| Havariekommando | |
 CCME Seal | |
| Co-ordinating body overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 2003 |
| Jurisdiction | German Maritime Emergencies Response |
| Headquarters | Cuxhaven |
| Motto | Rüm Hart, klaar Kiming |
| Employees | 40 |
| Parent department | Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport |
| Website | |
The German Central Command for Maritime Emergencies (CCME) (in German: Havariekommando) is the authority for mutual maritime emergency management in the German EEZ of North Sea and in the Baltic Sea. The federal office provides radar and air surveillance, piloting and emergency tugs for ships that are unable to manoeuvre. Head of CCME is Frigate captain Robby Renner.[1]
History
By law the German states Lower Saxony, Hanseatic City of Bremen, Hanseatic City of Hamburg, Schleswig-Holstein and Mecklenburg Vorpommern are responsible for maritime emergency response in their coastal waters. Federal agencies such as the Federal Coast Guard are responsible for certain tasks. The large number of organizations and authorities led to a great need for coordination. The process of German maritime rescue and relief operations has often been criticized as dangerously bureaucratic, too slow and uncoordinated. On October 25, 1998, the Cargo ship M/V Pallas, cargo of lumber caught fire while traveling the North Sea off the west coast of Jutland. Several attempts to get the ship under tow were unsuccessful, and it ran aground four days later off the German island of Amrum, in the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park. 250 tons of fuel oil were lost overboard, causing the biggest oil spill in German history, killing approximately 16.000 sea birds, predominantly common eiders. The case led to political discontent over a lack of coordinated emergency tow capabilities on the German coast, and contributed to the creation CCME.[1]
The Federal Coastal States and the Federal Government authorities founded CCME. On January 1, 2003, the Central Command for Maritime Emergencies (CCME) (in German: Havariekommando) commenced operations. It was established to set up and carry out a mutual maritime emergency management in the North Sea and in the Baltic Sea. It is based in Cuxhaven (Northwest Germany) and is headed by a federal official.[2]
Operation

The Maritime Emergencies Reporting and Assessment Centre is the 24/7 central point of contact for emergencies. In the event of an accident, it is usually necessary to rescue people, which is coordinated by the Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre Bremen (MRCC) of the German Sea Rescue Society (DGzRS). The havariekommando is in charge of the German ETV fleet. During daily work routine the CCME consists of about 40 employees, working in five different sections:[2]
- Maritime Emergencies Reporting and Assessment Centre (MERAC)
- Marine Pollution Control - High Sea and Salvage Section
- Marine Pollution Control - Coastal Section
- Fire Fighting, Rescue and Medical Response Section
- Public Relations Section
Capacity
One of the main capacities of CCME is a number of Emergency tow vessels.
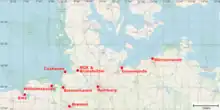
Emergency tow vessel stations
_2010-by-RaBoe-02.jpg.webp)
| No. | Area | Ship name | Bollard pull (in tons) | Typ | position of station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Sea | Nordic | 201 | chartered tug ship (Fairplay Towage Group) | 10 sm north of Norderney |
| 2 | North Sea | Mellum | 110 | Multi purpose ship of Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration (WSV) | 5 sm south-west of Heligoland |
| 3 | North Sea | Neuwerk | 110 | Multi purpose ship of Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration (WSV) | 5 sm south-west of Süderoogsand |
| 4 | Baltic Sea | Scharhörn | 40 | Multi purpose ship of Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration (WSV) | Kiel-Ostsee-Weg |
| 5 | Baltic Sea | Baltic | 127 | chartered tug ship (Fairplay Towage Group) | Warnemünde |
| 6 | Baltic Sea | Arkona | 40 | Multi purpose ship of Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration (WSV) | Stralsund |
| 7 | Baltic Sea | Bremen Fighter | 104 | chartered tug ship (Boluda Deutschland) | Sassnitz |
Special ability capacitys
The CCME has access and is in command of units of several organisations with special ability and equipment:
- DGzRS for maritime rescue
- Fire brigades, local coastal fire brigades with special ability for maritime fire fighting
- German Navy, especially naval aviation
- German Federal Coast Guard
- Federal Agency for Technical Relief (THW) for handling dangerous substances[4]
References
- 1 2 Preuschoff, von Olaf (2021-11-18). "Dr. Robby Renner übernimmt Leitung des Havariekommandos von Hans-Werner Monsees". Feuerwehr-Magazin (in German). Retrieved 2022-02-03.
- 1 2 "Havariekommando - Homepage". www.havariekommando.de. Retrieved 2022-02-03.
- ↑ "Manövrierunfähiger Frachter auf Nordsee: Lage entspannt sich". Die Welt. 30 January 2022.
- ↑ "THW und Havariekommando unterzeichnen Kooperationsvereinbarung". Bundesanstalt Technisches Hilfswerk (THW) (in German). April 29, 2019. Retrieved 2022-02-03.