylus micheneri non-phoretic (immobile) deutonymph.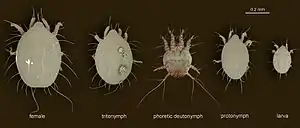 Life stages of Chaetodactylus krombeini (Astigmata); non-phoretic deutonymph and male not shown.
Life stages of Chaetodactylus krombeini (Astigmata); non-phoretic deutonymph and male not shown.
The presence of the inert non-phoretic deutonymph along with the phoretic deutonymph is the most conspicuous feature in the life-cycle of this genus. The inert deutonymph is a highly regressive, cyst-like morph with legs and most setae greatly reduced. It is capable of surviving in old bee nests and infesting new hosts that reuse these nests or the nest material. When mites are trapped in the innermost cells of an infested nest or all bee larvae are killed and therefore cannot transfer mites to a new nest as adults, inert deutonymphs can be very important for mite survival.[1]
Systematics
- Subgenus Chaetodactylus Rondani, 1866 (Also called Trichotarsus Canestrini, 1888)
- Chaetodactylus chrysidis Fain & Baugnee, 1996 — host: Chrysura trimaculata;
- Chaetodactylus dalyi Fain, 1974
- Chaetodactylus hirashimai Kurosa, 1987 — host: Osmia excavata;
- Chaetodactylus ludwigi (Trouessart, 1904)
- Chaetodactylus nipponicus Kurosa, 1987 —host: Osmia cornifrons;
- Chaetodactylus osmiae (Dufour, 1839) (Previously called Trichodactylus osmiae Dufour, 1839)
- Chaetodactylus panamensis Baker, Roubik & Delfinado-Baker, 1987
- Chaetodactylus reaumuri Oudemans, 1905
- Subgenus Ochaetodactylus Fain, 1981
- Chaetodactylus decellei Fain, 1974
- Subgenus Spinodactylus Fain, 1981
- Chaetodactylus claviger Oudemans, 1928
- Chaetodactylus krombeini Baker, 1962
- Subgenus Achaetodactylus Fain, 1981
- Chaetodactylus ceratinae Fain, 1976
- Chaetodactylus dementjevi Zachvatkin, 1941
- Chaetodactylus leleupi Fain, 1974
- Unknown
- Chaetodactylus zachvatkini Klimov and OConnor, 2008
- Chaetodactylus micheneri Klimov and OConnor, 2008
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Klimov, P.B.; B. OConnor; R. Ochoa; G.R. Bauchan; A.J. Redford; J. Scher (2016). "Chaetodactylus". Bee Mite ID: Bee-Associated Mite Genera of the World. Fort Collins, CO: USDA APHIS Identification Technology Program (ITP). Retrieved 2018-08-15.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ Park, Y.-L.; Kondo, V.; White, J.; West, T.; McConnell, B.; McCutcheon, T. (April 2009). "Nest-to-nest dispersal ofChaetodactylus krombeini(Acari, Chaetodactylidae) associated withOsmia cornifrons(Hym., Megachilidae)". Journal of Applied Entomology. 133 (3): 174–180. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0418.2008.01351.x. ISSN 0931-2048.